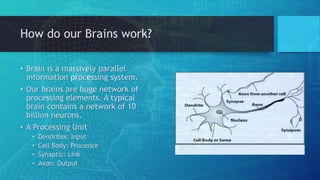
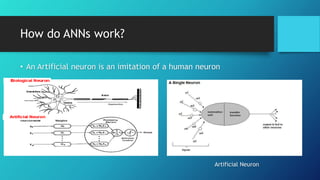
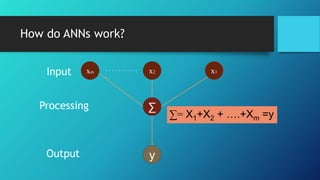
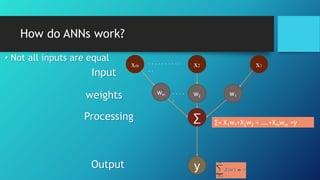
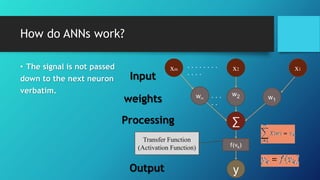
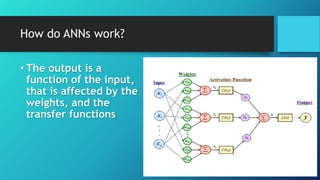
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are computing systems inspired by biological neural networks. ANNs consist of interconnected nodes that mimic neurons and pass signals to each other via weighted connections. There are two main reasons for building ANNs: to solve problems like pattern recognition that require massively parallel processing, and to better understand natural information processing in the brain. ANNs process information in parallel through a large number of simple nodes. The output of each node is determined by the inputs it receives and the weights assigned to those connections. ANNs can be used for applications like pattern recognition, control systems, and forecasting.