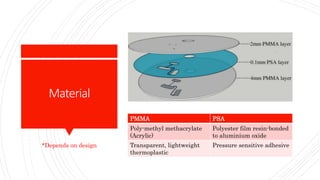
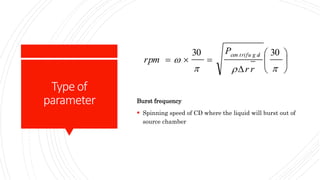
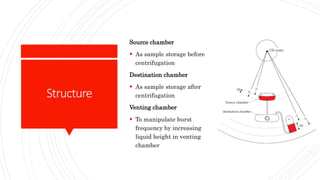
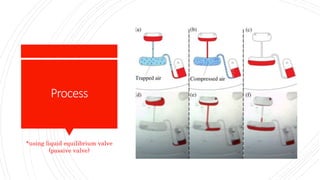
The document discusses a centrifugal microfluidic CD platform, which is a medical diagnostic tool utilizing spinning techniques to control liquid dynamics for various applications like dengue detection and DNA purification. It outlines two types of valves: passive and active, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages in controlling liquid movement. The proposed liquid equilibrium valving method eliminates the need for external pumps, reduces contamination, and enhances control over liquid flow.