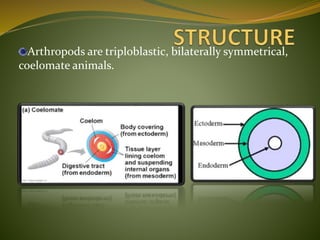
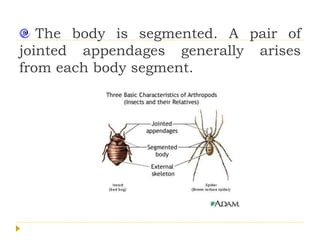
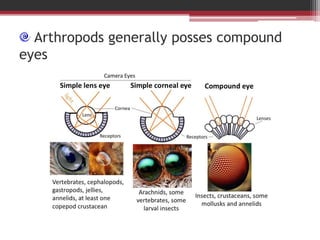
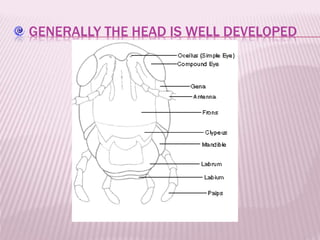
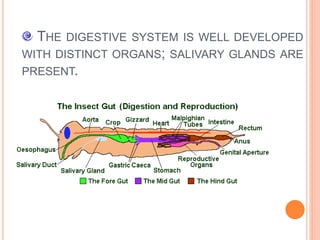
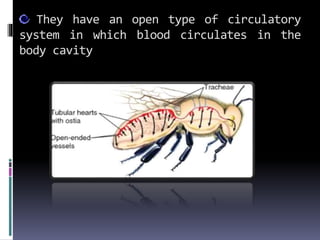
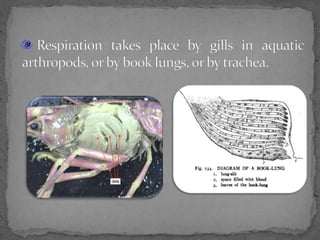
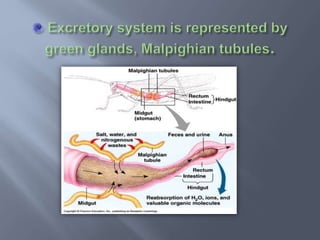
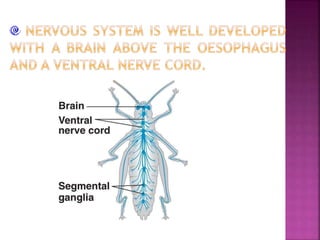
Phylum Arthropoda is the largest phylum of animals and includes organisms with jointed legs and segmented bodies such as insects, spiders, crustaceans and others. Arthropods live in nearly all environments on Earth, from deserts to oceans. They have an exoskeleton, segmented body, jointed appendages, and shed their exoskeleton through molting. As the most diverse and abundant group of animals, arthropods play important economic roles through products like honey and silk, but some also spread diseases and damage crops.