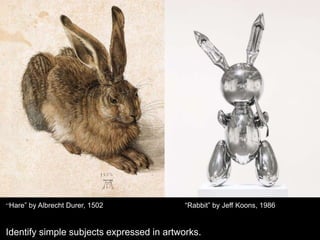
The document outlines the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for kindergarten art education. It discusses how the fine arts develop key skills like critical thinking, communication, and collaboration. It also explains that the kindergarten art curriculum focuses on four strands: observation and perception, creative expression, historical and cultural relevance, and critical evaluation and response. Some examples of concepts and skills covered include identifying elements of art, using a variety of materials and techniques to create artworks, developing awareness of different cultures, and analyzing artwork.