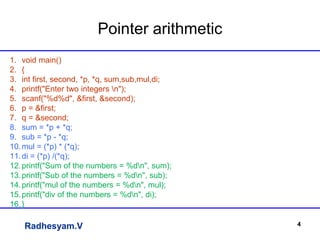
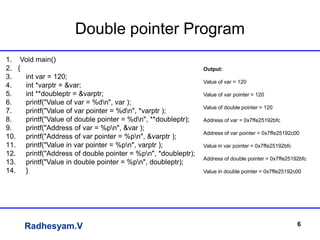
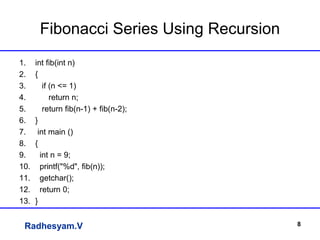
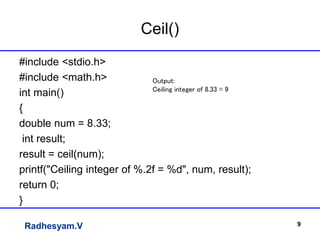
This document summarizes an lecture on applications of strings and pointers in C programming. It includes examples of using arrays of strings, pointer arithmetic, double pointers, scanf vs gets functions, generating Fibonacci series using recursion, and using the ceil() and floor() math functions. The lecture covers basic and advanced concepts of strings and pointers through examples and explanations.

![Radhesyam.V
Array of Strings
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. int main()
3. {
4. char charr[7][10] = {"sun","mon","tue","wed","thu","fri","sat"};
5. int i;
6. for(i=0;i<7;i++)
7. printf("%sn",charr[i]);
8. return 0;
9. }
2
Output:
sun
mon
tue
wed
thu
fri
sat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraystrings-210415055644/85/Array-strings-2-320.jpg)
![Radhesyam.V
Array of Strings
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. Void main()
3. {
4. char charr[7][10];
5. int i;
6. printf("enter string");
7. for(i=0;i<7;i++)
8. scanf("%s",charr[i]);
9. printf("string is ");
10. for(i=0;i<7;i++)
11. printf("%sn",charr[i]);
12. }
3
Maximum no of strings
Maximum string length](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraystrings-210415055644/85/Array-strings-3-320.jpg)