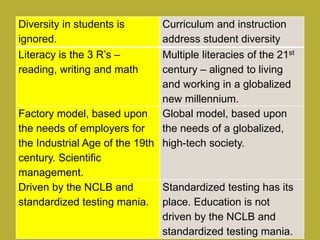
This document discusses 21st century education and the skills needed for students in the modern world. It outlines three main points:
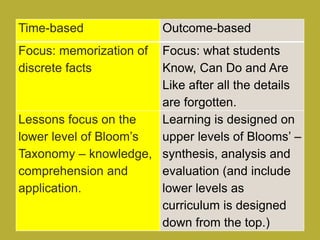
1) 21st century education focuses on developing skills like critical thinking, collaboration, communication and adapting to change, rather than memorization of facts. It emphasizes project-based and active learning.
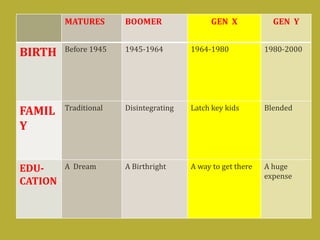
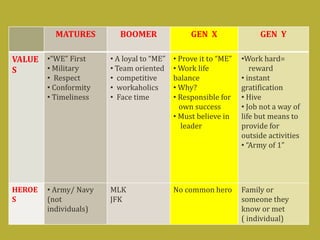
2) Today's students, called digital natives, have grown up with technology and need education to incorporate their skills and interests. They want voice, transparency, creativity and connections through technology.
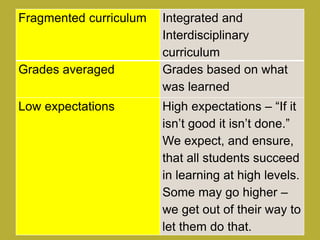
3) The modern classroom shifts from teacher-centered learning to student-centered models that are outcome-based, integrated, and allow for diversity, multiple literacies and relevance to students' lives outside of