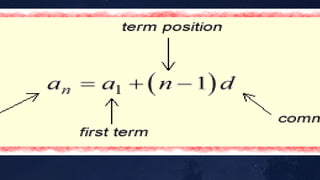
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. For example, the sequence 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 is an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 2. The nth term (an) of an arithmetic sequence can be calculated as an = a1 + (n-1)d, where a1 is the first term and d is the common difference. The sum (Sn) of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence is calculated as Sn = n/2(a1 + an), where a1 is the first term and an is the nth term.