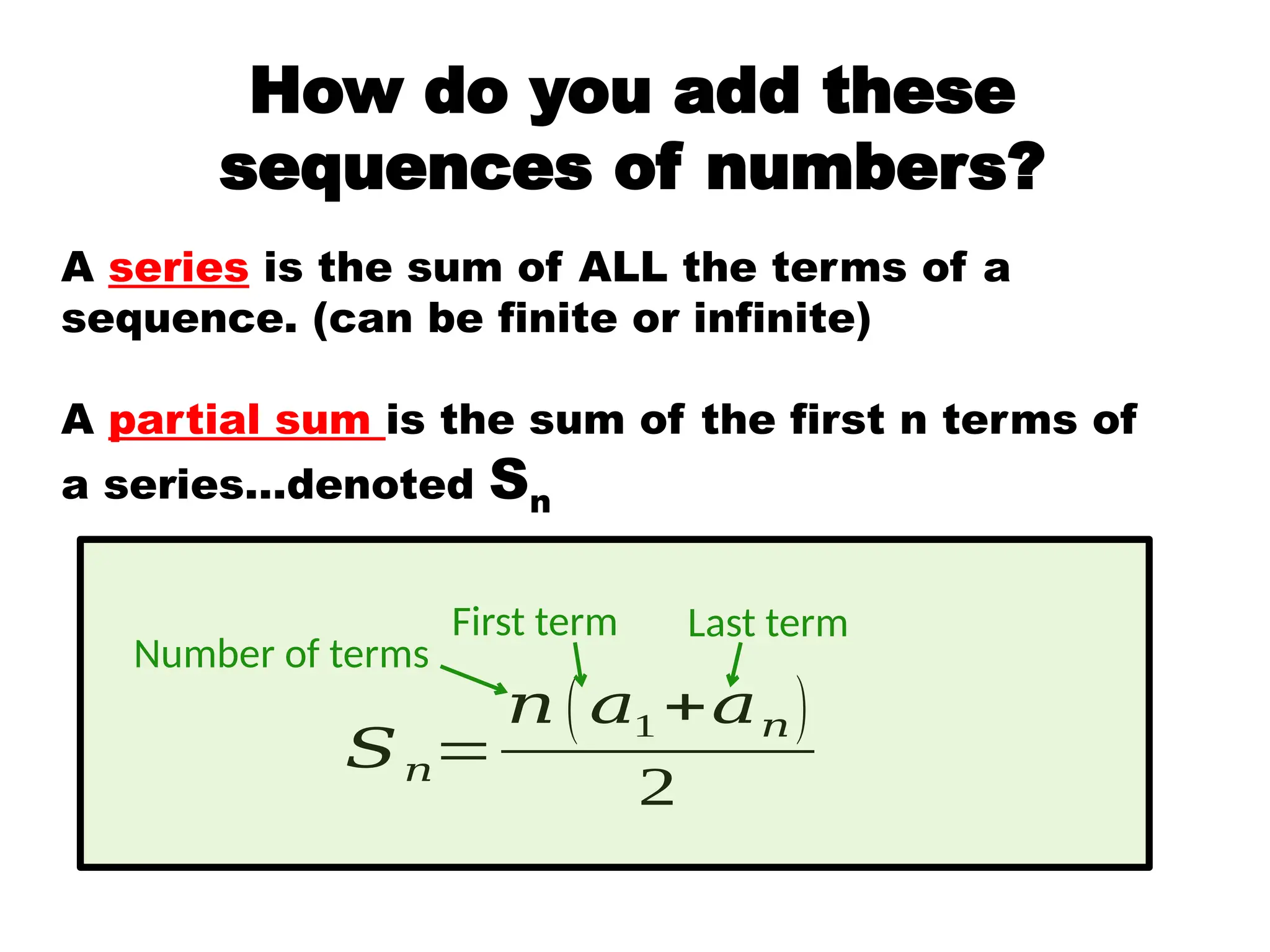
This document explains arithmetic sequences, characterized by a repeated addition of a constant called the common difference. It outlines how to express these sequences using both explicit and recursive formulas, providing examples to illustrate the calculations involved. Additionally, it introduces the concept of series as the sum of sequence terms and discusses the computation of partial sums.