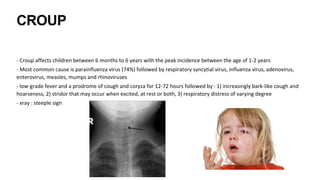
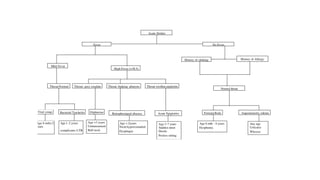
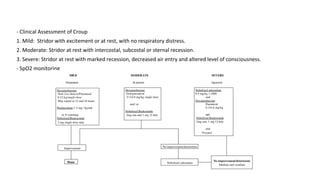
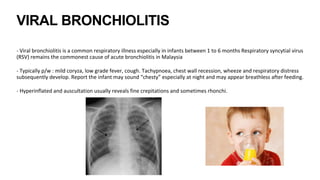
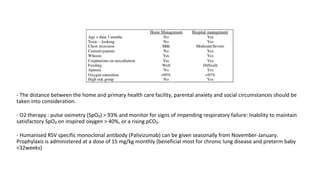
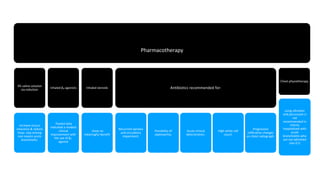
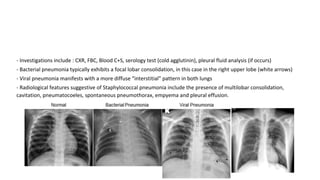
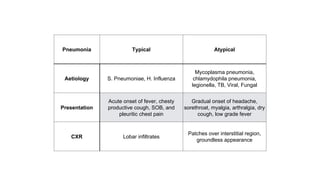
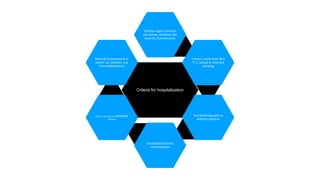
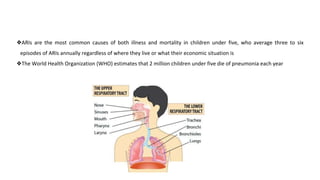
This document discusses acute respiratory infections (ARIs) in children, which are the most common causes of illness and mortality in children under five years old. It covers both upper respiratory infections like the common cold, rhinosinusitis, sore throat, and ear infections as well as lower respiratory infections like pneumonia, croup, and bronchiolitis. For each condition, it discusses causes, signs and symptoms, investigations, management including medications, and criteria for hospitalization. The goal is to provide guidance on diagnosing and treating the various ARIs that commonly affect children.








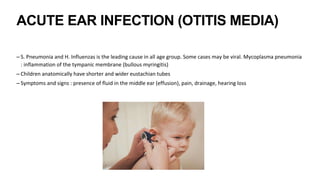
![- otoscopy
- Management :
1. OME : steroid <6weeks
2.Children six months or older with otorrhea/severe signs
or symptoms (moderate or severe otalgia, otalgia for
at least 48 hours, or temperature of 102.2°F [39°C] or higher):
antibiotic therapy for 10 days
3. Treat pain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arinew-230315155325-151b1209/85/ARI-new-pptx-13-320.jpg)