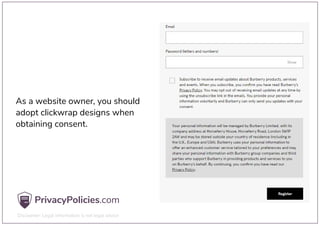
The document outlines key requirements for compliance with the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which went into effect on May 25th. It emphasizes the need for informed consent, the right to access and erase data, and the importance of privacy by design in website functionality. Businesses face significant penalties for non-compliance, making it essential to update privacy policies and practices accordingly.