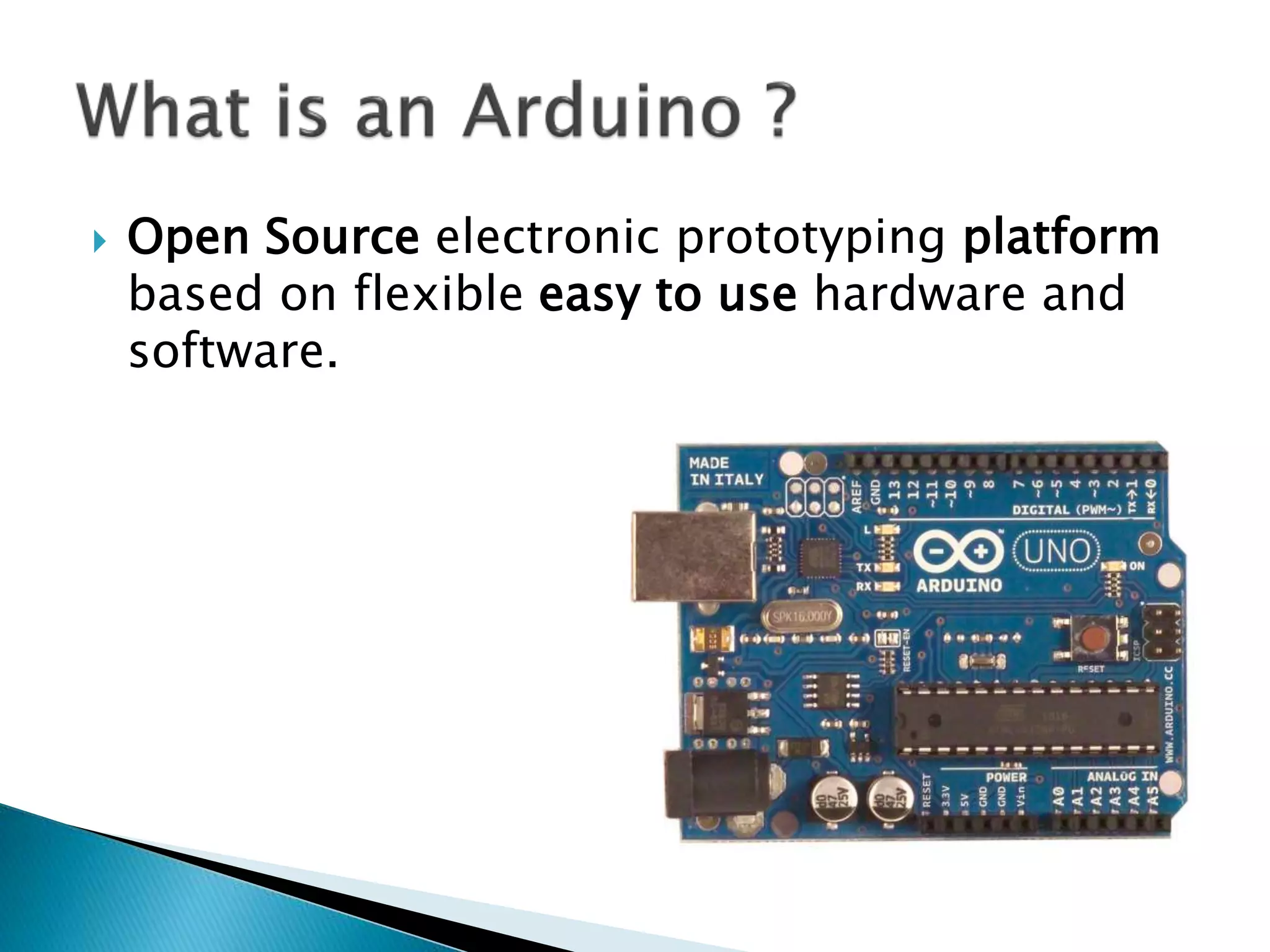
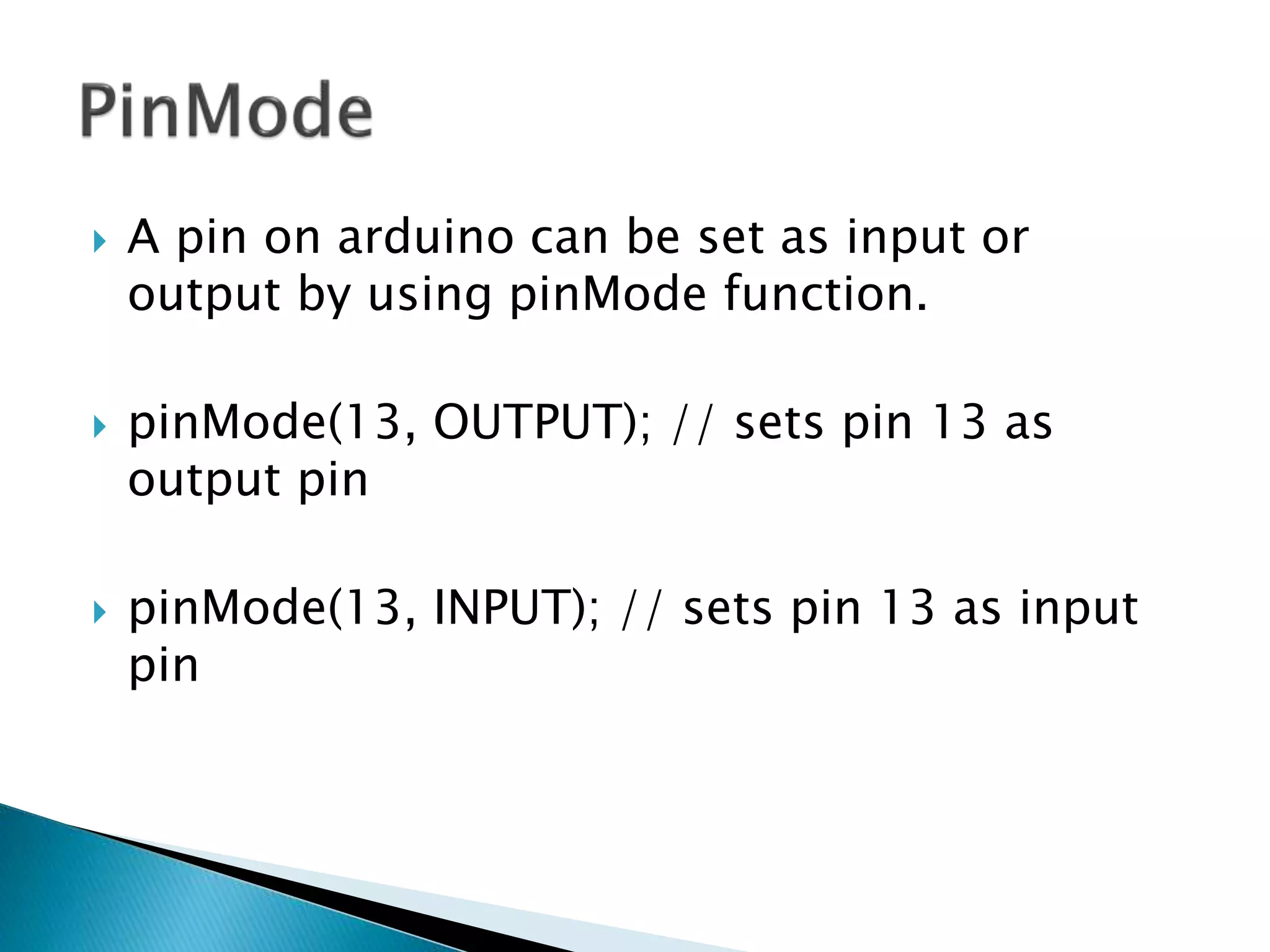
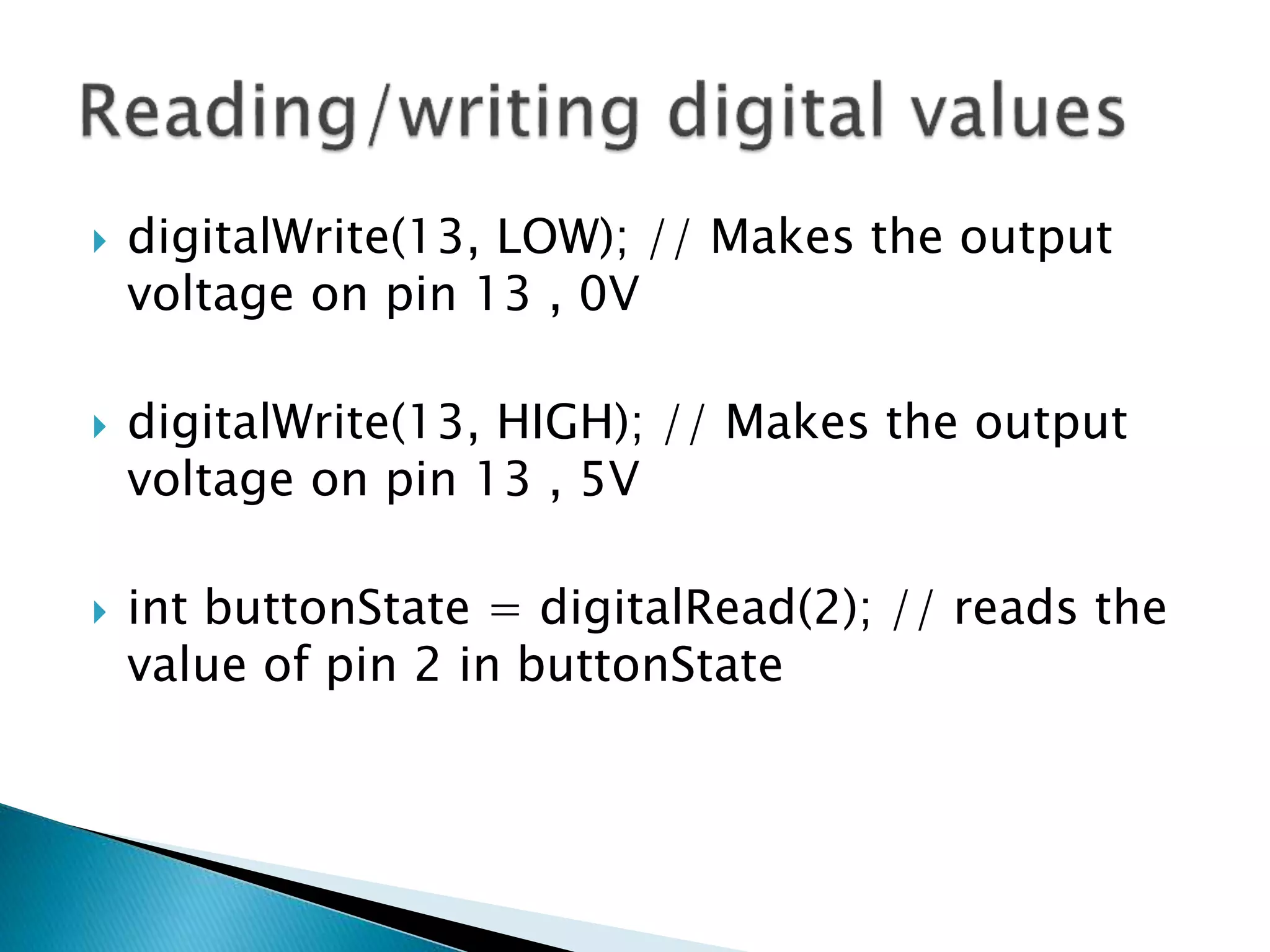
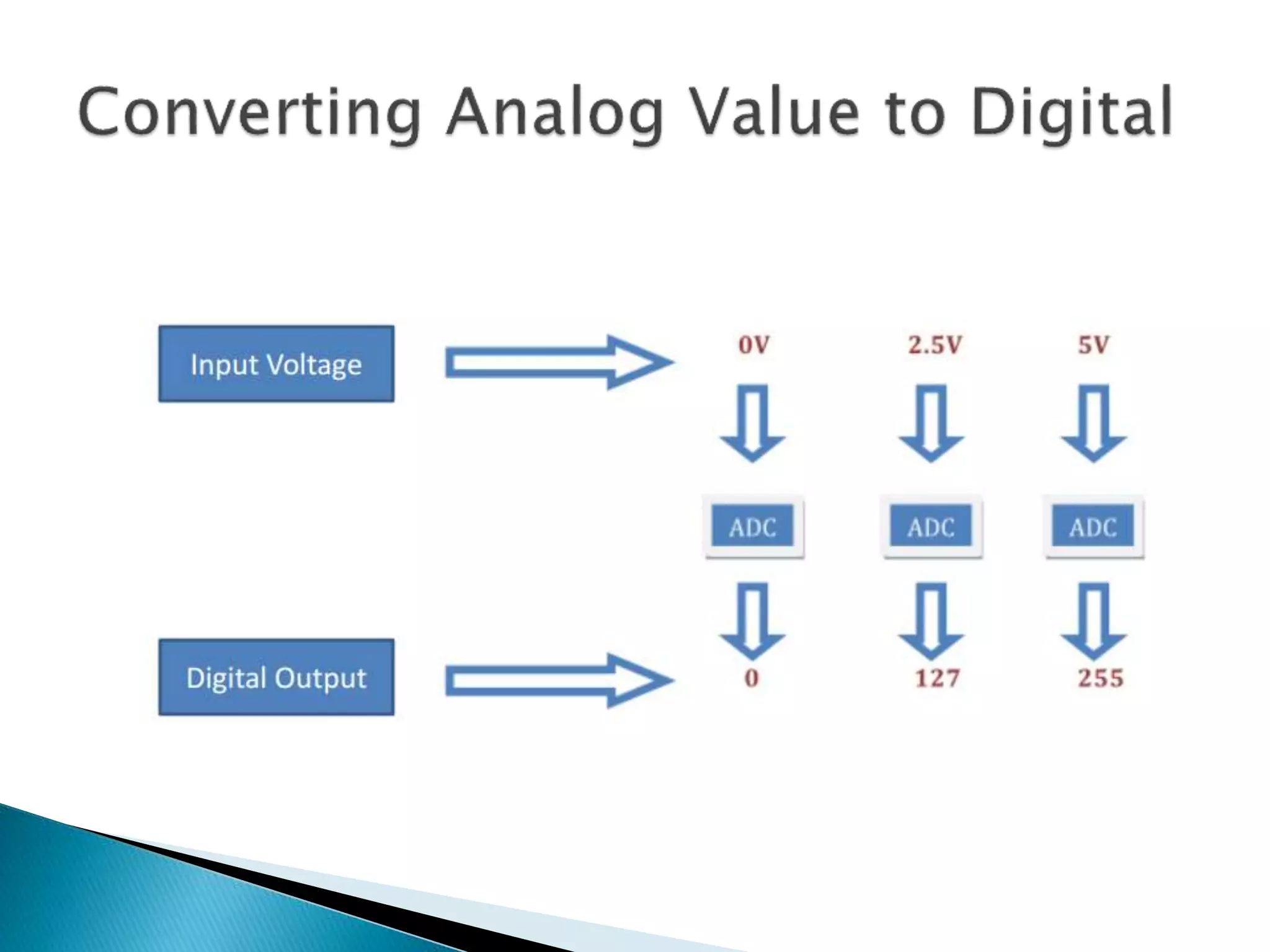
The Arduino is an open source prototyping platform that uses flexible hardware and software. The setup function initializes variables and pin modes and runs once when the board is powered on, while the loop function contains the main program logic and runs continuously. Pins on the Arduino can be configured as inputs or outputs using pinMode, and their states can be set or read with digitalWrite and digitalRead. Analog signals are converted to digital values between 0-1023 for processing by the microcontroller.