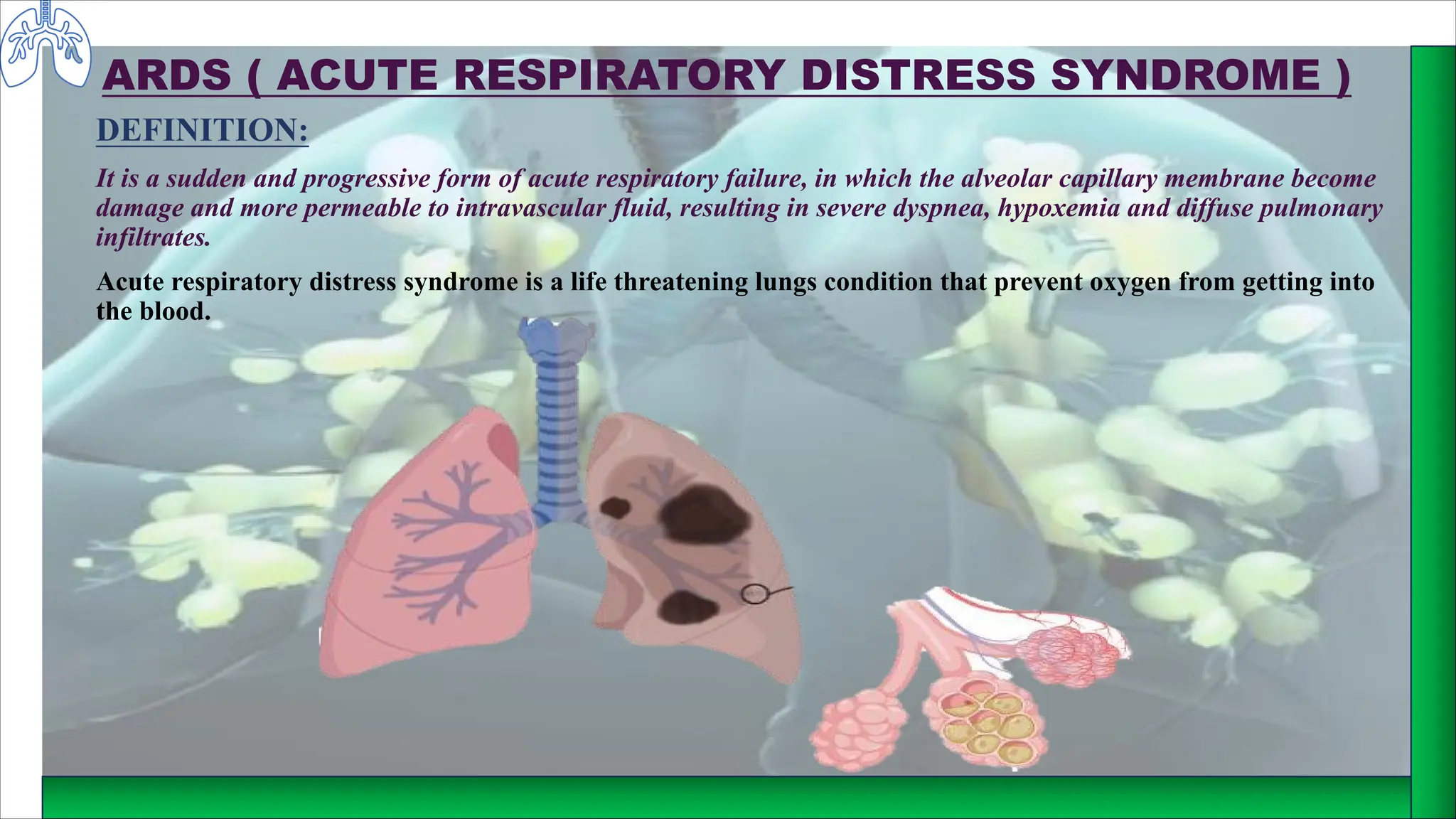
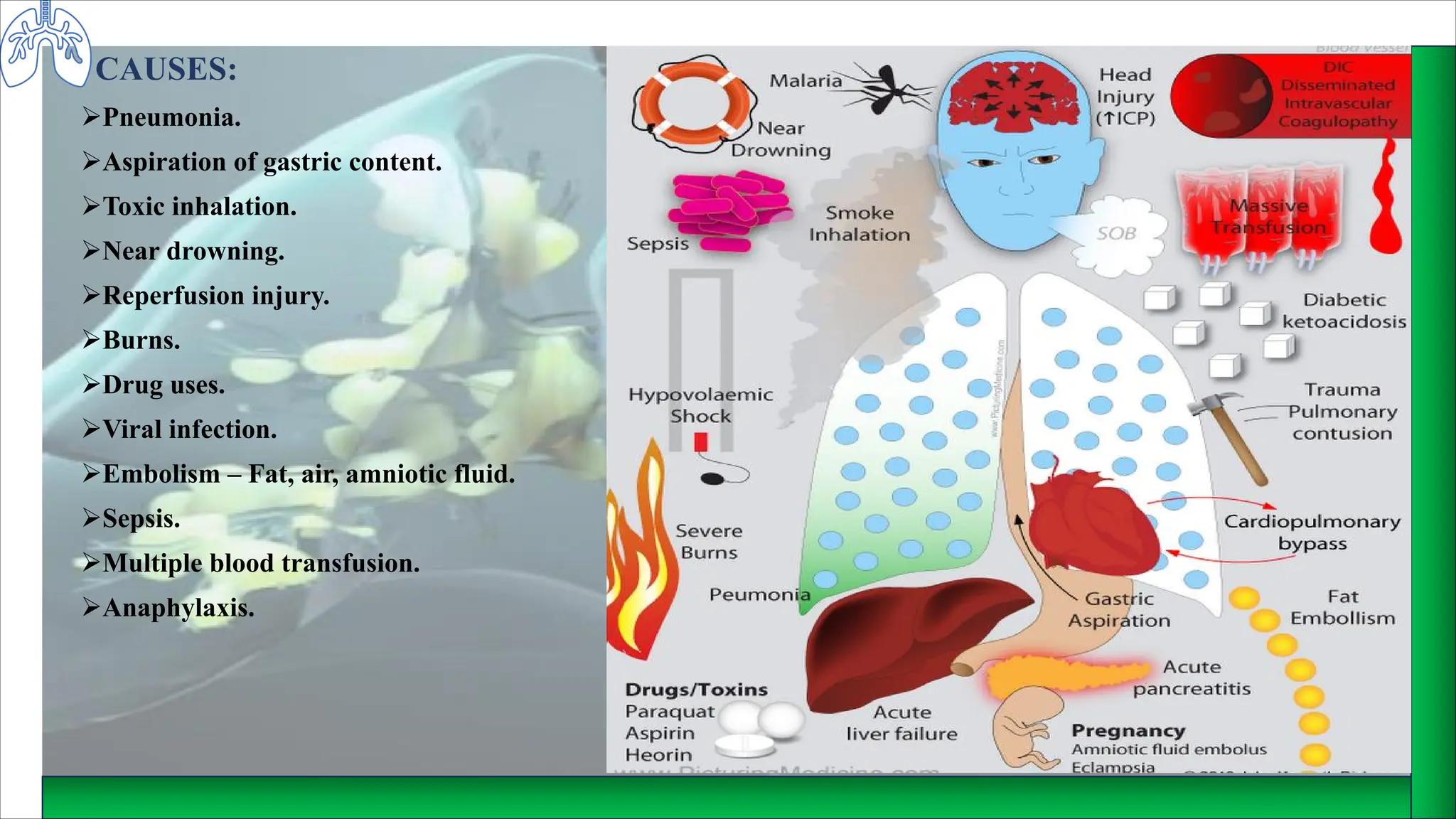
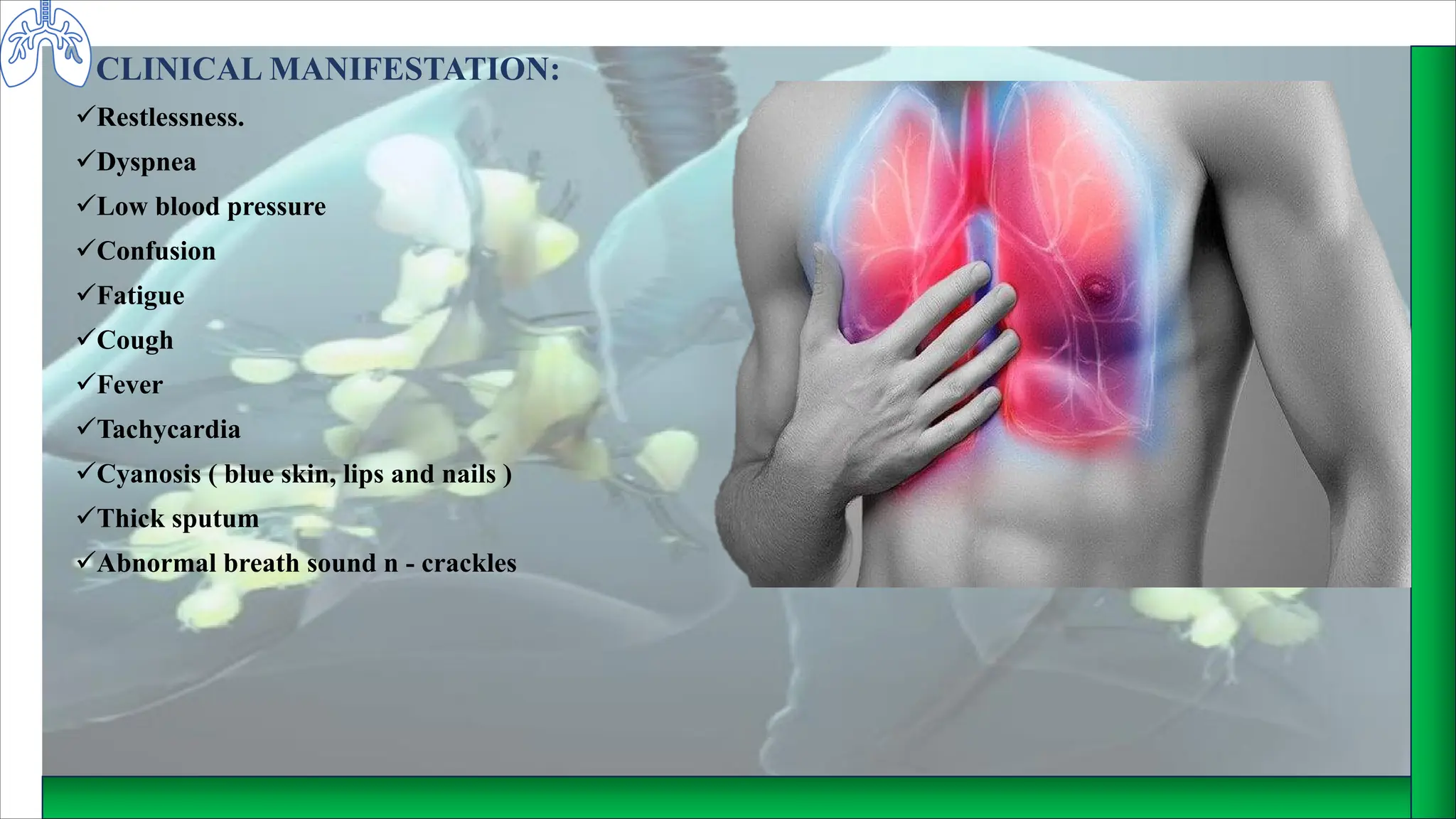
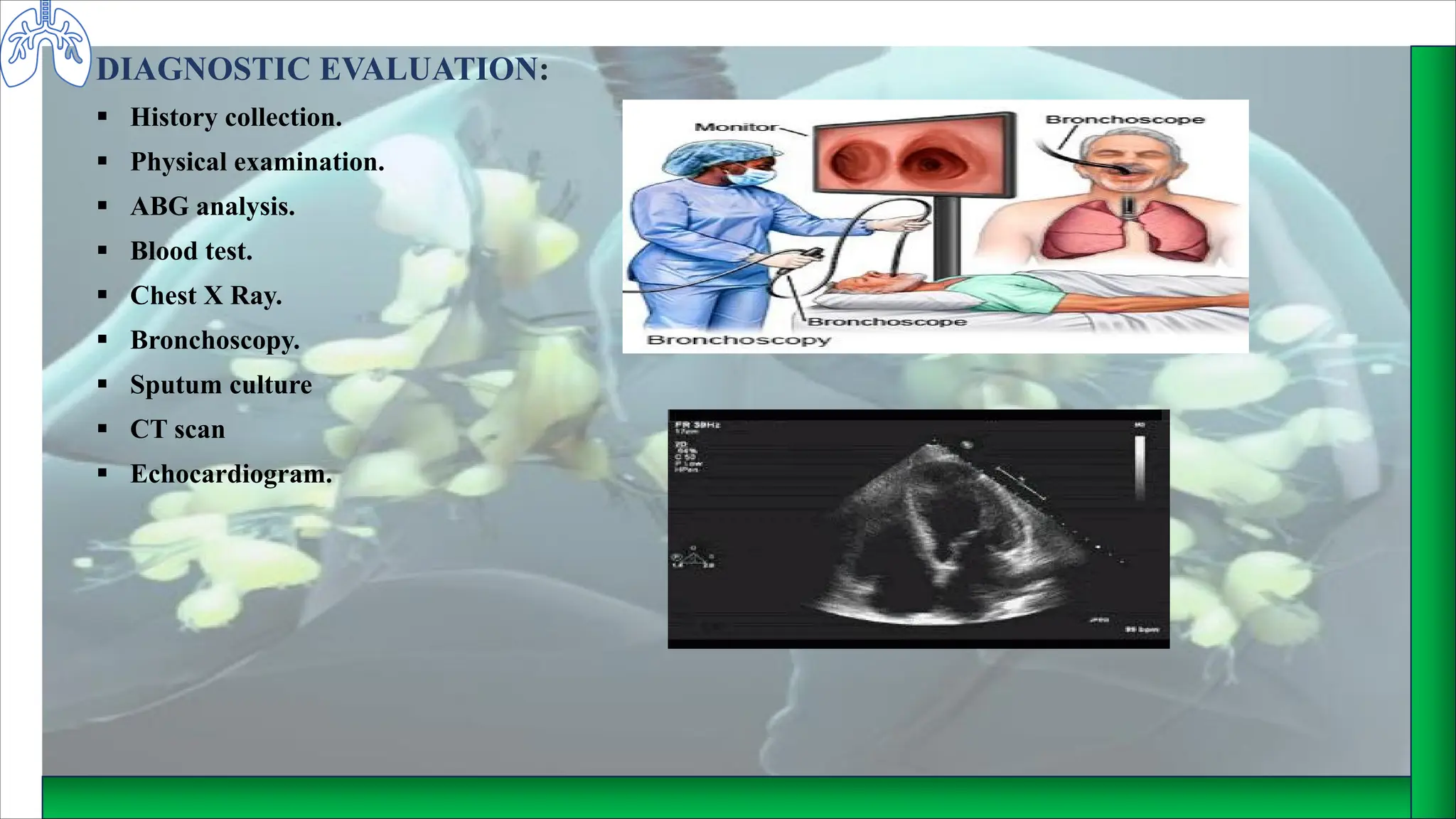
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening condition characterized by progressive respiratory failure due to damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane, leading to severe hypoxemia. Causes include pneumonia, near drowning, sepsis, and drug use, with symptoms such as dyspnea, confusion, and cyanosis. Management involves ICU care, supplemental oxygen, fluid therapy, and medications like antibiotics, corticosteroids, and bronchodilators, alongside nursing care focused on nutrition and monitoring.