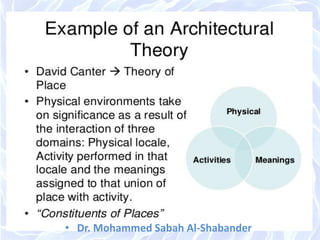
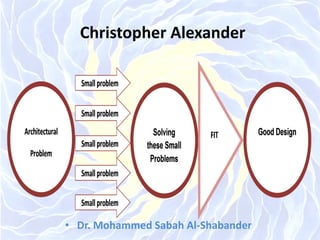
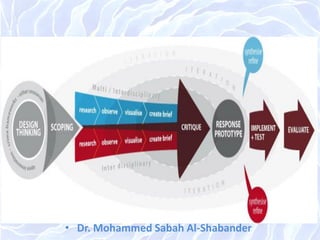
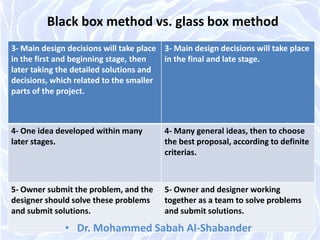
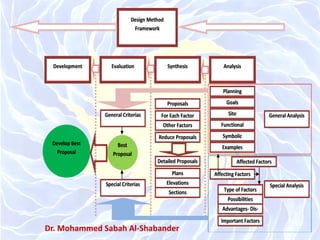
The document discusses architectural design methods, emphasizing the varied interpretations of design among professionals and the significance of human needs in the design process. It highlights key architectural schools such as Beaux-Arts and Bauhaus, as well as the evolution of design methodologies throughout the 20th century. Furthermore, it compares 'black box' and 'glass box' design methods, proposing a new compromised design method focused on transparency and teamwork.