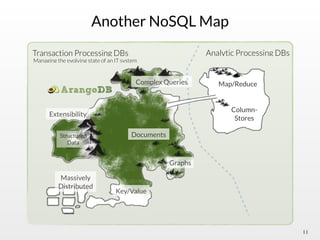
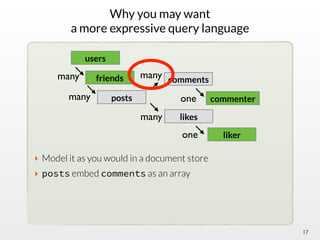
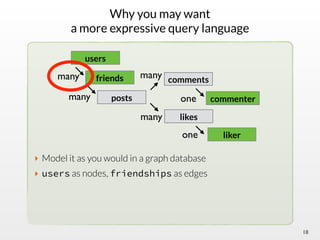
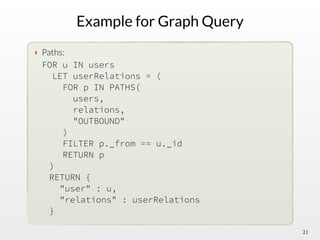
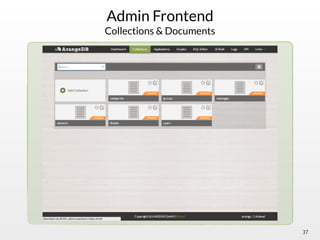
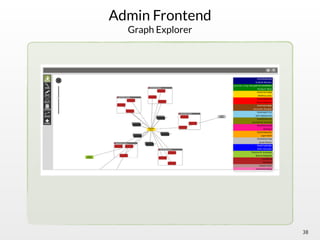
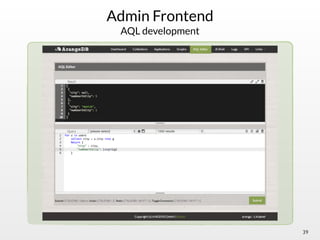
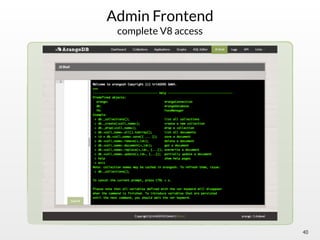
The document summarizes the multi-purpose NoSQL database ArangoDB. It describes ArangoDB as a second generation database that is open source, free, and supports multiple data models including documents, graphs, and key-value. It highlights main features such as being extensible through JavaScript, having high performance, and being easy to use through its web interface and query language AQL.





















![ArangoDB.explain()
{
"type": "2nd generation NoSQL database",
"model": [ "document", "graph", "key-value" ],
"openSource": true,
"license“: "apache 2",
"version": [ "1.3 stable", "1.4 alpha" ],
"builtWith": [ "C", "C++", "JS" ],
"uses": [ "Google V8" ],
"mainFeatures": [
"Multi-Collection-Transaction",
"Foxx API Framework",
"ArangoDB Query Language",
"Various Indexes",
"API Server",
"Automatic Schema Recognition"
]
}
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arangodbv3-shortcopy-140522223653-phpapp02/85/ArangoDB-43-320.jpg)