1. Aquatic ecosystems can be categorized based on factors such as salinity, flow, depth, and permanence. They support a diversity of life including plankton, nekton, benthos, and neuston.
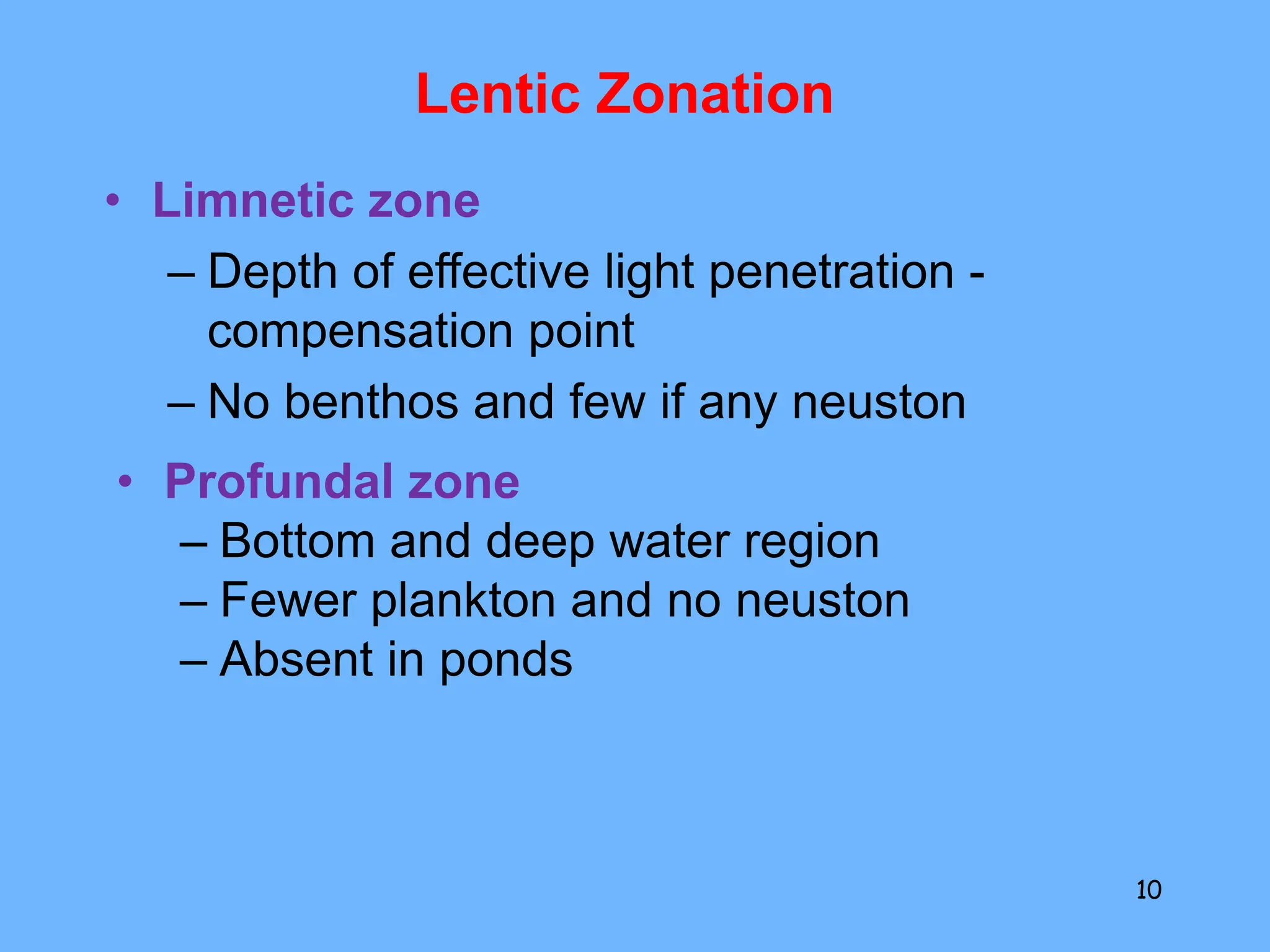
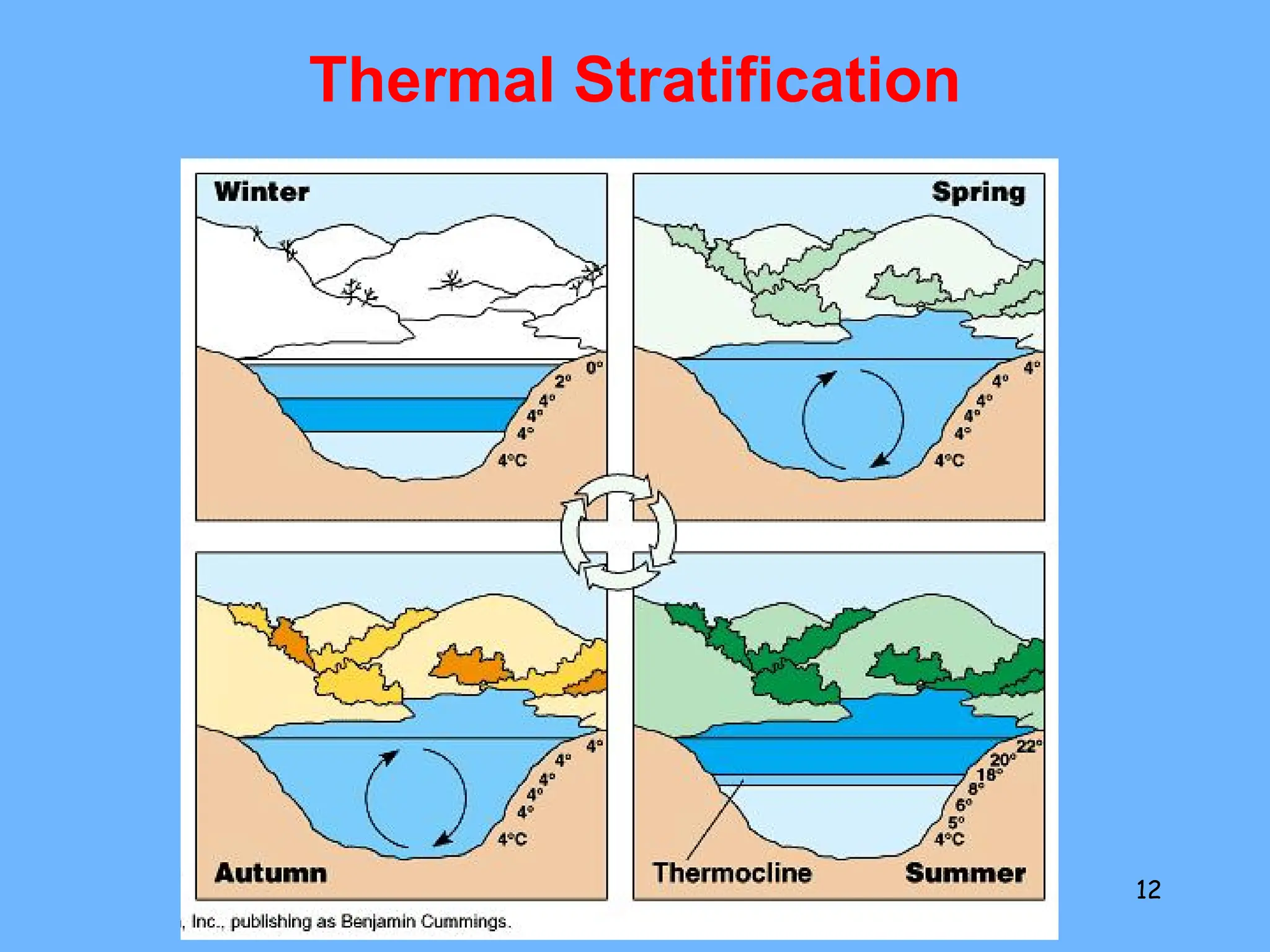
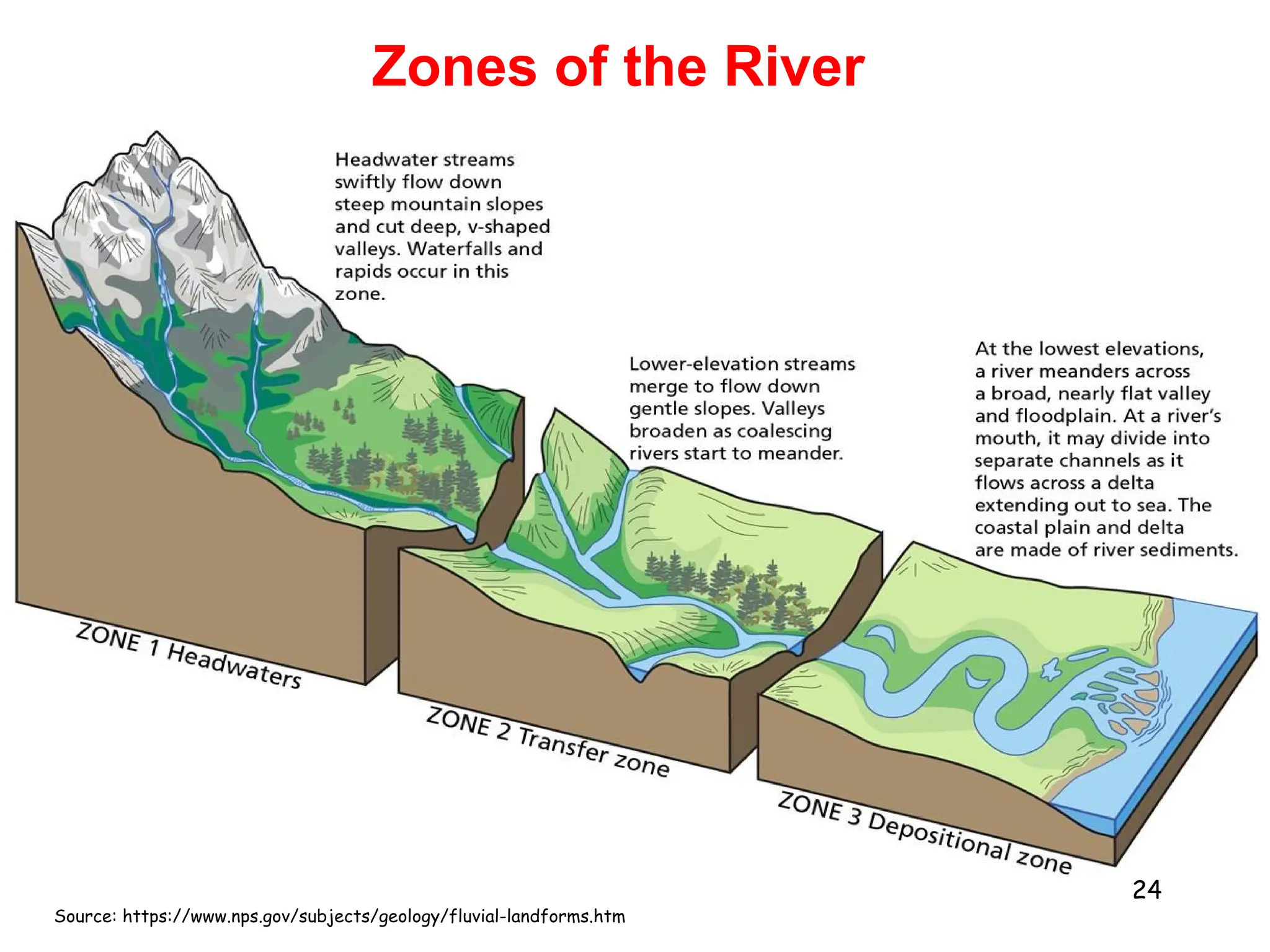
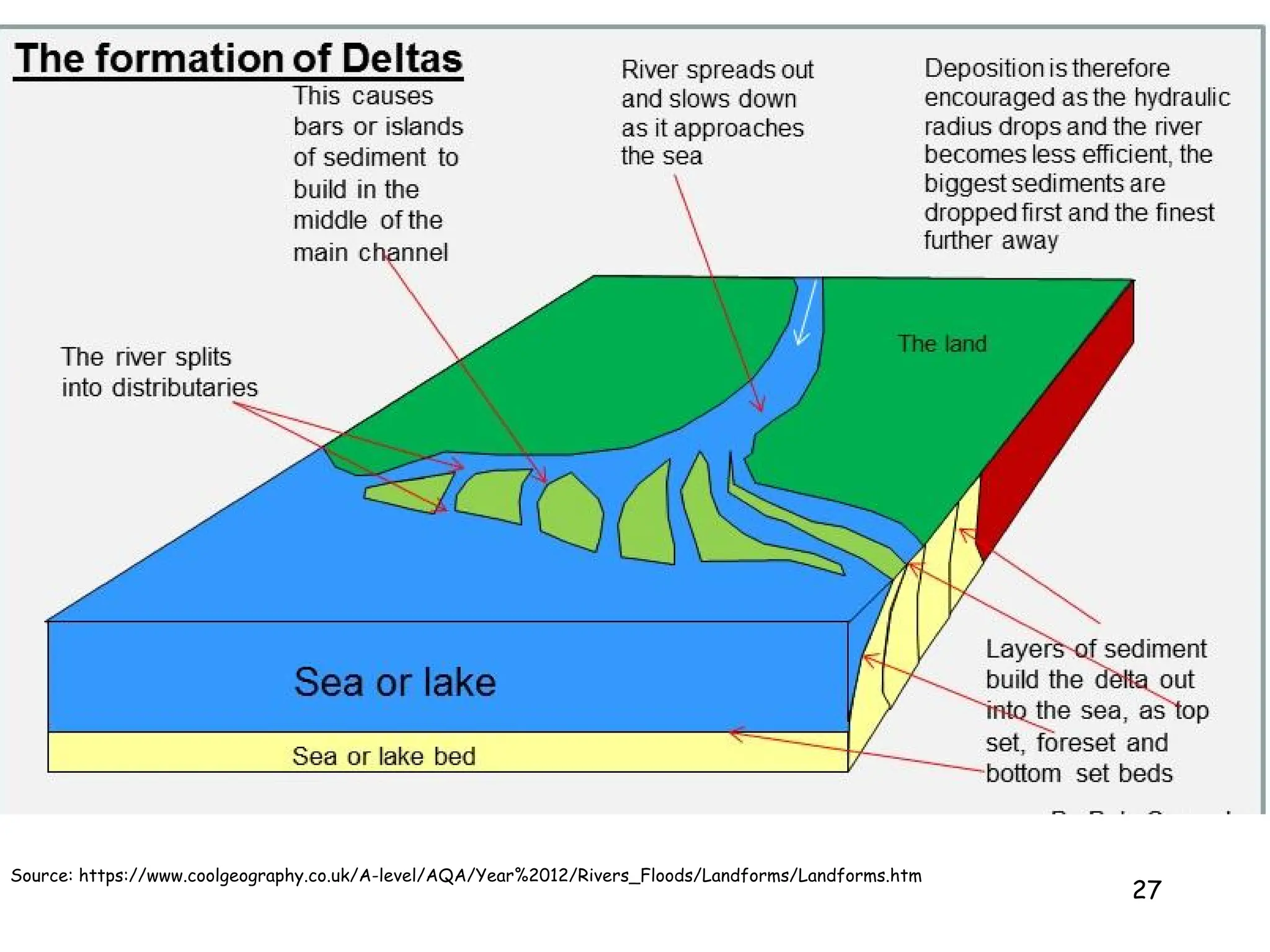
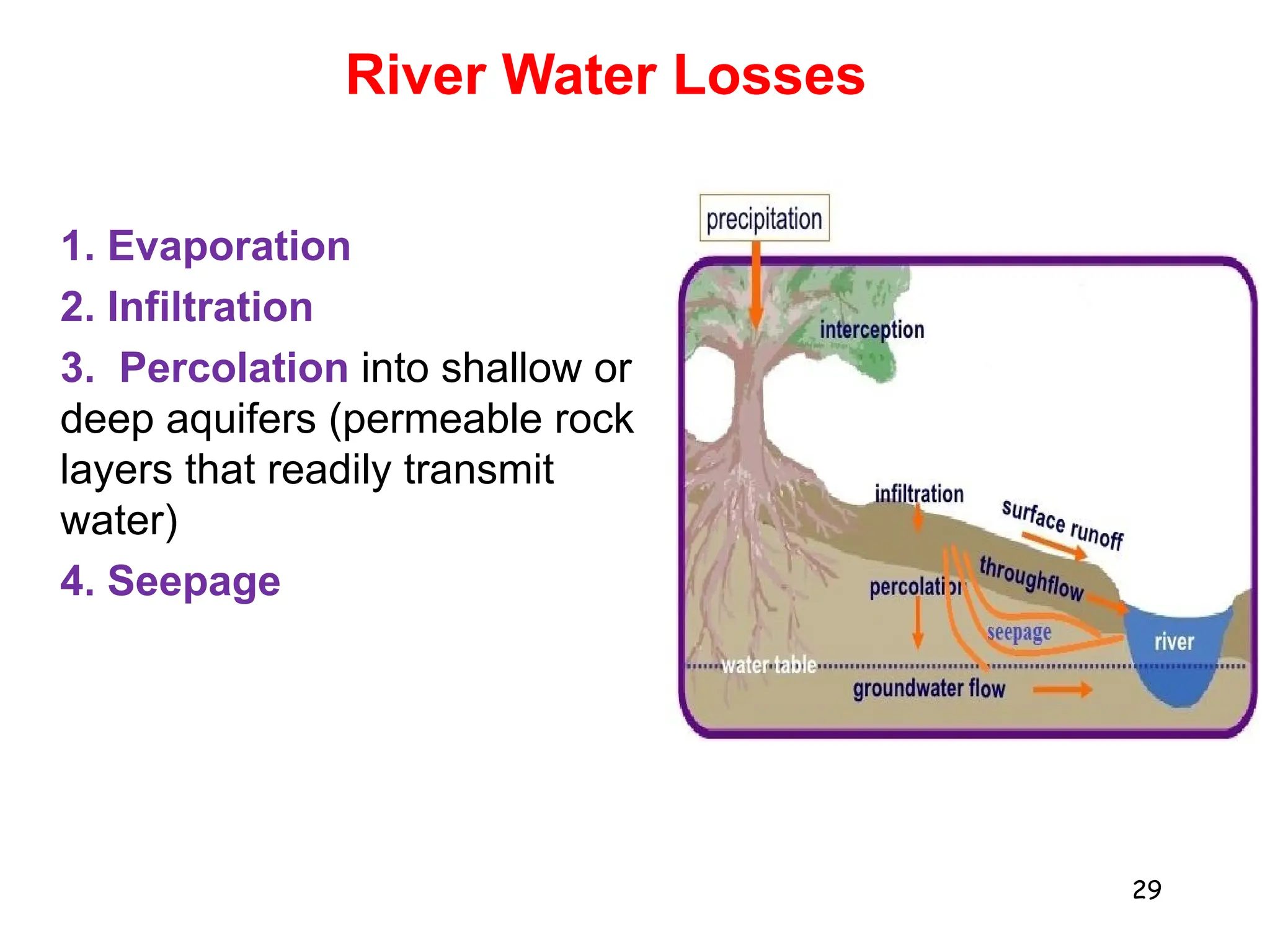
2. Freshwater ecosystems include lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams. Lakes can be stratified into zones based on light penetration and temperature. Rivers flow from upper to lower courses, eroding and depositing sediment along their paths.
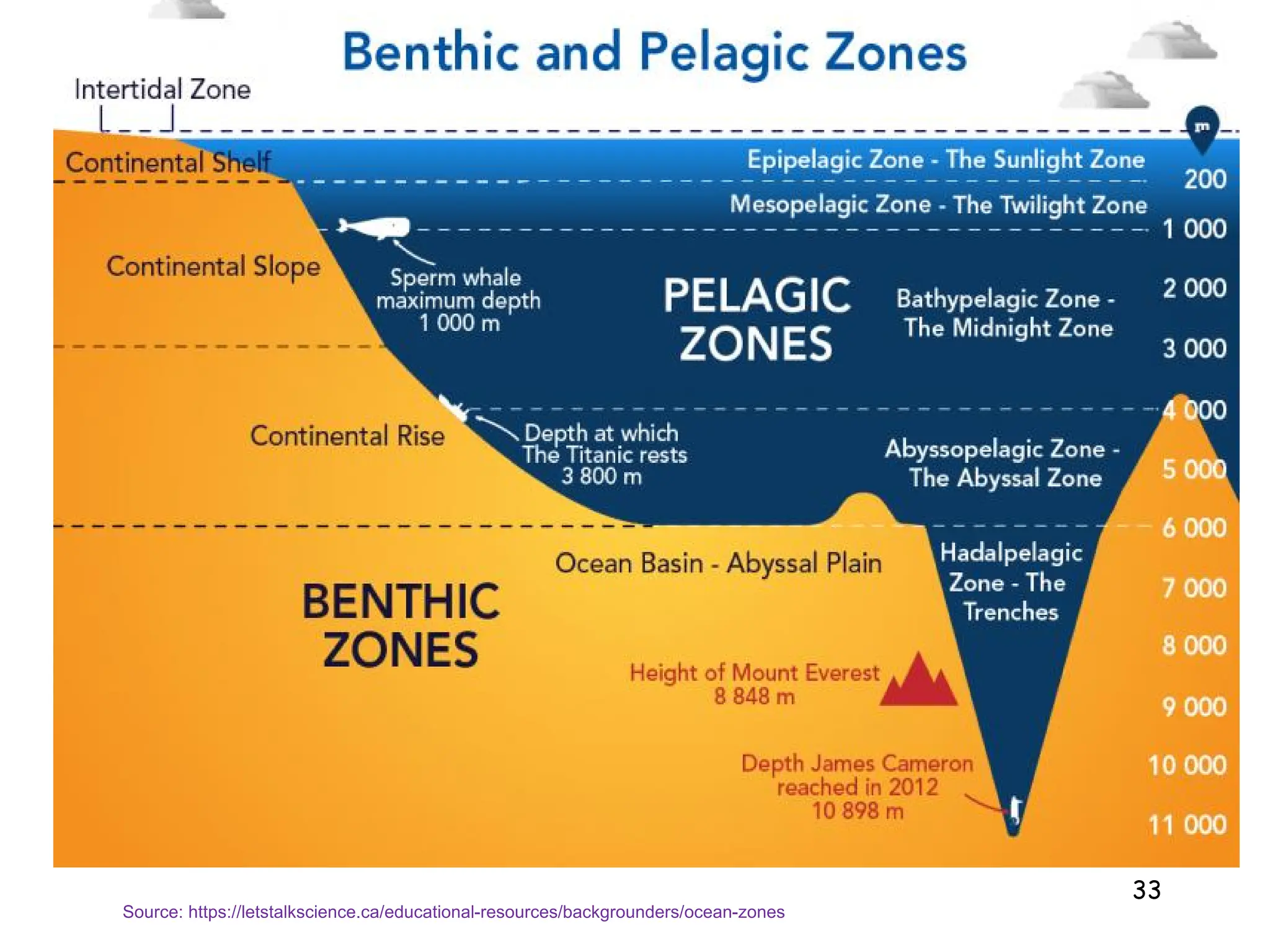
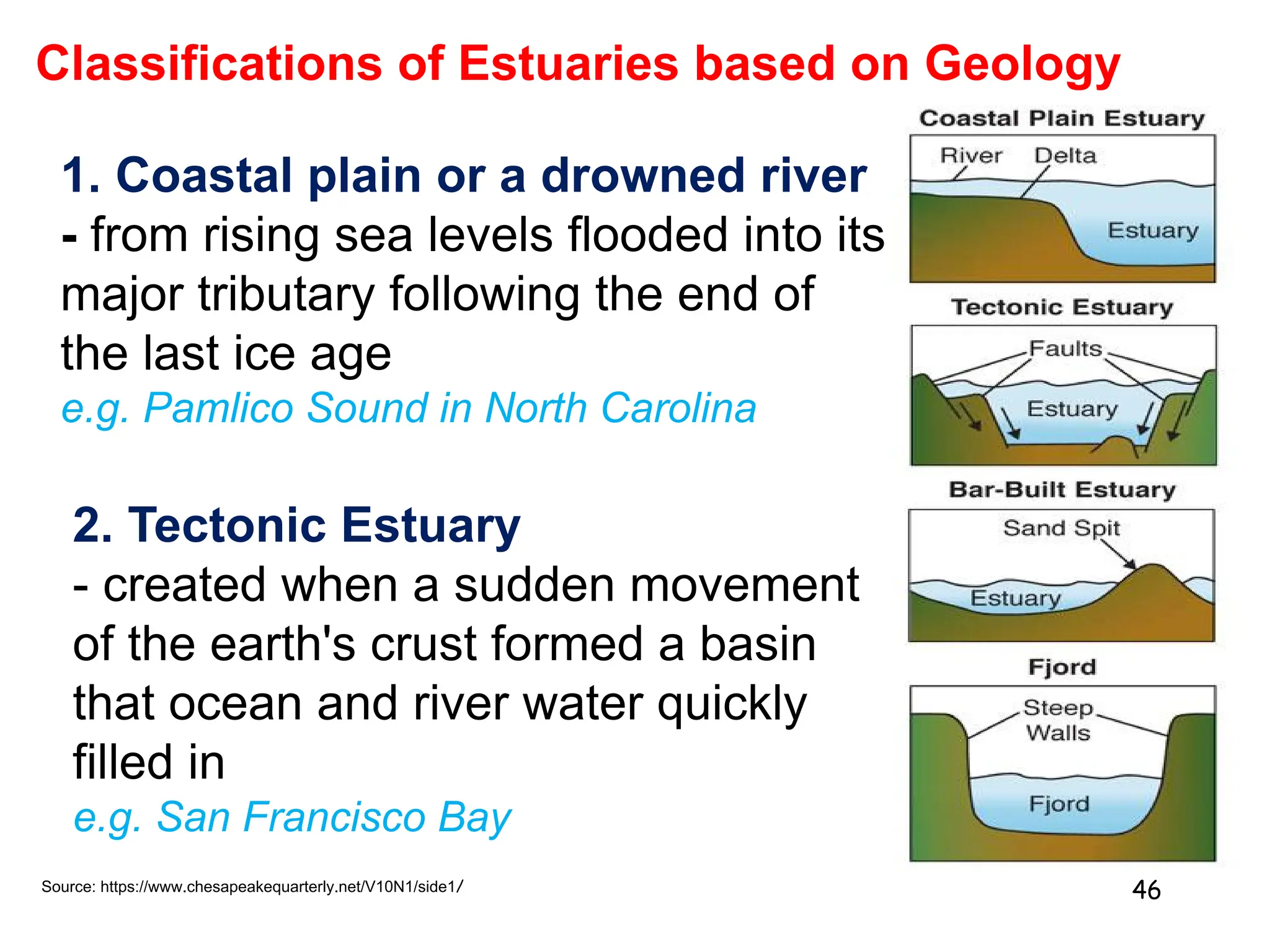
3. Marine ecosystems cover most of the Earth and include the ocean, which is stratified into pelagic zones. Estuaries form where freshwater mixes with saltwater, supporting complex food webs.