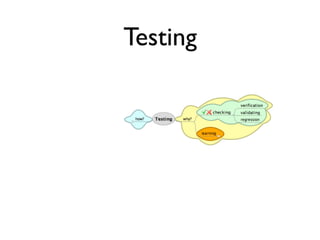
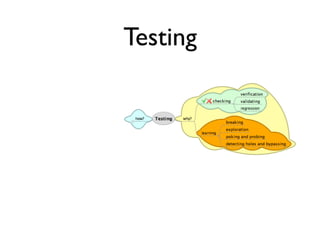
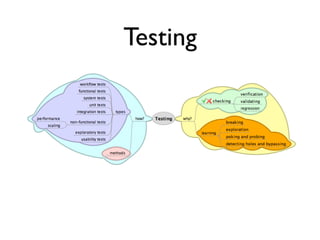
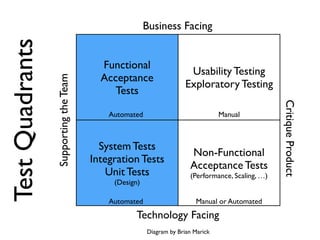
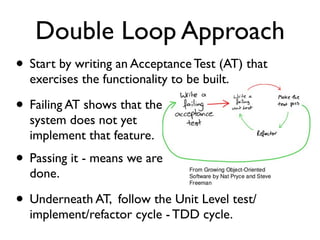
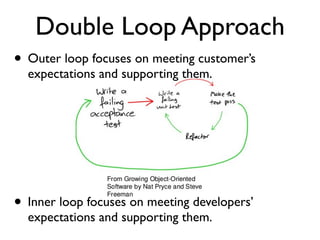
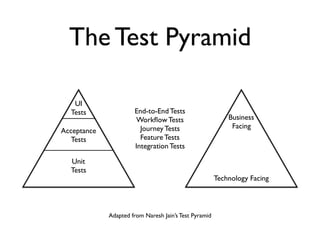
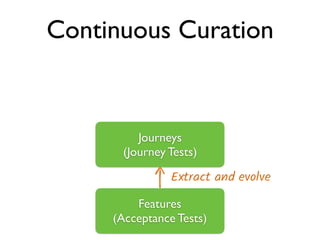
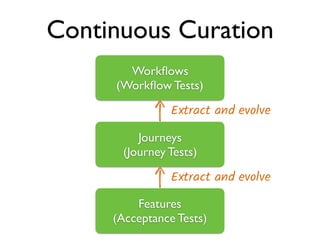
This document discusses approaches to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD) and behavior-driven development (BDD). It defines ATDD and BDD, compares them, and outlines best practices like the double loop approach, continuous curation of tests, and ensuring tests are maintained as code. It also discusses test pyramids and different types of tests like unit, integration, acceptance, and how they should be balanced.