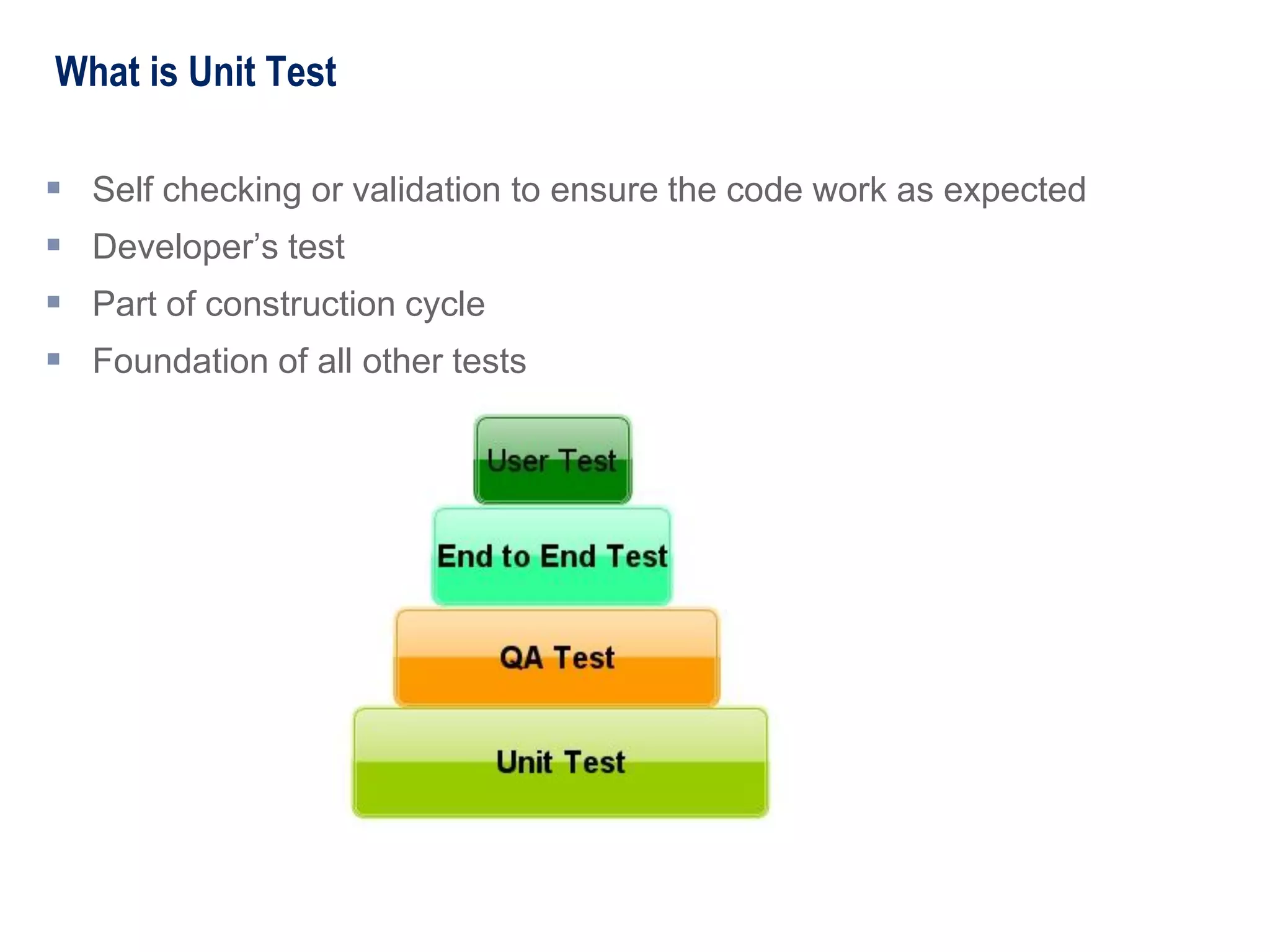
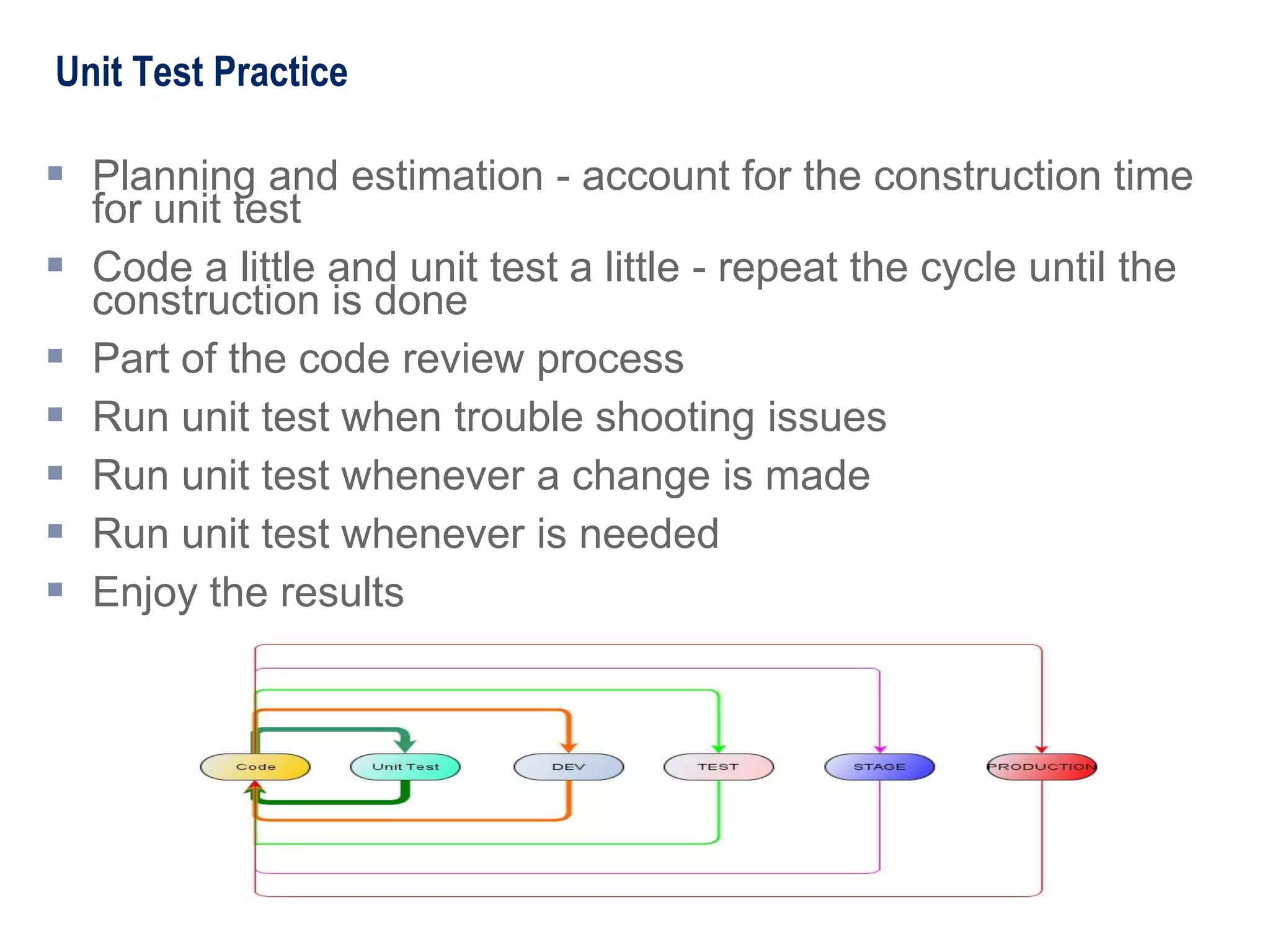
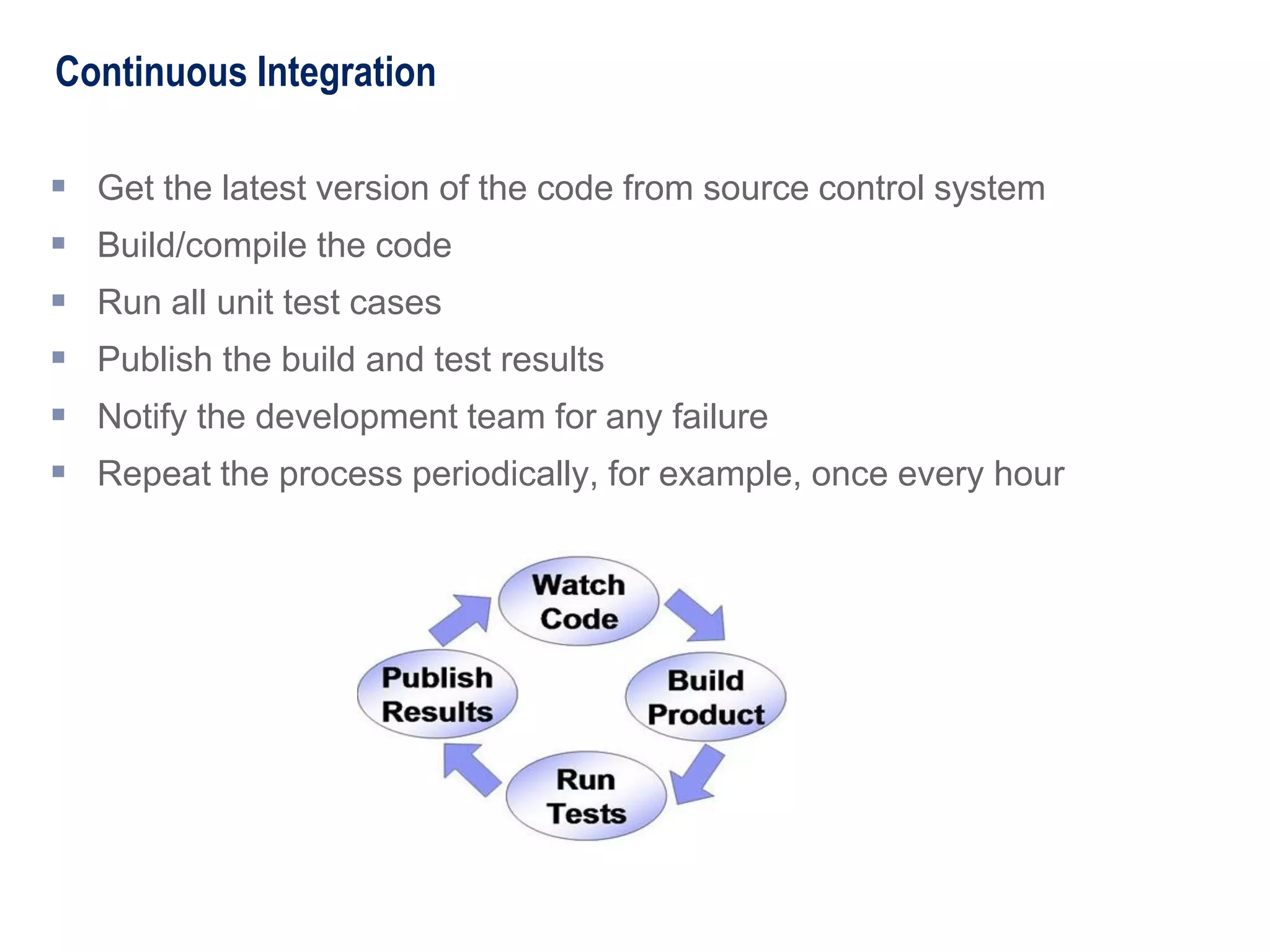
The document introduces unit testing to management and business stakeholders, explaining that unit tests are written by developers to test their code, catch errors early in the development process when they are cheaper to fix, and ensure code works as intended as well as provide many other benefits like establishing a safety net and writing cleaner code. Unit tests should be implemented throughout the software development lifecycle from initial coding through integration and regression testing.