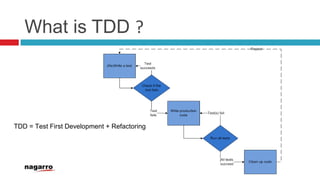
This document discusses Test Driven Development (TDD). It defines TDD, outlines the TDD process which involves writing tests first and then code to pass the tests, and emphasizes refactoring. Benefits of TDD include improved code quality, reduced bugs, and serving as documentation. Key TDD terms and libraries like JUnit and Mockito are explained. Continuous Integration (CI) is also discussed as it automates testing and builds when code is committed.