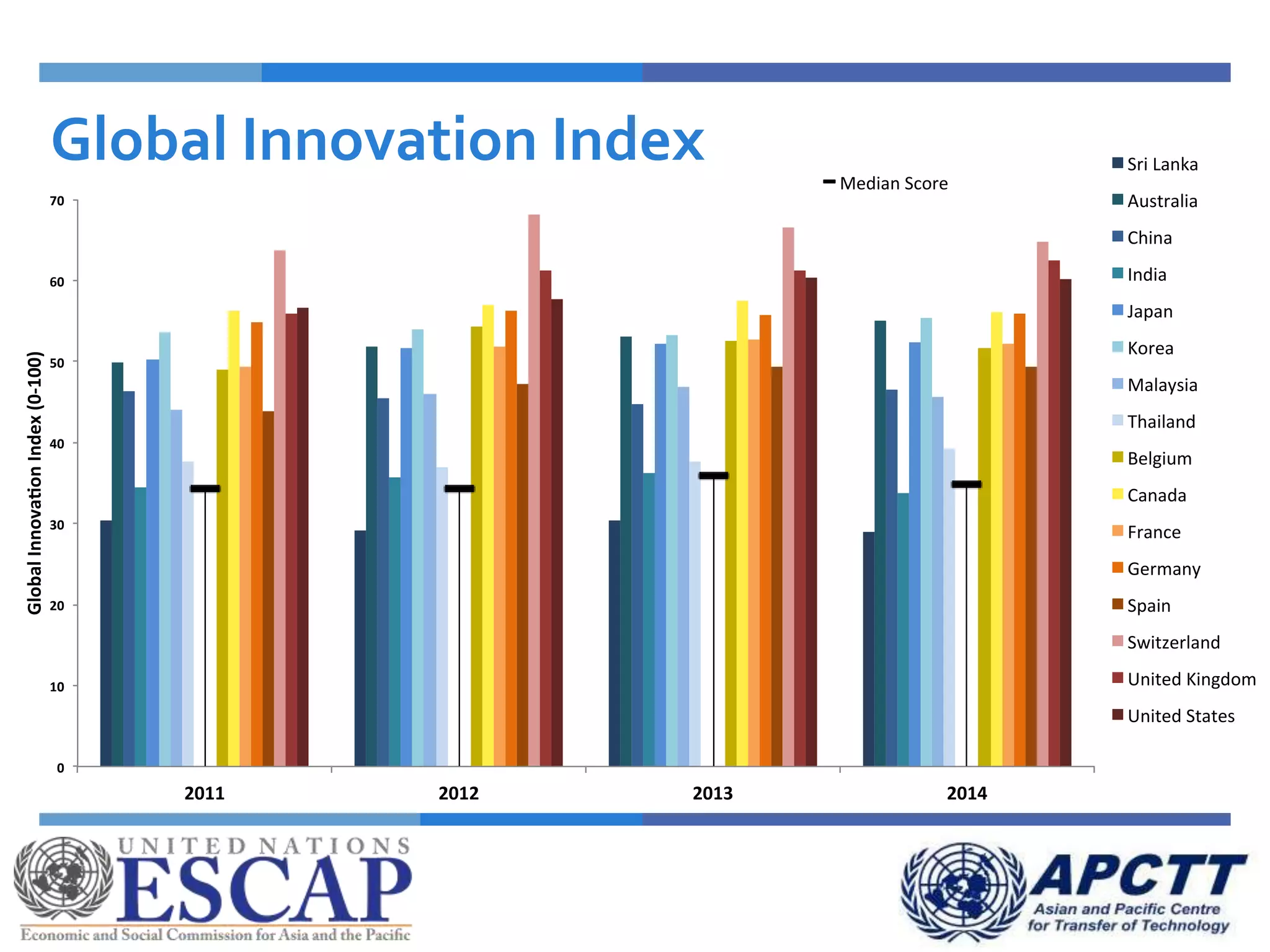
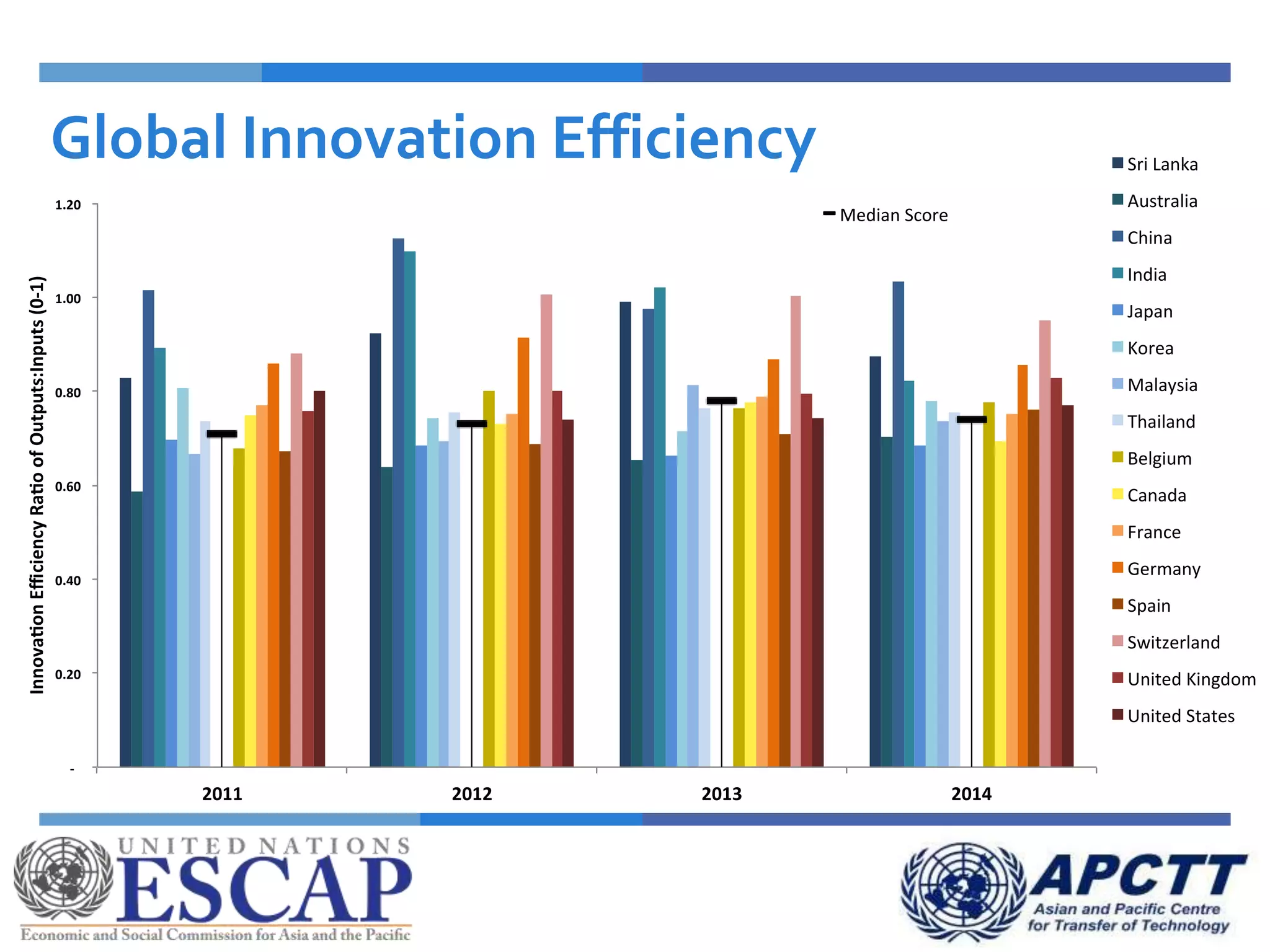
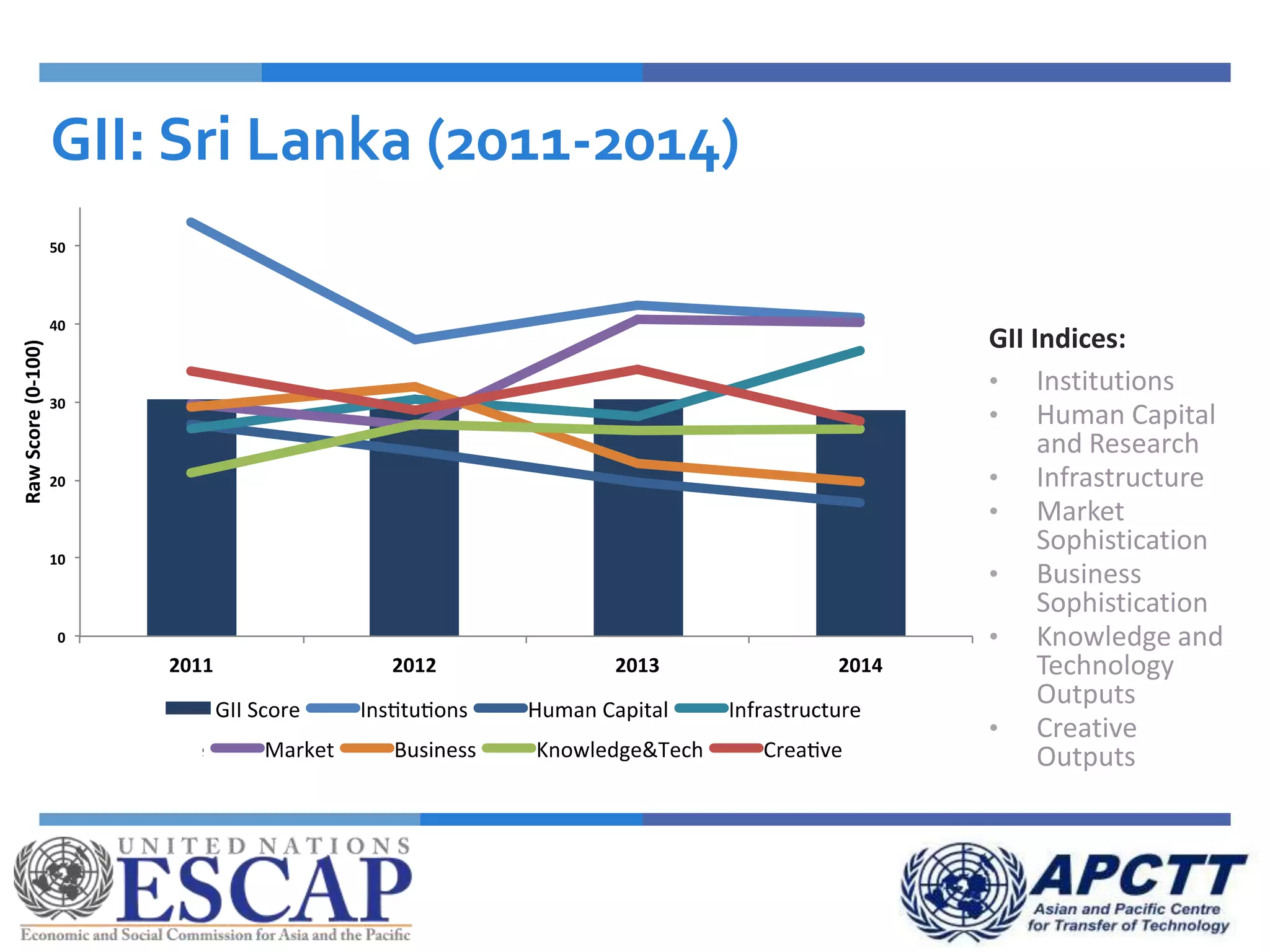
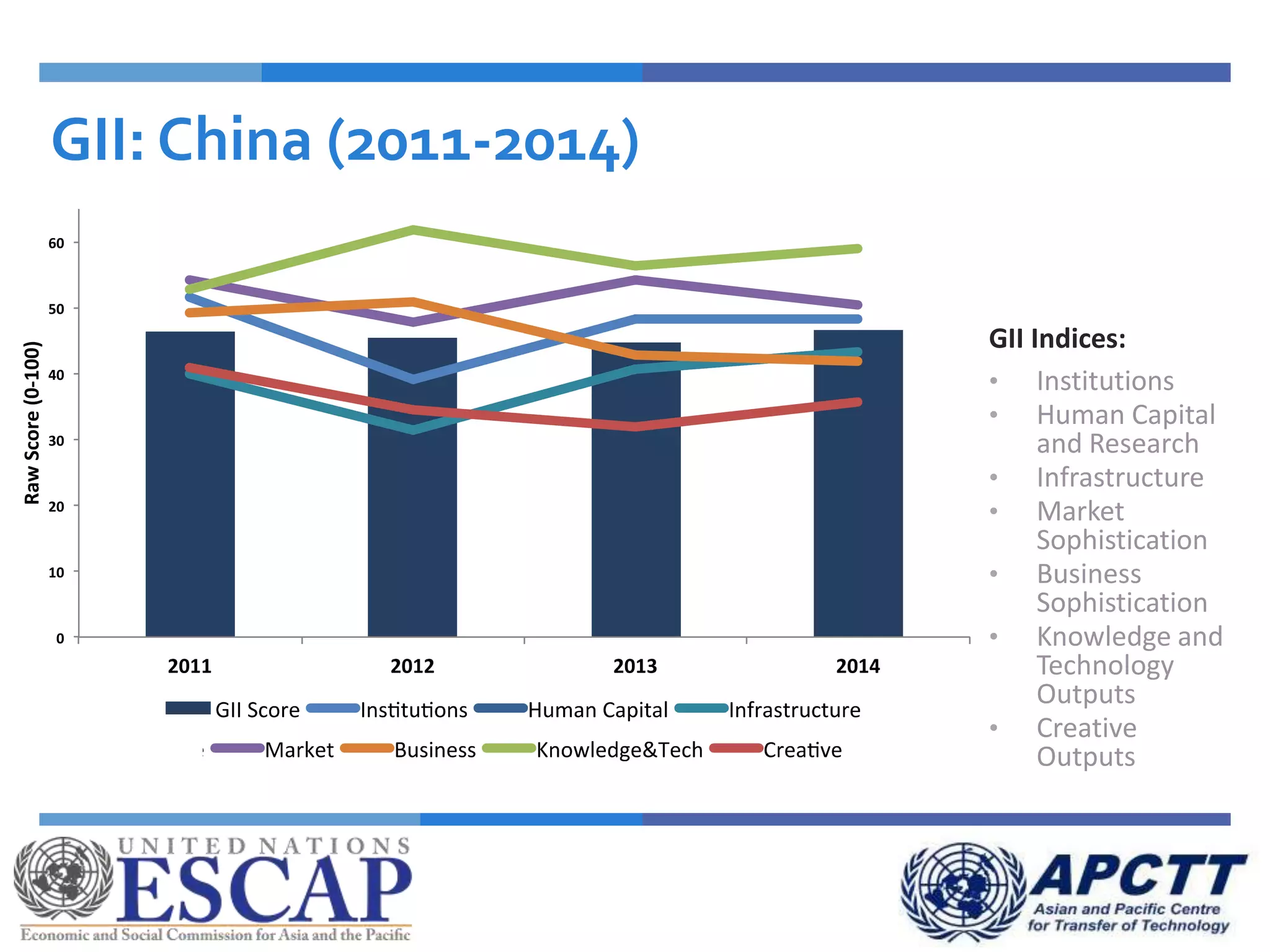
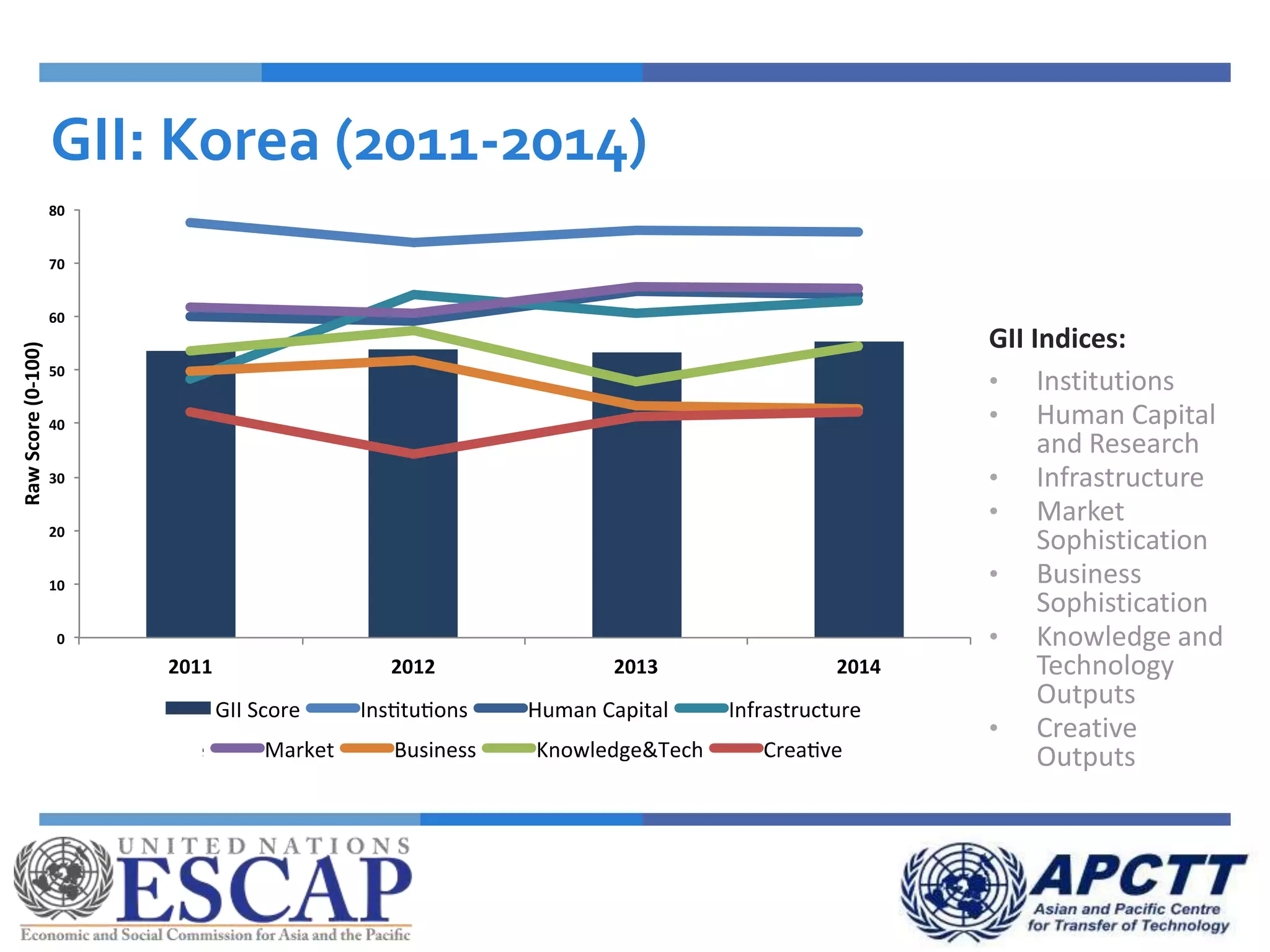
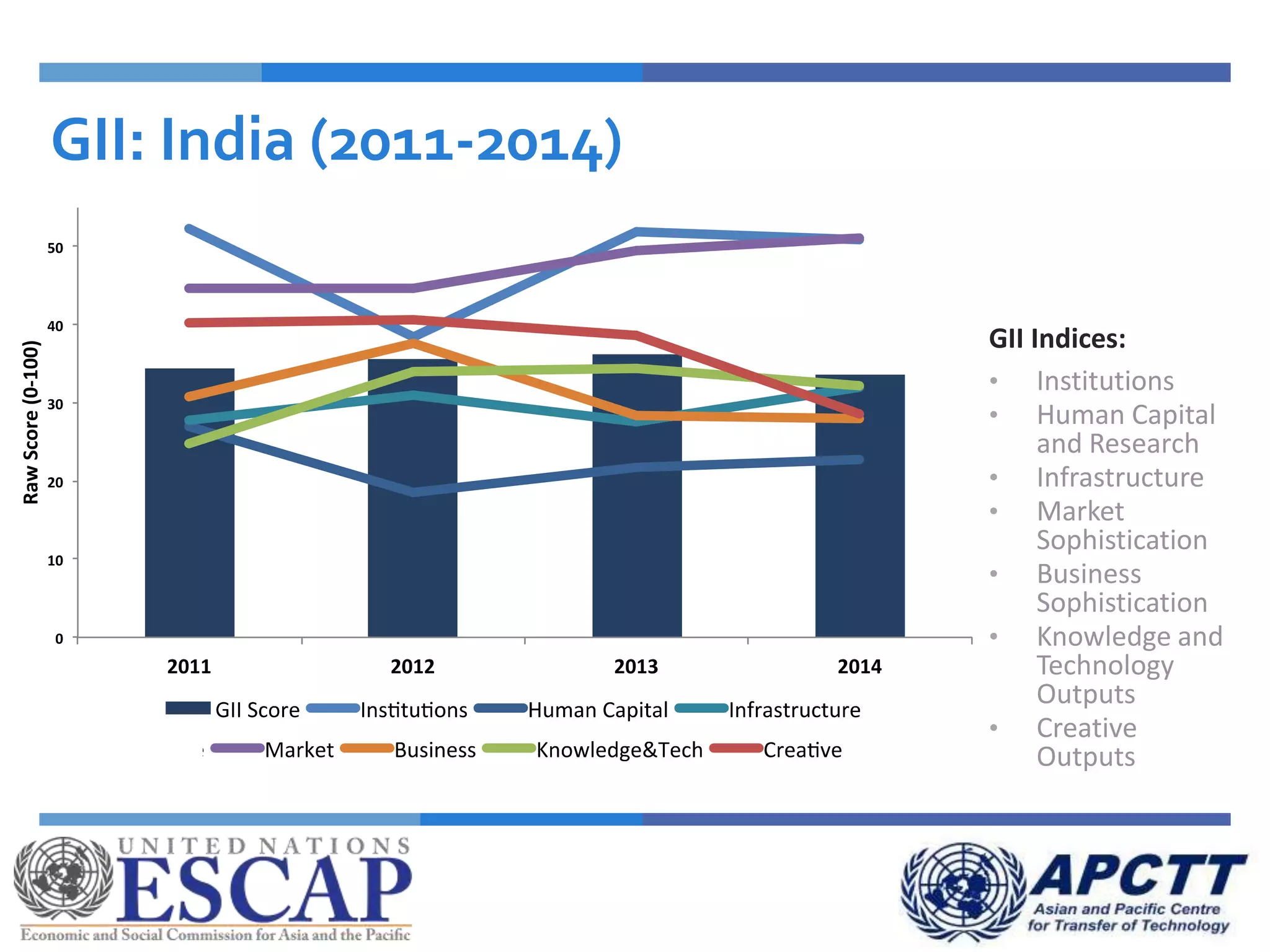
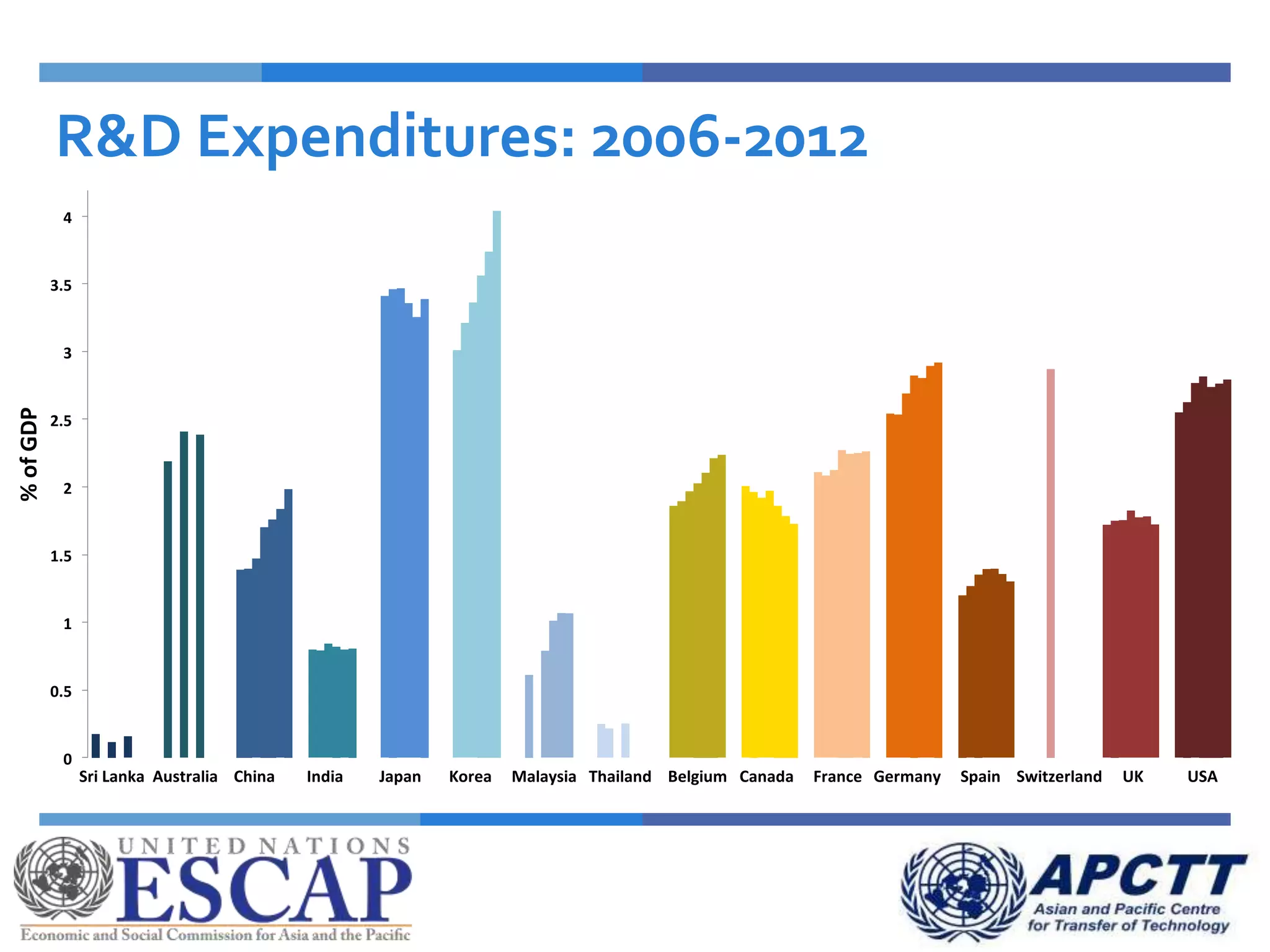
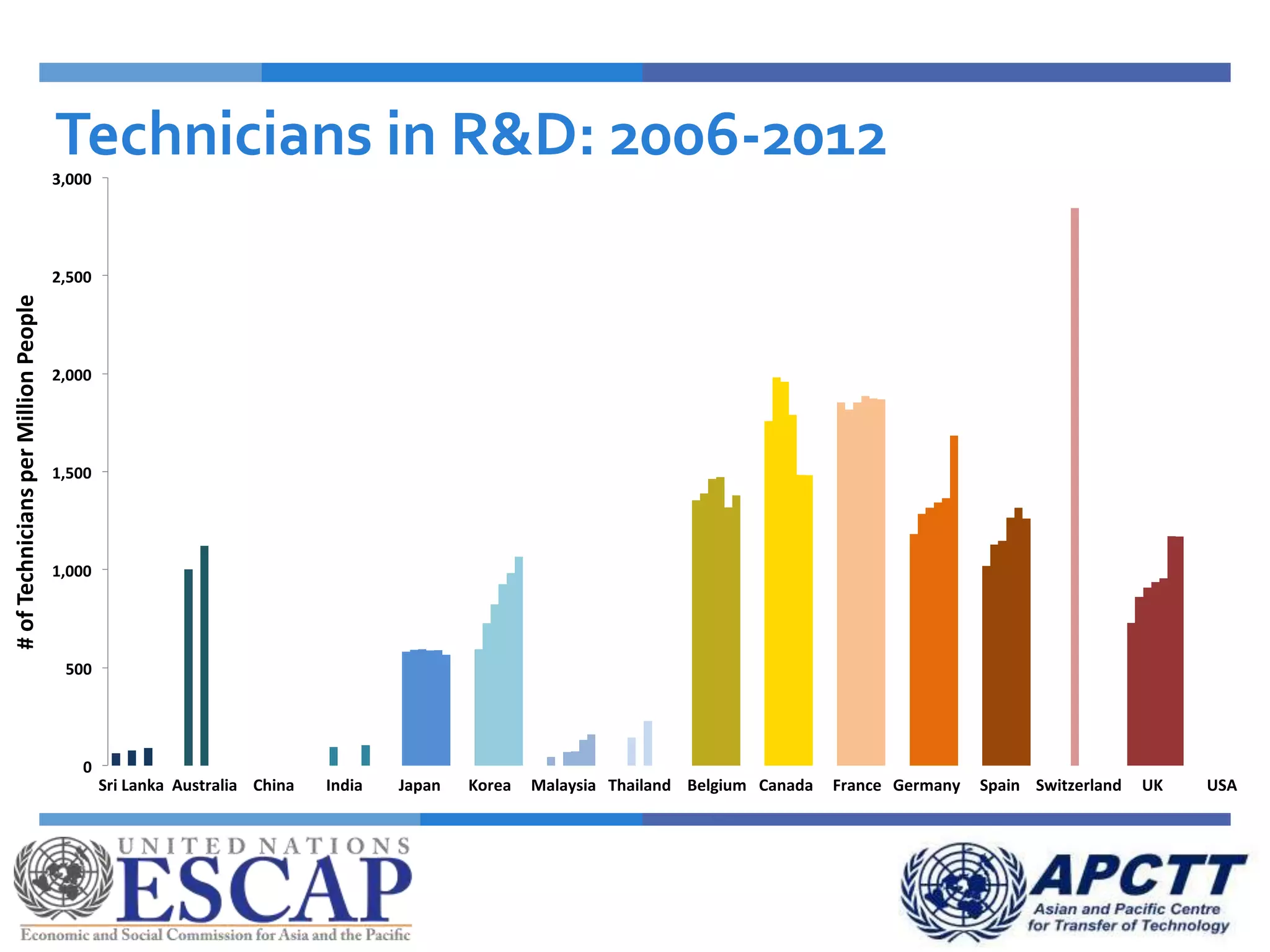
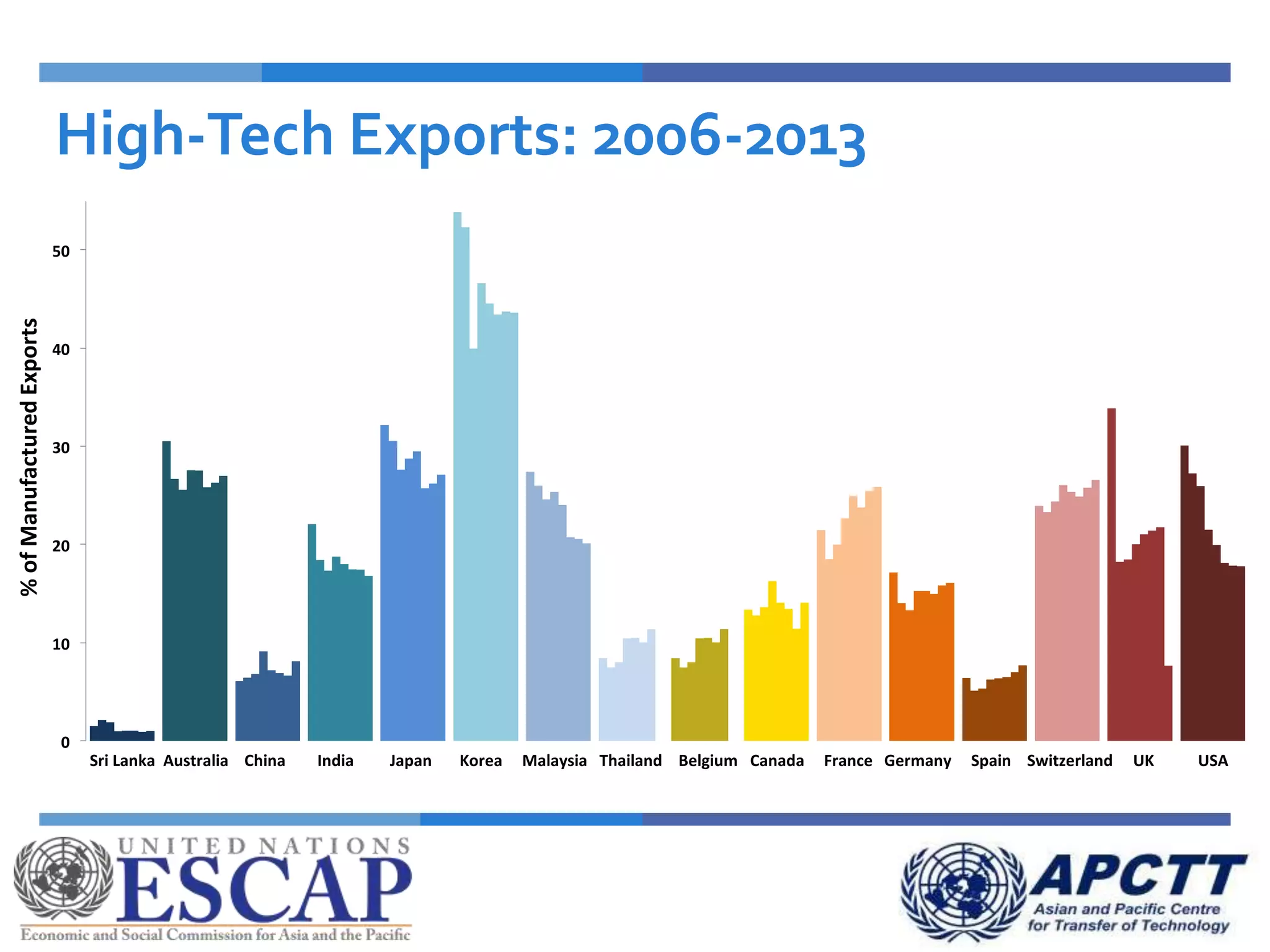
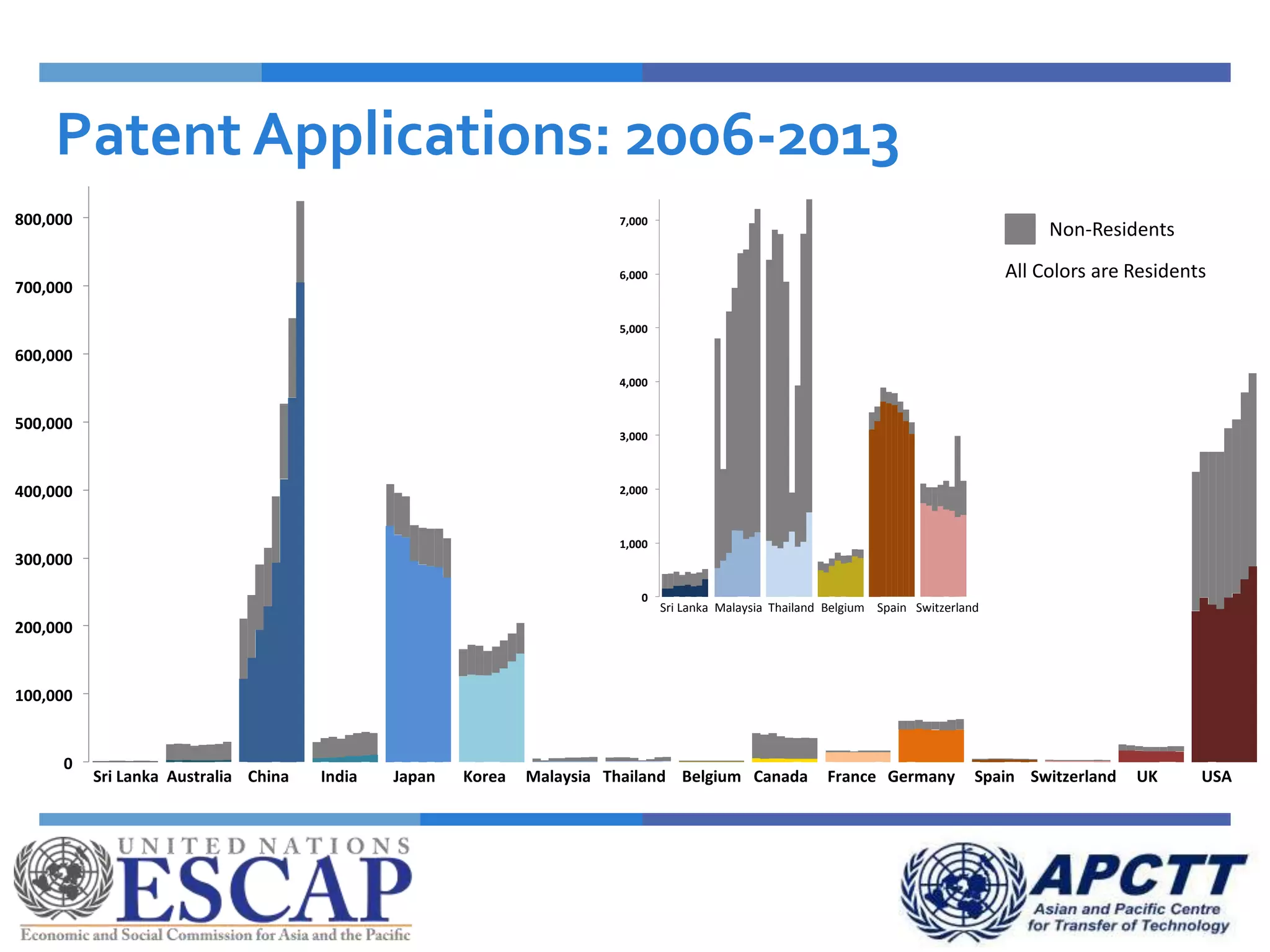
This document summarizes approaches and strategies for measuring science, technology, and innovation (STI). It discusses current STI indicators and databases like the Global Innovation Index, which ranks countries based on enabling environments and innovation outputs. The presentation provides an overview of the Global Innovation Index and examines STI metrics like R&D expenditures, researchers, technicians, patents, and high-tech exports for countries like Sri Lanka, China, Korea, and India from 2006-2014. It finds that Asian countries have improved on indicators but still lag behind leaders like the US and Germany. The document advocates using a balanced set of STI indicators for evidence-based policymaking.