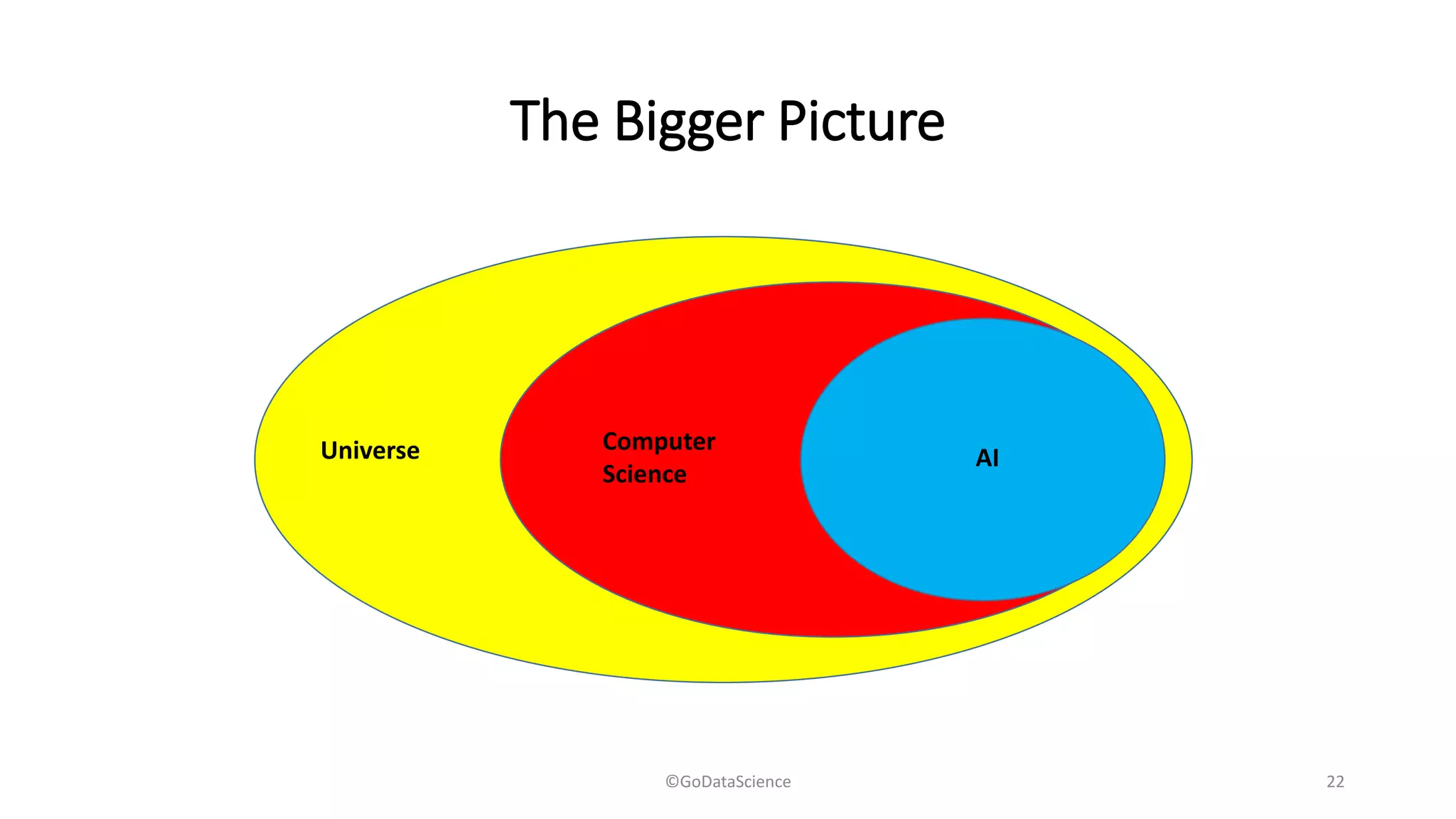
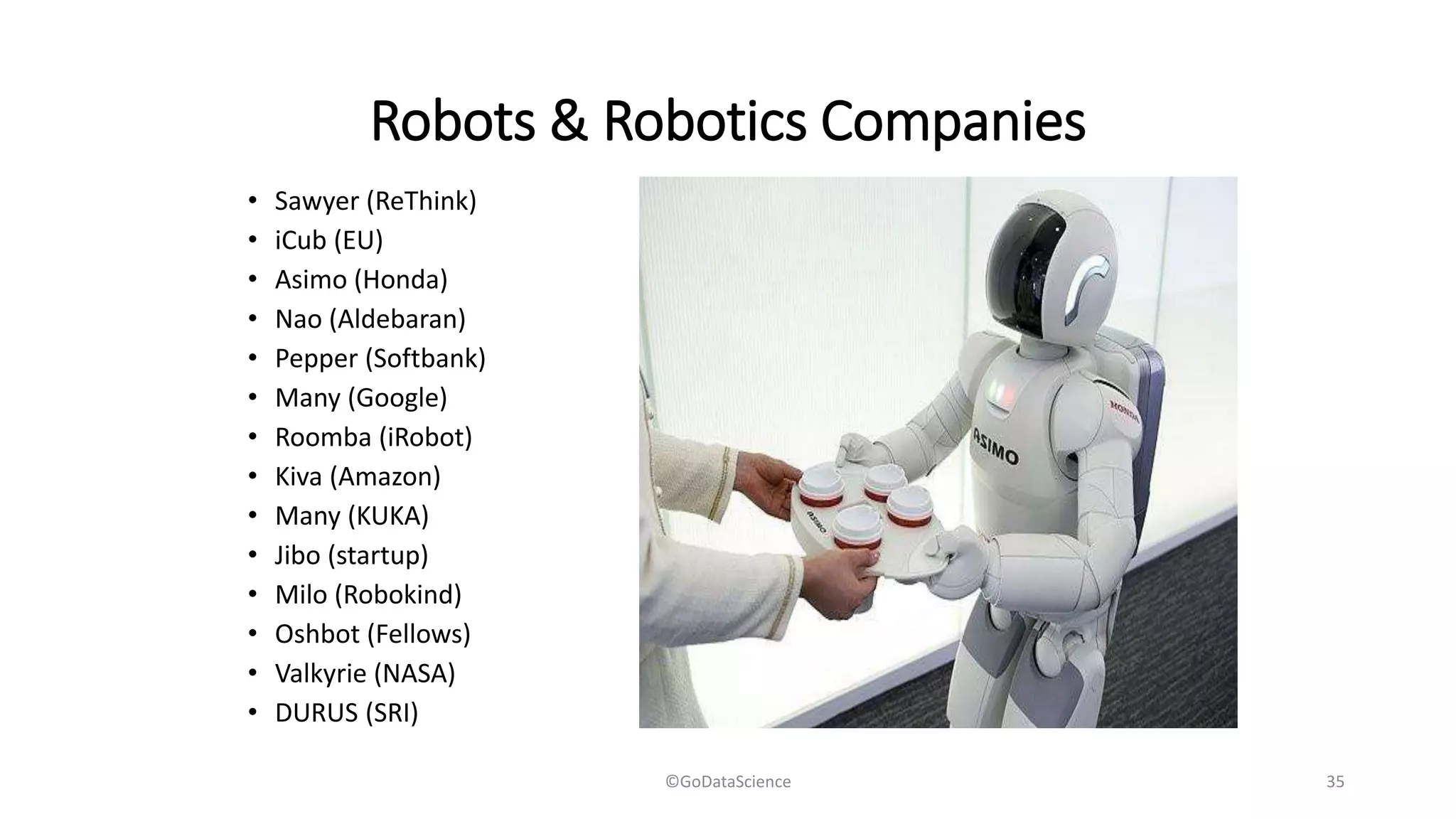
The document discusses the applications, algorithms, and advancements in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), emphasizing their importance in various business and technological contexts. It details types of learning, various ML and deep learning toolkits, notable AI companies, and milestones in AI history. The document also explores the opportunities and threats presented by AI and robotics in modern society.