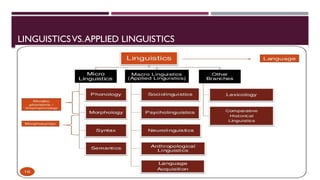
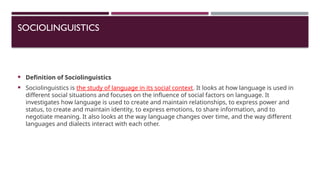
Applied linguistics is an interdisciplinary field that investigates the relationship between language and society, focusing on language use in social and cultural contexts. It encompasses areas like language teaching, bilingualism, and language policy, and has theoretical foundations based on cognitive and structural approaches. The field continues to evolve, informing educational practices and language planning while presenting opportunities for future research on language acquisition and the effects of language policies.