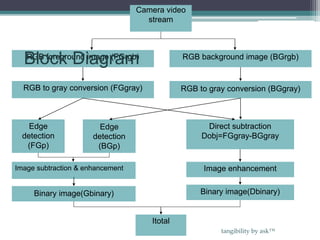
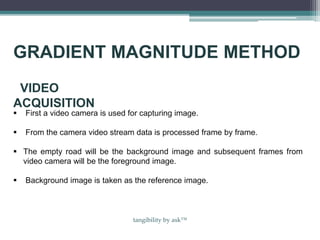
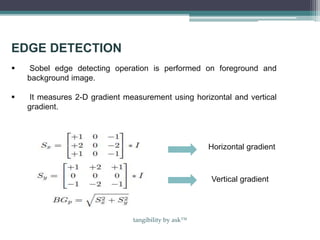
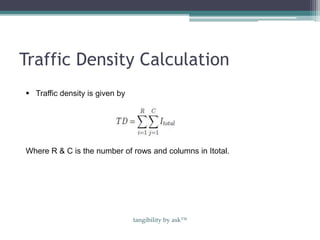
This document discusses a method for traffic congestion detection using image processing techniques, aiming to reduce manpower and waste of resources. The proposed technique utilizes video analysis to assess traffic density by comparing captured images and involves several processing steps including edge detection, filtering, and image enhancement. A more efficient automatic traffic control system is presented, which could potentially employ satellite imagery and vehicle identification for improved traffic management.