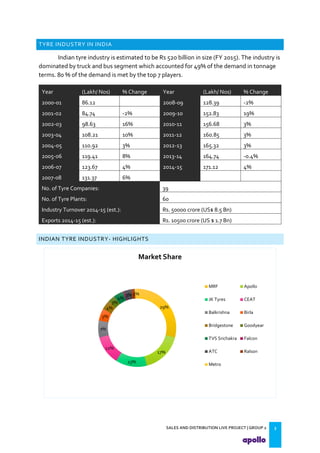
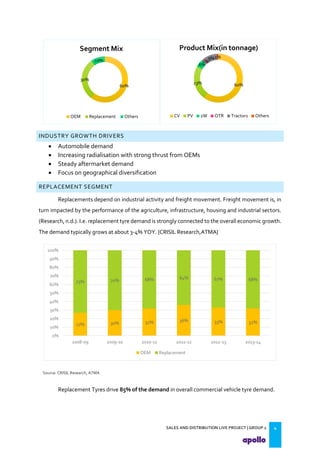
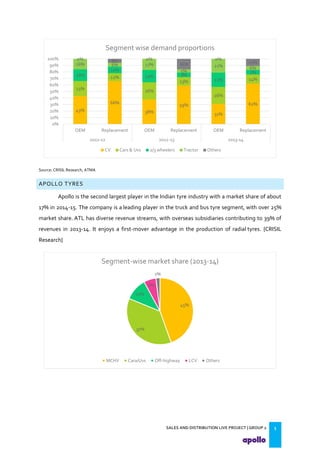
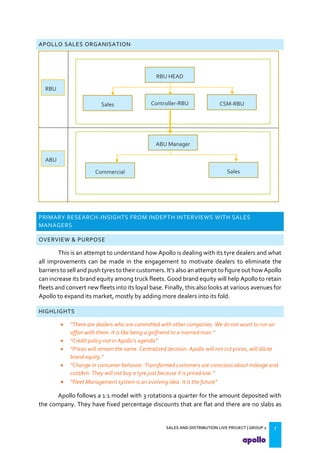
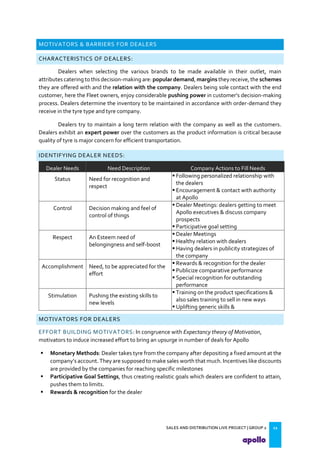
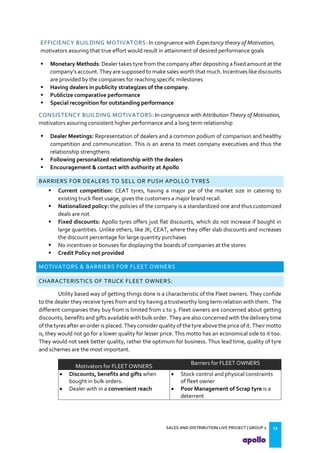
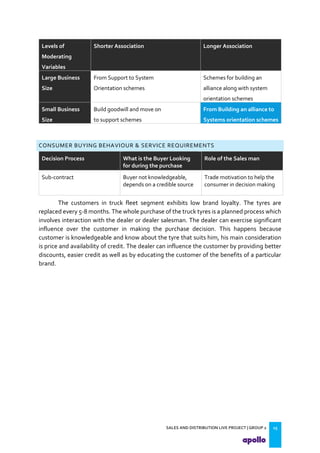
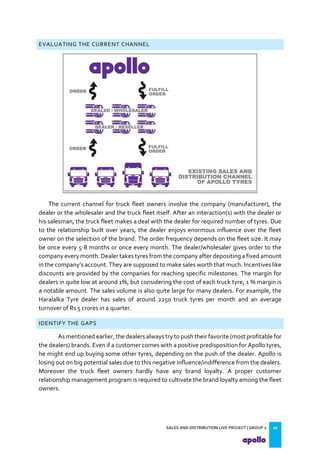
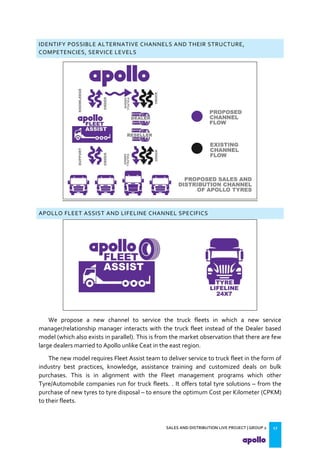
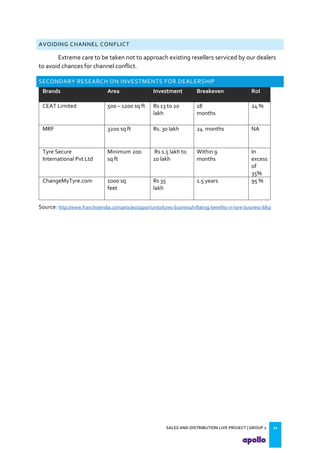
This document provides an overview of the tyre industry in India and Apollo Tyres' position within it. It summarizes insights from primary research interviews with Apollo sales managers, tyre dealers, and truck fleet owners. Key findings include: Apollo follows a fixed discount structure, while competitors offer increasing discounts based on volume; dealers prefer Apollo's structure as it benefits small and large dealers equally. Fleet owners prioritize durability, credit terms, and timely delivery when choosing tyres. The document also outlines motivators and barriers for dealers and fleet owners in selling or purchasing Apollo Tyres. It proposes strategies like expanding the dealer network and conceptualizing a fleet management system to increase Apollo's market share.