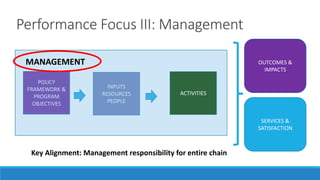
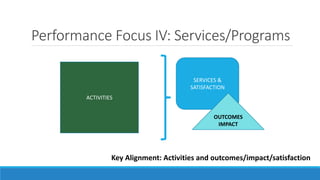
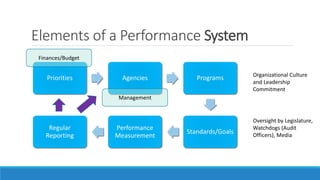
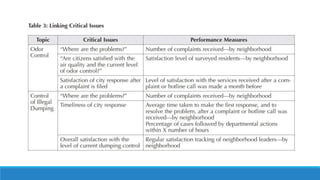
This document discusses elements of performance management in the public sector. It begins by noting key differences between the public and private sectors that impact performance measurement. These include a wider range of stakeholders, longer results chains, partnerships in delivery, and service monopolies in the public sector.
The document then presents a public sector value chain model and discusses focusing performance on different parts of the chain, such as strategy, expenditures, management, and services. It also discusses challenges in aligning these different performance focuses into an overall performance management system. Finally, the document provides examples of performance management frameworks from Canada and case studies from other jurisdictions.


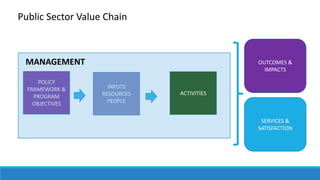
![Performance Focus I: Strategy
POLICY FRAMEWORK &
PROGRAM OBJECTIVES
INPUTS
RESOURCES
PEOPLE
OUTCOMES &
IMPACTS
Key Alignment: Policy, inputs [resources and people] to outcomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apolecture3pmelements-171211195753/85/APO-Lecture-PM-Elements-5-320.jpg)
![Performance Focus II: Expenditures
INPUTS
RESOURCES ACTIVITIES
Key Alignment: Inputs [finances], activities, outputs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apolecture3pmelements-171211195753/85/APO-Lecture-PM-Elements-6-320.jpg)