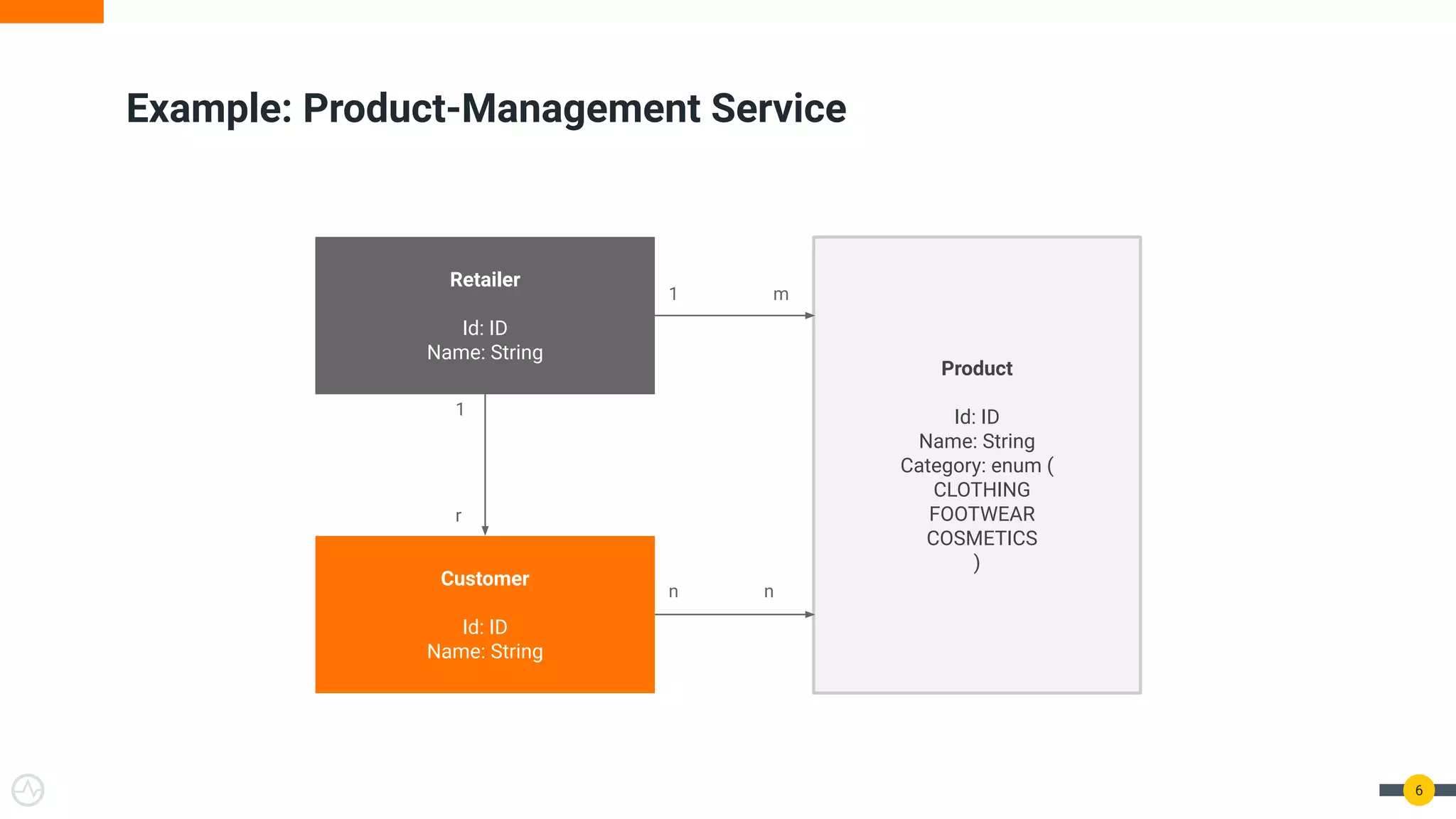
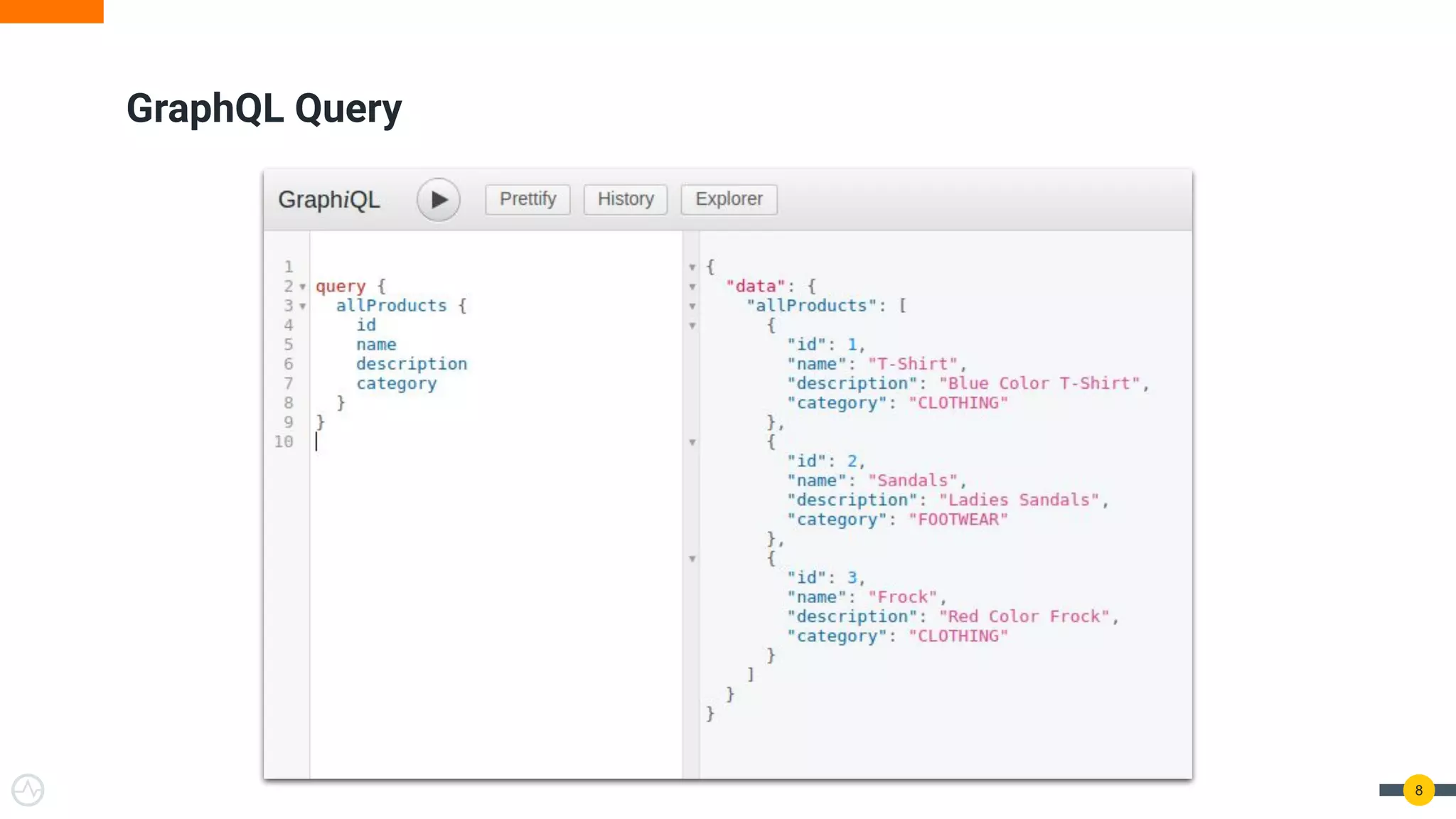
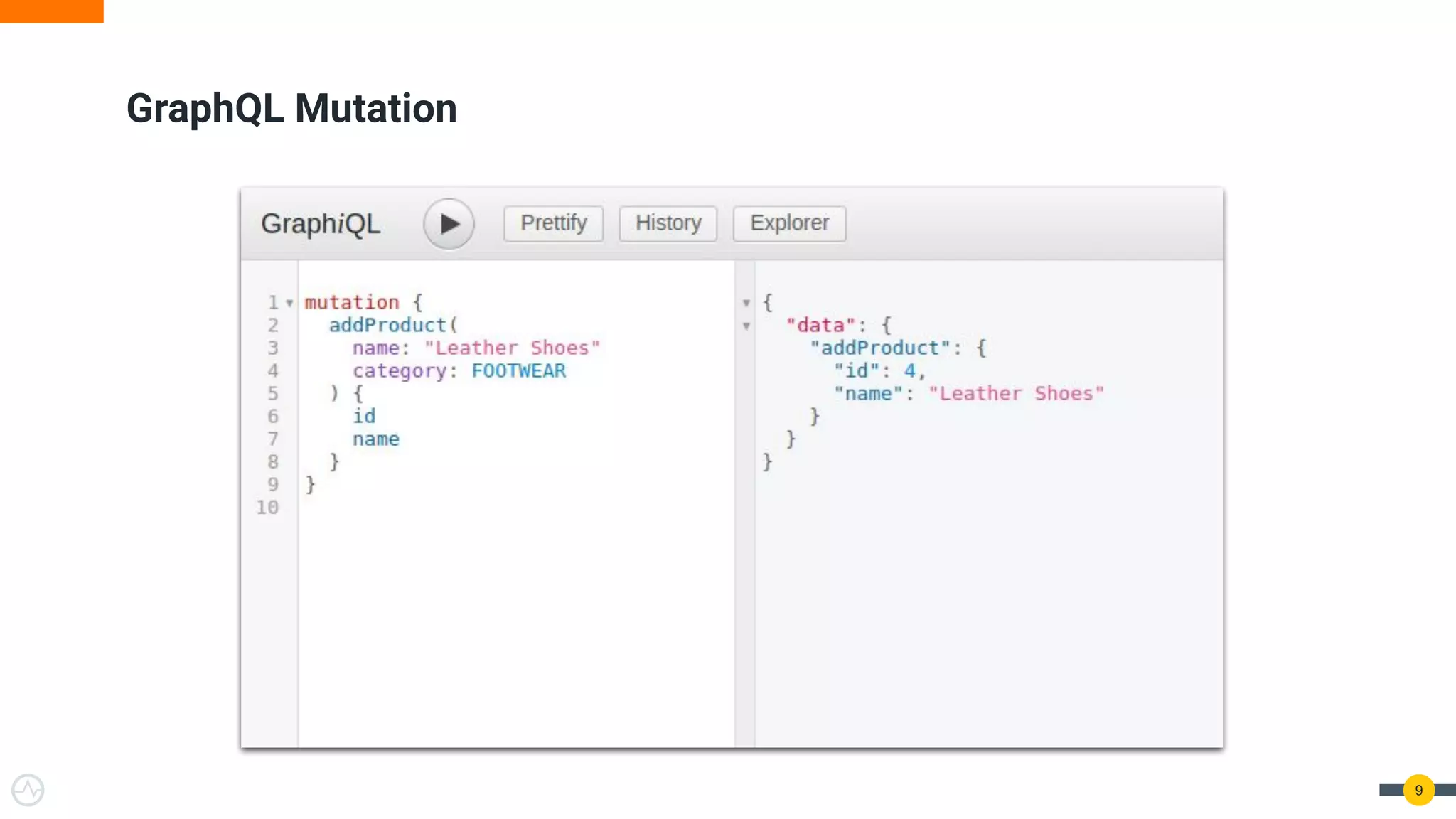
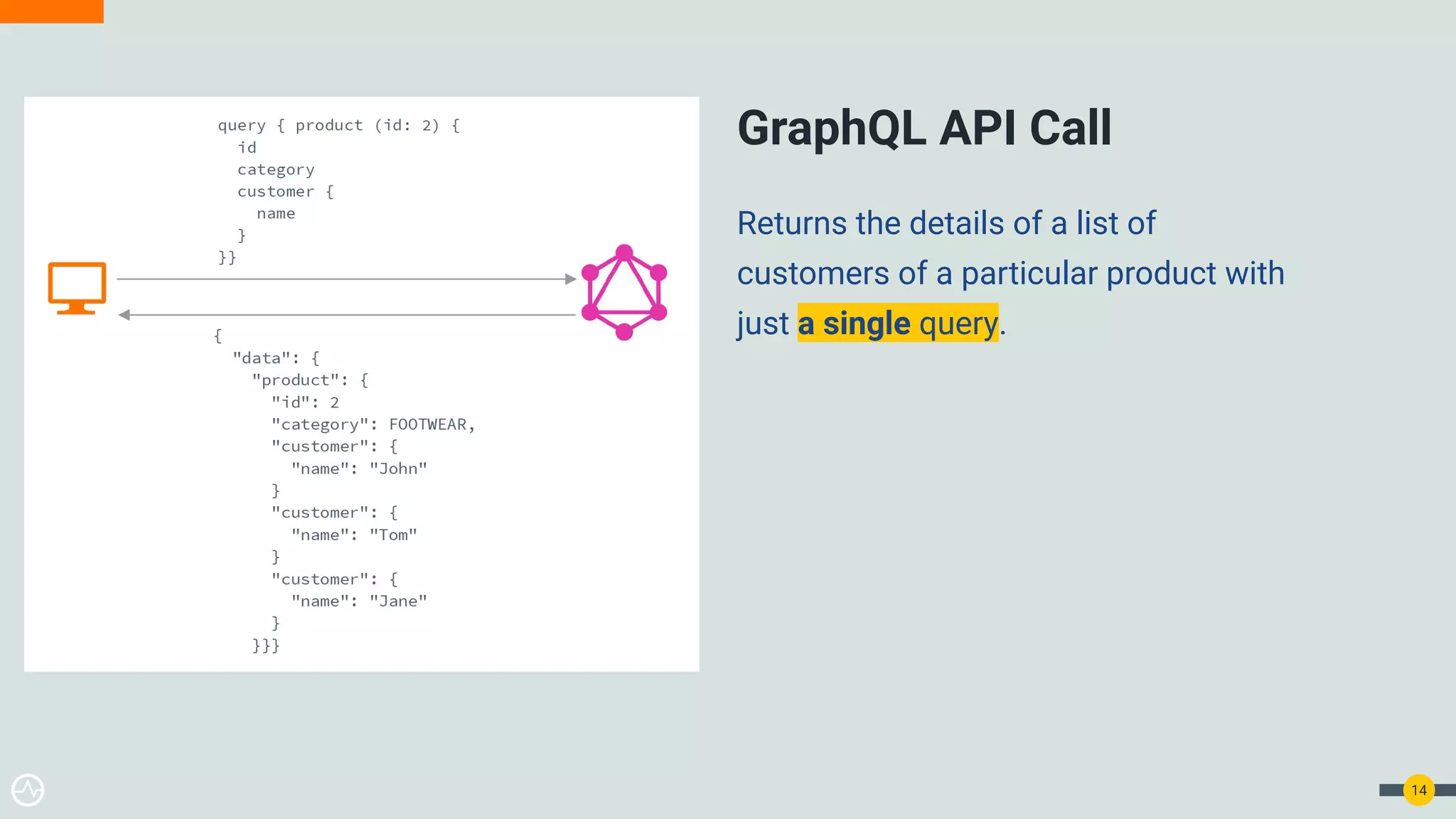
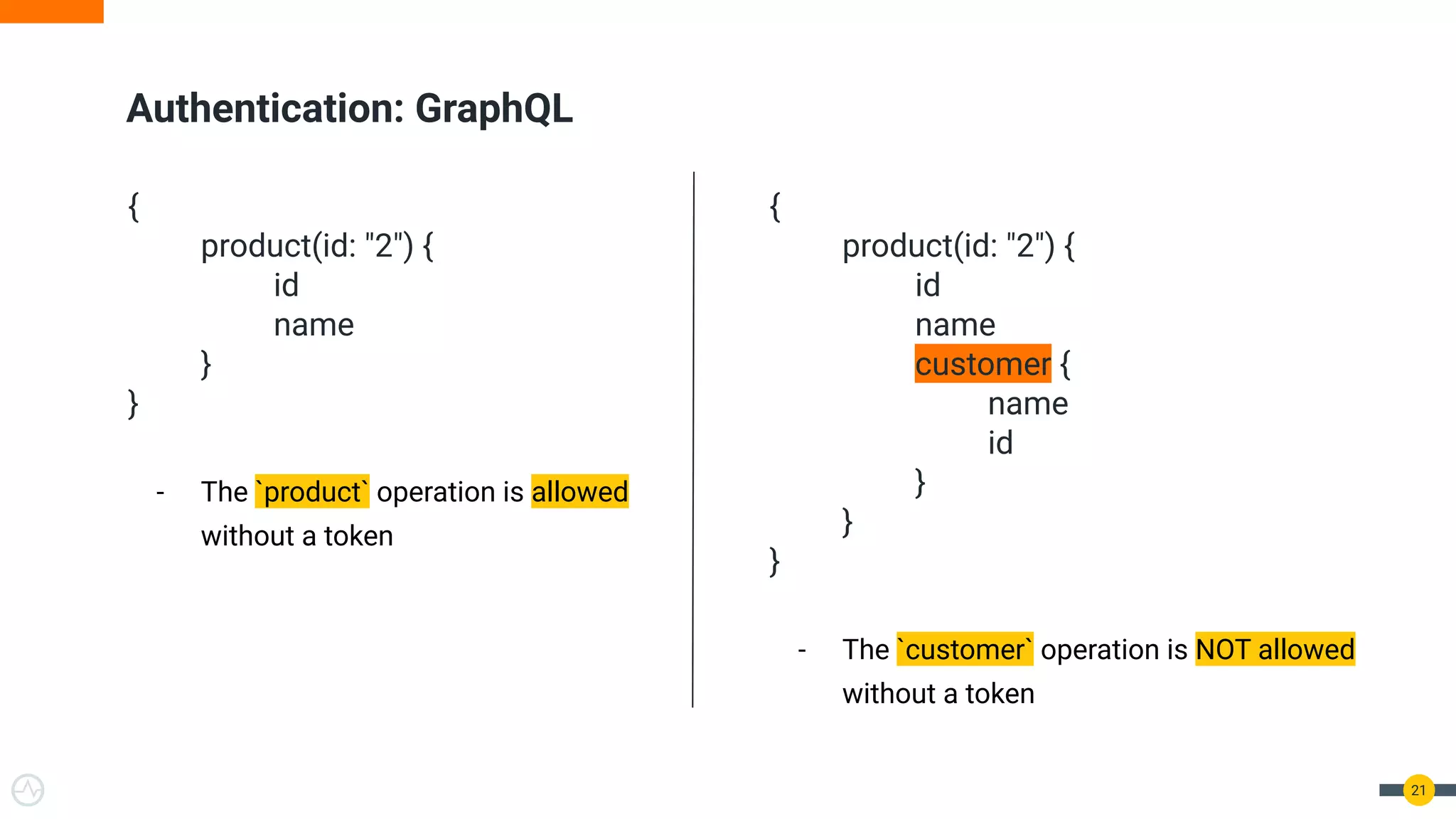
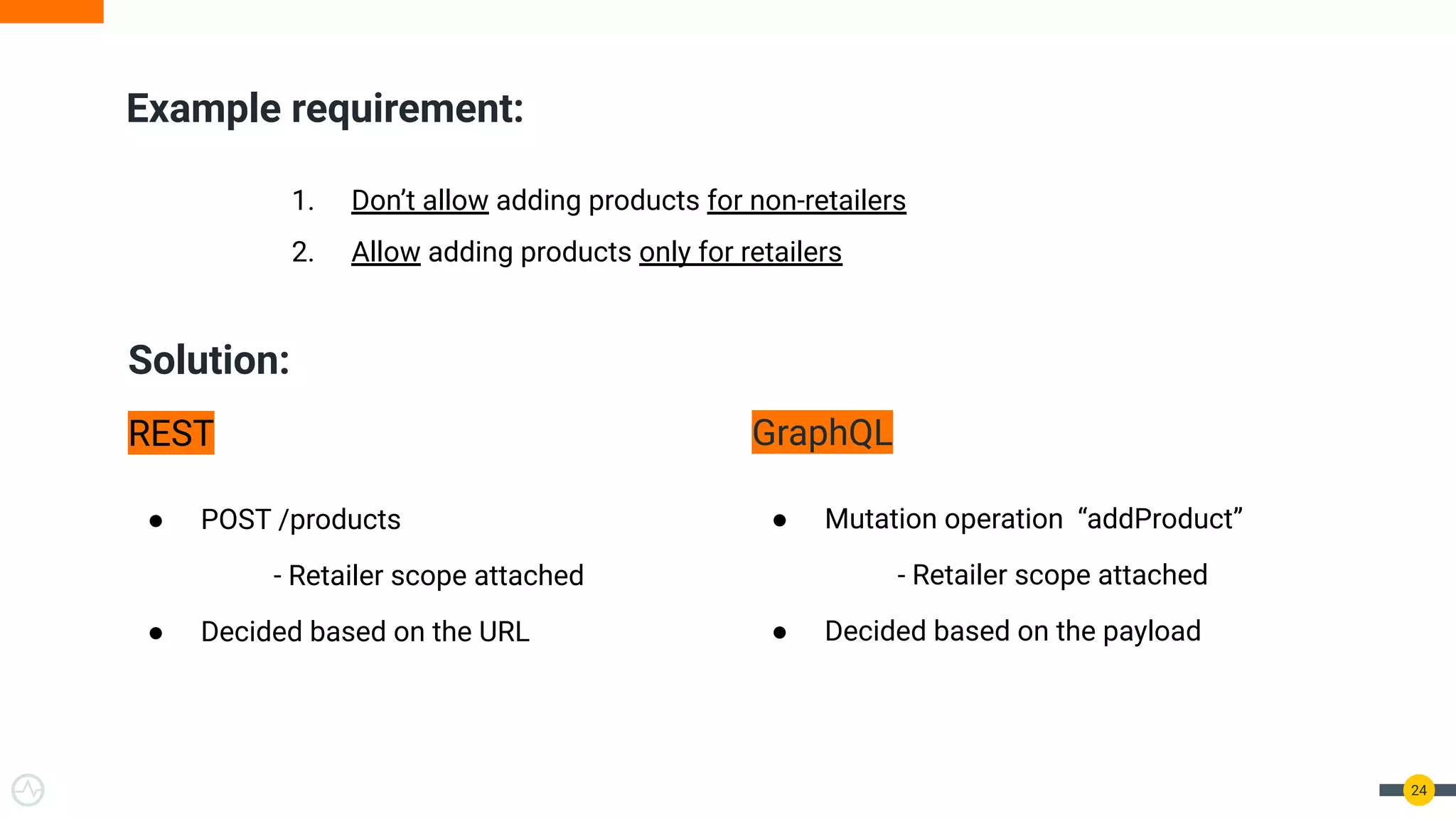
The document is a practical guide on API management for GraphQL, detailing its advantages over REST, including efficient querying and real-time subscriptions. It discusses key topics such as authentication, authorization, rate-limiting, and analytics relevant to GraphQL API management. The guide emphasizes the importance of security and performance considerations while implementing GraphQL APIs.