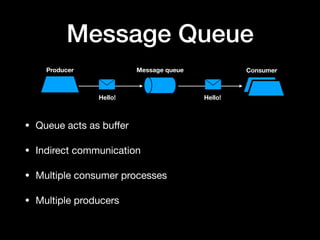
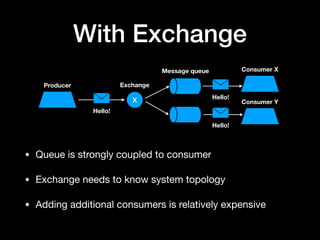
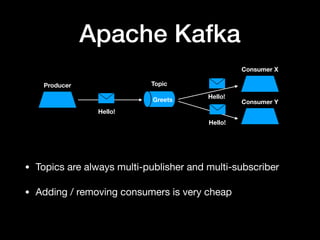
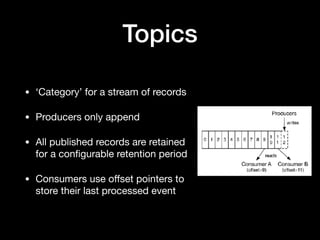
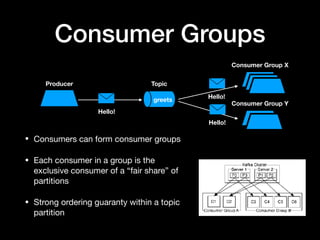
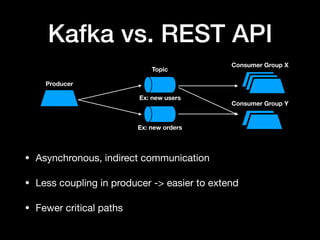
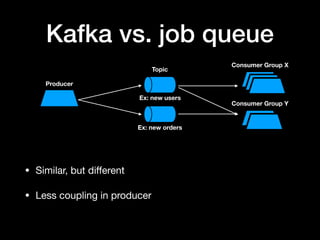
The document discusses the use of Apache Kafka as a message queue for microservices, highlighting its features like multi-publisher and multi-subscriber topics, and fault-tolerant stream storage. It contrasts Kafka with REST APIs and job queues, emphasizing benefits such as reduced coupling and easier scalability. The document also addresses challenges with using Kafka, including asynchronicity, error handling, and event loops, while providing practical tips for effective integration.