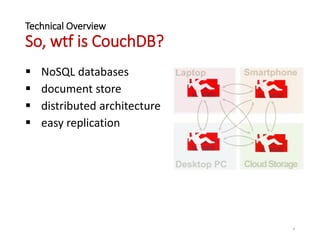
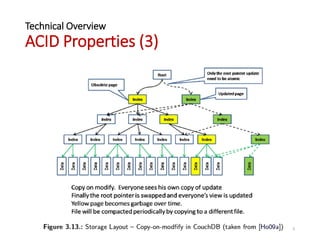
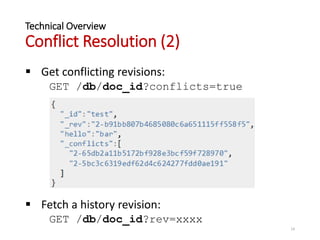
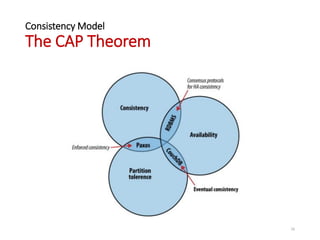
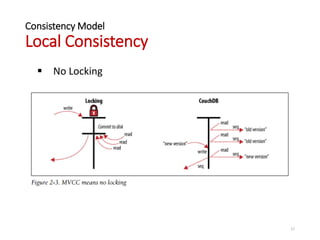
The document provides an overview of Apache CouchDB, focusing on its technical features including document storage, ACID properties, compaction, views, distributed updates, and conflict resolution. It highlights CouchDB's capabilities as a NoSQL database with a distributed architecture, allowing for easy replication and decentralized conflict resolution. Additionally, it mentions the consistency model and includes links to further resources for learning about CouchDB.