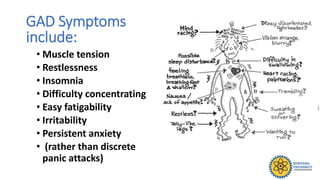
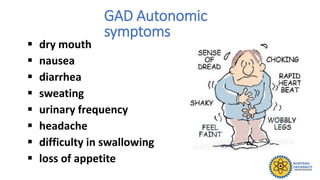
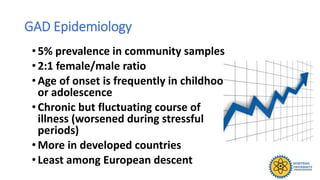
The document outlines different types of anxiety disorders, including Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Substance Induced Anxiety Disorder, detailing their diagnostic criteria, symptoms, epidemiology, and treatment options. GAD is characterized by excessive worry lasting at least six months, while Substance Induced Anxiety is linked to specific substances causing anxiety symptoms. Treatment approaches involve both pharmacologic and psychologic methods, including medications and various types of therapy.