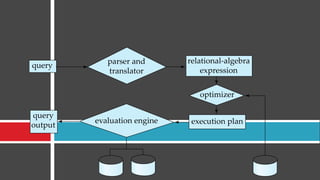
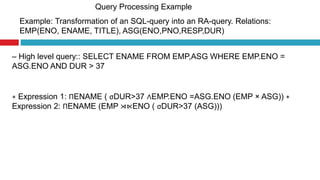
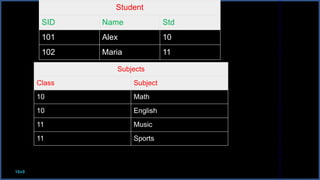
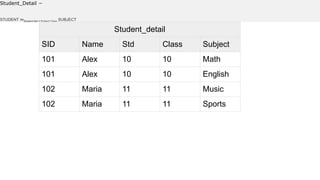
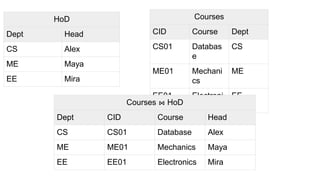
Query processing involves transforming a high-level query, such as SQL, into an efficient execution plan expressed in a low-level language. It goes through several phases including syntax checking, translating the query into an algebraic expression, optimization to generate the lowest cost plan, and evaluation where the engine executes the plan and returns answers. An example shows transforming an SQL query into a relational algebra expression through joining relations where matching tuples satisfy the join condition.