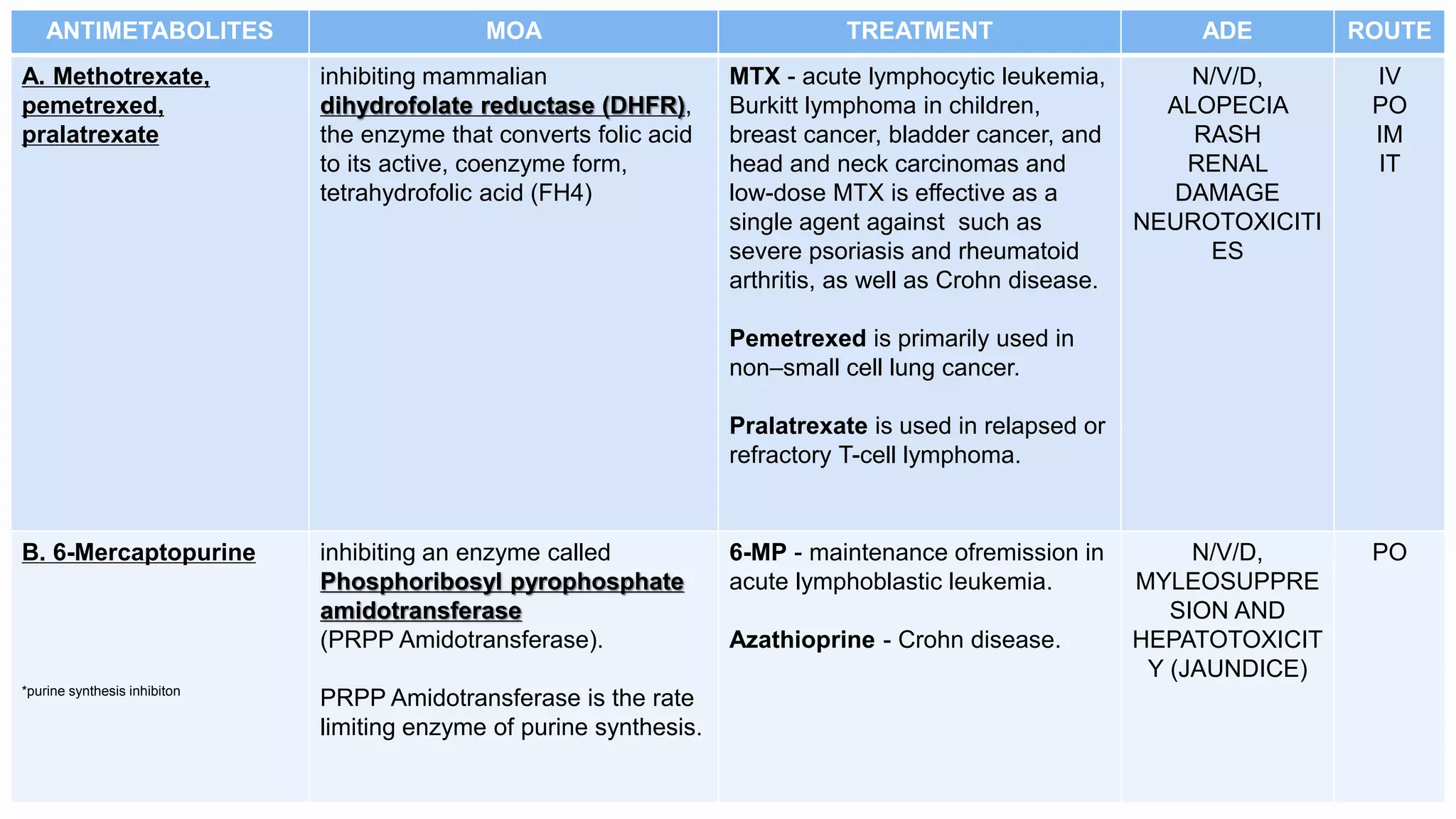
Antimetabolites are structurally similar to normal cell compounds and interfere with purine or pyrimidine synthesis or incorporation into DNA/RNA. Common antimetabolites include methotrexate, 6-mercaptopurine, fludarabine, cladribine, 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine, cytarabine, and azacitidine. They are cell cycle specific and used to treat cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, lung cancer, and breast cancer. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, myelosuppression, and renal toxicity.


![ANTIMETABOLITES MOA TREATMENT ADE ROUTE
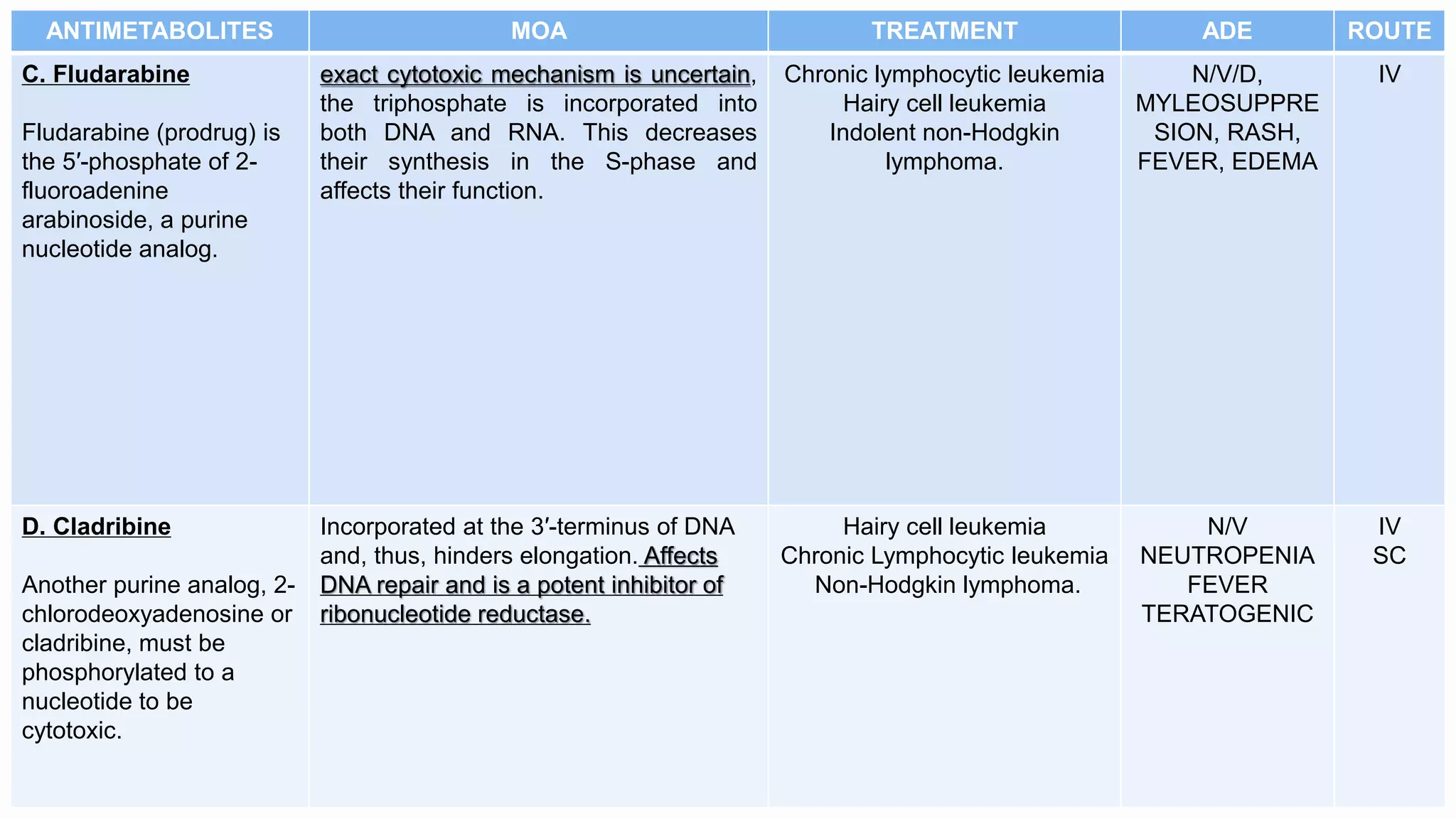
E. 5-Fluorouracil
a pyrimidine analog, has
a stable fluorine atom in
place of a hydrogen atom
at position 5 of the uracil
ring.
5-FU itself is converted to the corresponding
deoxynucleotide (5-fluorodeoxyuridine
monophosphate [5-FdUMP] which competes
with deoxyuridine monophosphate for
thymidylate synthase, thus inhibiting its action.
DNA synthesis decreases due to lack of
thymidine, leading to imbalanced cell growth
and “thymidine-less death” of rapidly dividing
cells.
slowly growing solid
tumors
(for example,
colorectal,breast, ovarian,
pancreatic, and gastric
carcinomas).
When applied topically, 5-
FU is also effective for the
treatment of superficial
basal cell carcinomas.
DIARRHEA
ALOPECIA
HAND FOOT
SYNDROME
IV
F. Capecitabine Capecitabine is metabolised to 5-FU which in
turn is a thymidylate synthase inhibitor, hence
inhibiting the synthesis of thymidine
monophosphate (ThMP), the active form of
thymidine which is required for the de novo
synthesis of DNA.
Thus, the cytotoxic activity of capecitabine is
the same as that of 5-FU and is tumor specific.
Olorectal
Metastatic breast cancer
DIARRHEA
CHEST PAIN
HAND FOOT
SYNDROME
PO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcol2table-171013021645/75/Anticancer-drugs-Pharmacology-5-2048.jpg)














![B. Paclitaxel and docetaxel
Paclitaxel [PAK-li-tax-el] was the first member of the taxane family
to be used in cancer chemotherapy. A semisynthetic paclitaxel is
now available through chemical modification of a precursor found in
the needles of Pacific yew species. An albumin-bound form is also
available. Substitution of a side chain has resulted in docetaxel,
which is the more potent of the two drugs.
PACLITAXEL - advanced ovarian cancer and metastatic
breast cancer
DOCETAXEL - prostate, breast, GI, and non–small cell lung
cancers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcol2table-171013021645/75/Anticancer-drugs-Pharmacology-20-2048.jpg)
