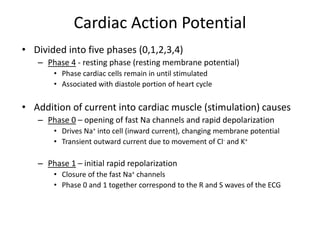
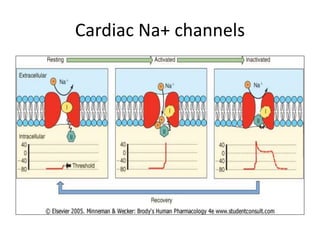
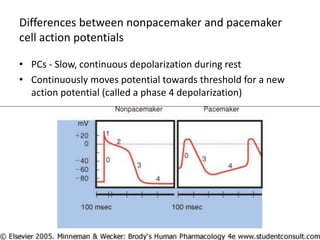
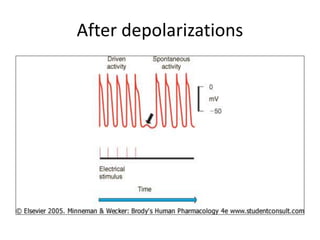
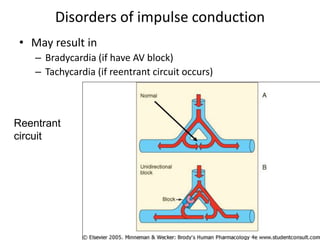
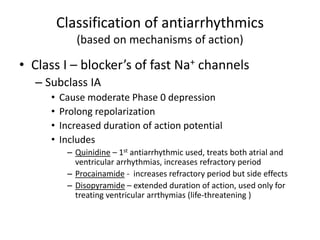
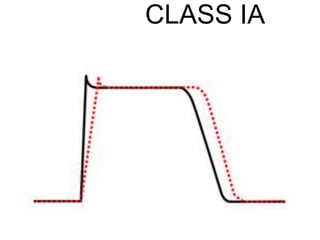
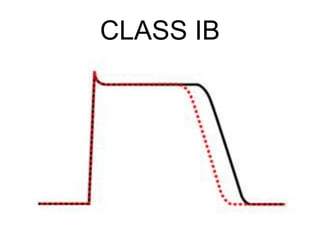
This document discusses antiarrhythmic drugs, which are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms called arrhythmias. It begins by explaining how the normal heartbeat works and the causes of arrhythmias. It then covers the classification of antiarrhythmic drugs based on their mechanisms of action, including class I drugs that block sodium channels, class II drugs that are beta blockers, and class III drugs that block potassium channels. Specific drugs from each class are discussed, along with their mechanisms and uses for treating different types of arrhythmias. The goal of antiarrhythmic drug treatment is to restore the heart's normal rhythm and rate while avoiding dangerous side effects.

![Background
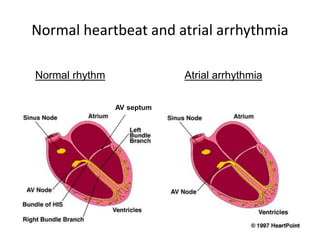
• to function efficiently, heart needs to contract sequentially
(atria, then ventricles) and in synchronicity
• Relaxation must occur between contractions (not true for
other types of muscle [exhibit tetany contract and hold
contraction for certain length of time])
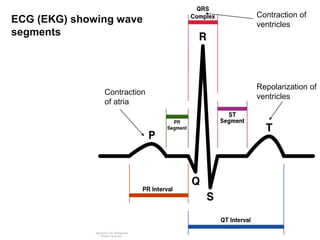
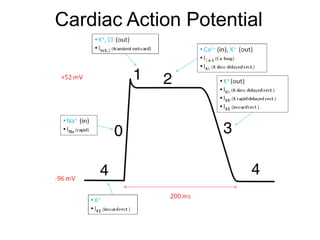
• Coordination of heartbeat is a result of a complex,
coordinated sequence of changes in membrane potentials
and electrical discharges in various heart tissues](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiarrythmicdrugs-200812074413/85/Antiarrythmic-drugs-2-320.jpg)