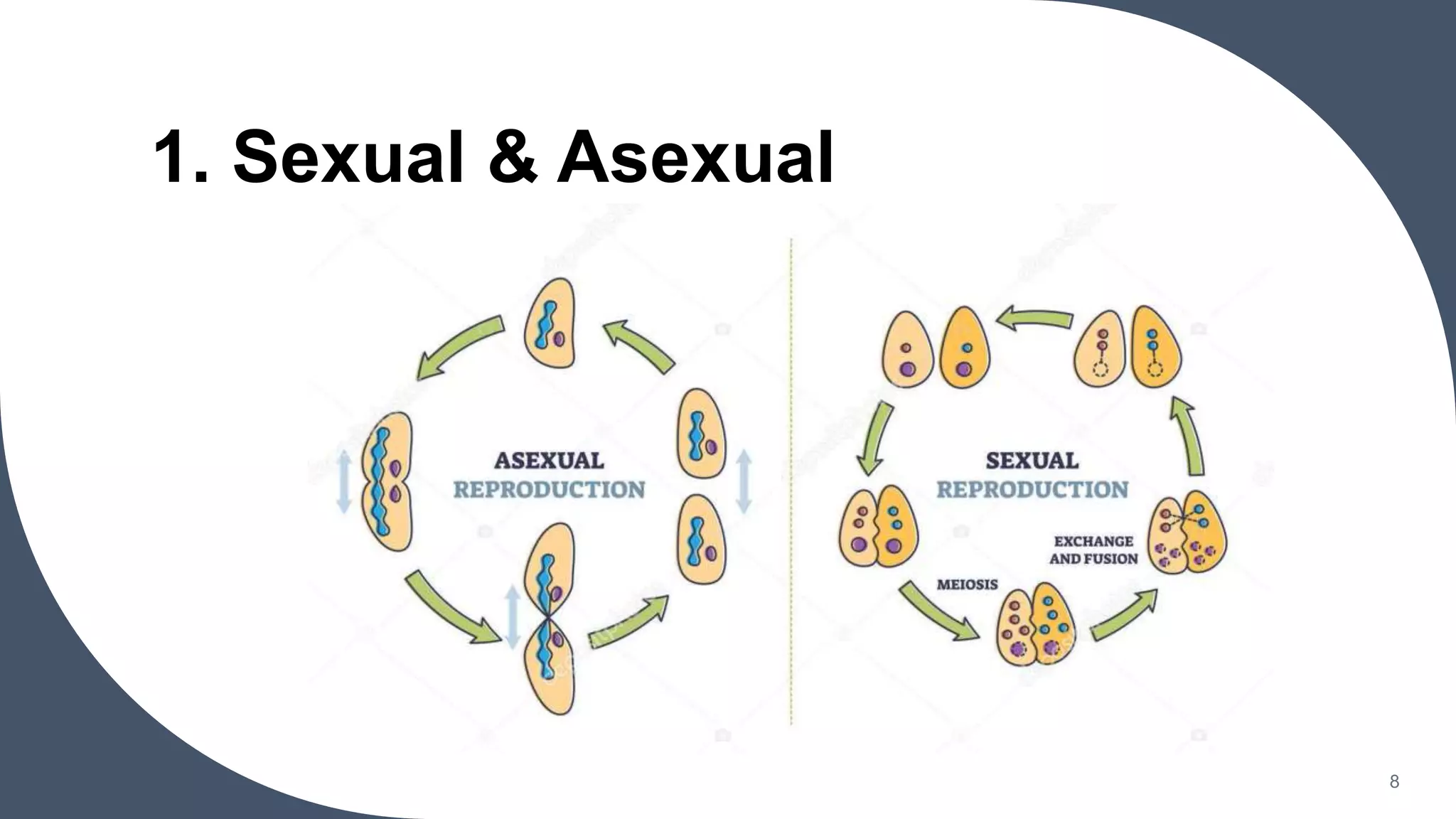
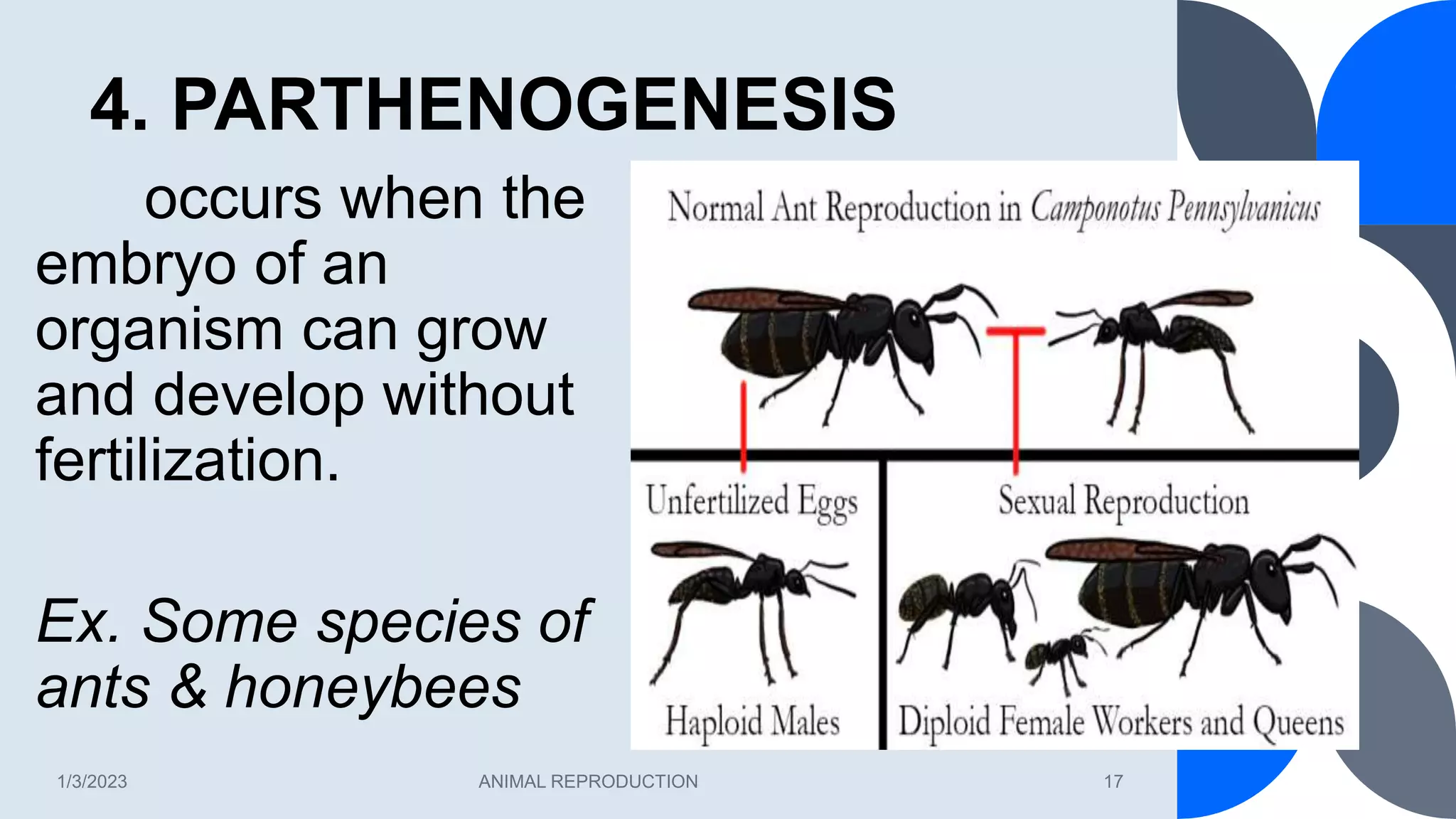
This document discusses animal reproduction, including both sexual and asexual reproduction. It defines reproduction as the way organisms continue their species through mating and producing offspring. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, while asexual reproduction requires only one parent and produces genetically identical clones. The document outlines different types of asexual reproduction like binary fission, fragmentation, budding, and parthenogenesis. It also describes the mechanics of fertilization, whether internally like oviparity, viviparity, and ovoiviparity, or externally.