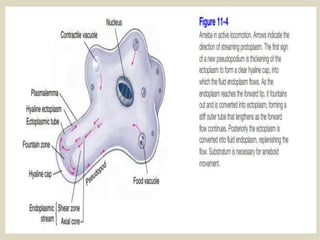
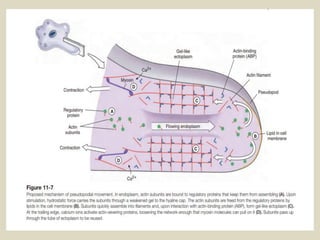
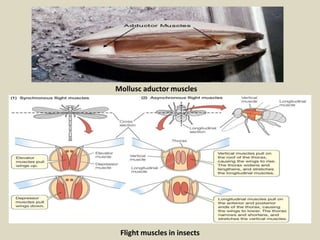
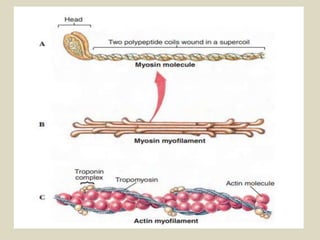
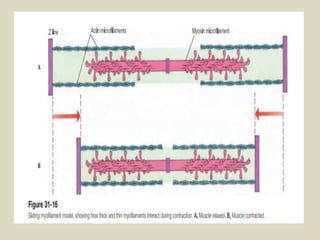
The document discusses animal movement, emphasizing the role of contractile proteins, particularly the actomyosin system, which is ubiquitous across animal species. It details various modes of movement, including ameboid, ciliary, and muscular movements, along with the structural and functional characteristics of different muscle types in both invertebrates and vertebrates. The document also covers the physiological mechanisms underlying muscle contraction, control mechanisms, and energy requirements for muscle activity.