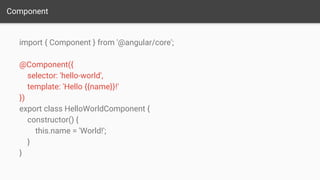
Angular 2 is a JavaScript framework for building client applications. It uses TypeScript for static typing and supports mobile and desktop applications. The key aspects covered are components, which encapsulate templates and logic, bindings for data flow, services for reusable logic, routers for navigation, and directives for extending DOM elements. The document recommends using the Angular CLI for building applications and compares Angular 2 to other frameworks, noting its emphasis on simplicity, functionality, and convenience.
















![Two-way data binding
<input [(value)]="todo.text">](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-18-320.jpg)



![Router
@Routes([
{path: '/my-route', component: MyRouteComponent},
{path: '/my-other-route', component: MyOtherComponent},
])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-22-320.jpg)
![Router
@Routes([
{path: '/my-route', component: MyRouteComponent},
{path: '/my-other-route', component: MyOtherComponent},
])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-23-320.jpg)
![Router
@Routes([
{path: '/my-route', component: MyRouteComponent},
{path: '/my-other-route', component: MyOtherComponent},
])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-24-320.jpg)


![@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<vaadin-pie-chart>
…
</vaadin-pie-chart>
`,
directives: [VaadinCharts,
DataSeries]
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-27-320.jpg)
![@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<vaadin-pie-chart>
…
</vaadin-pie-chart>
`,
directives: [VaadinCharts,
DataSeries]
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-newhope-160628020751/85/Angular-2-a-New-Hope-28-320.jpg)