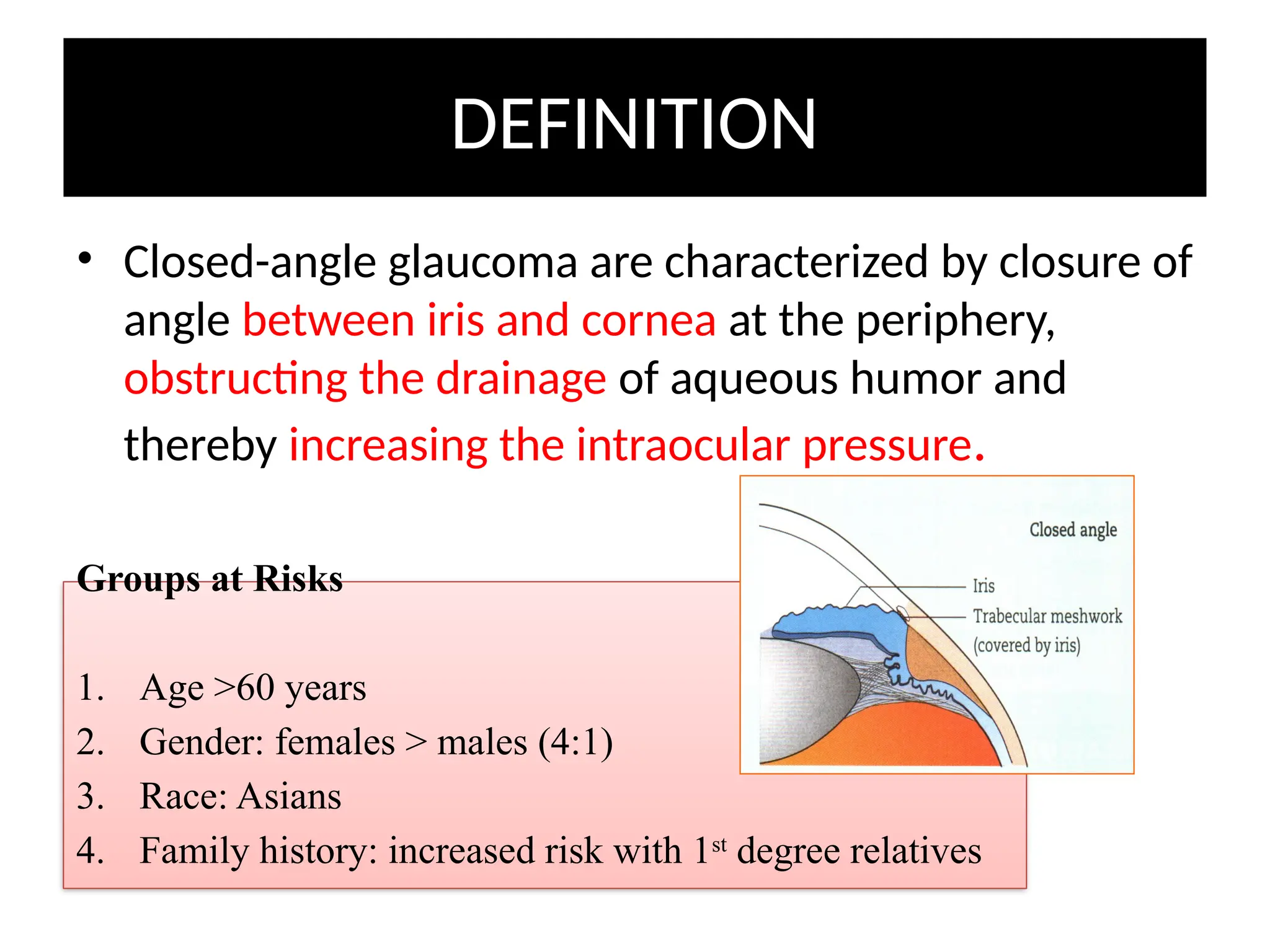
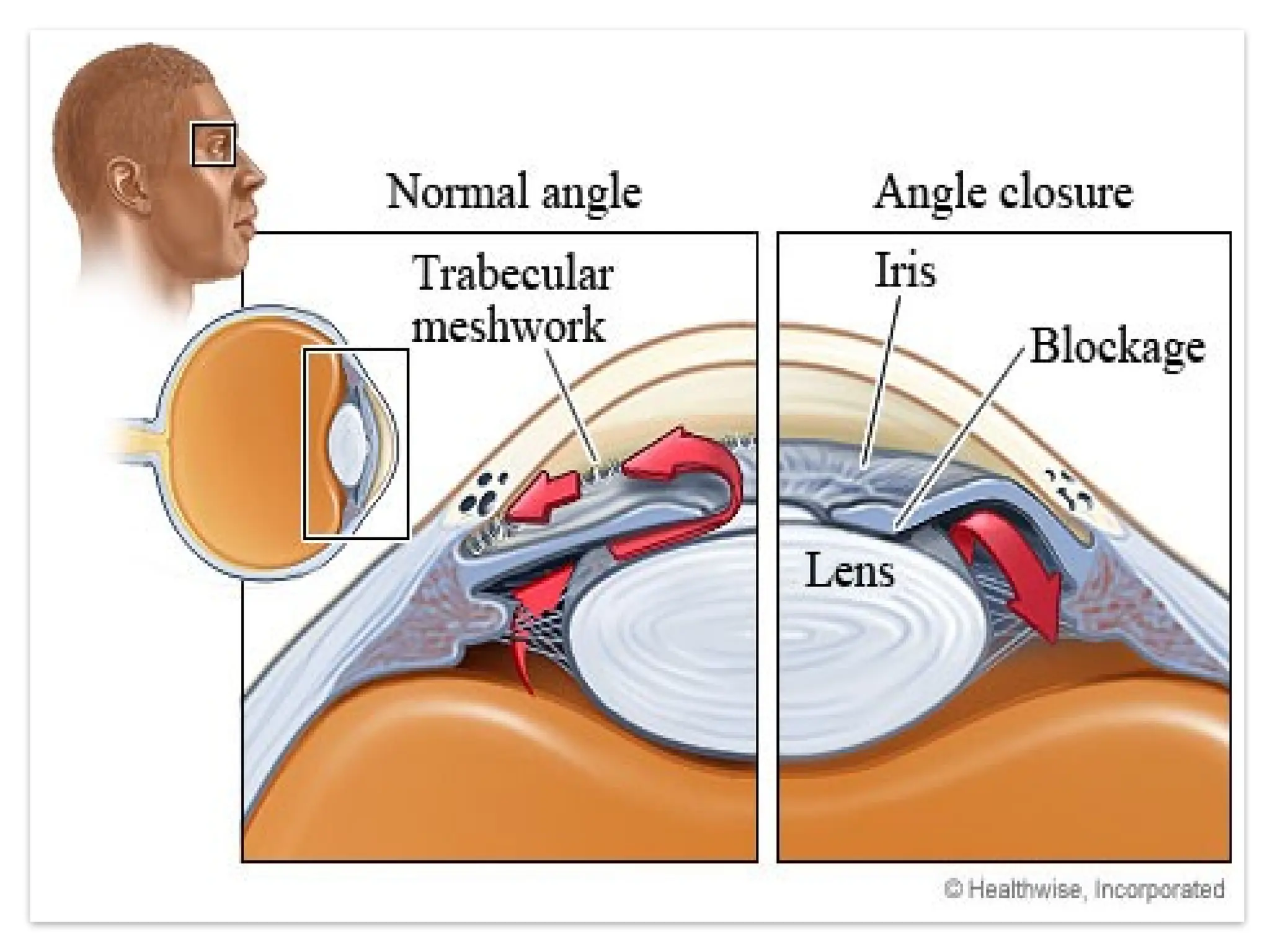
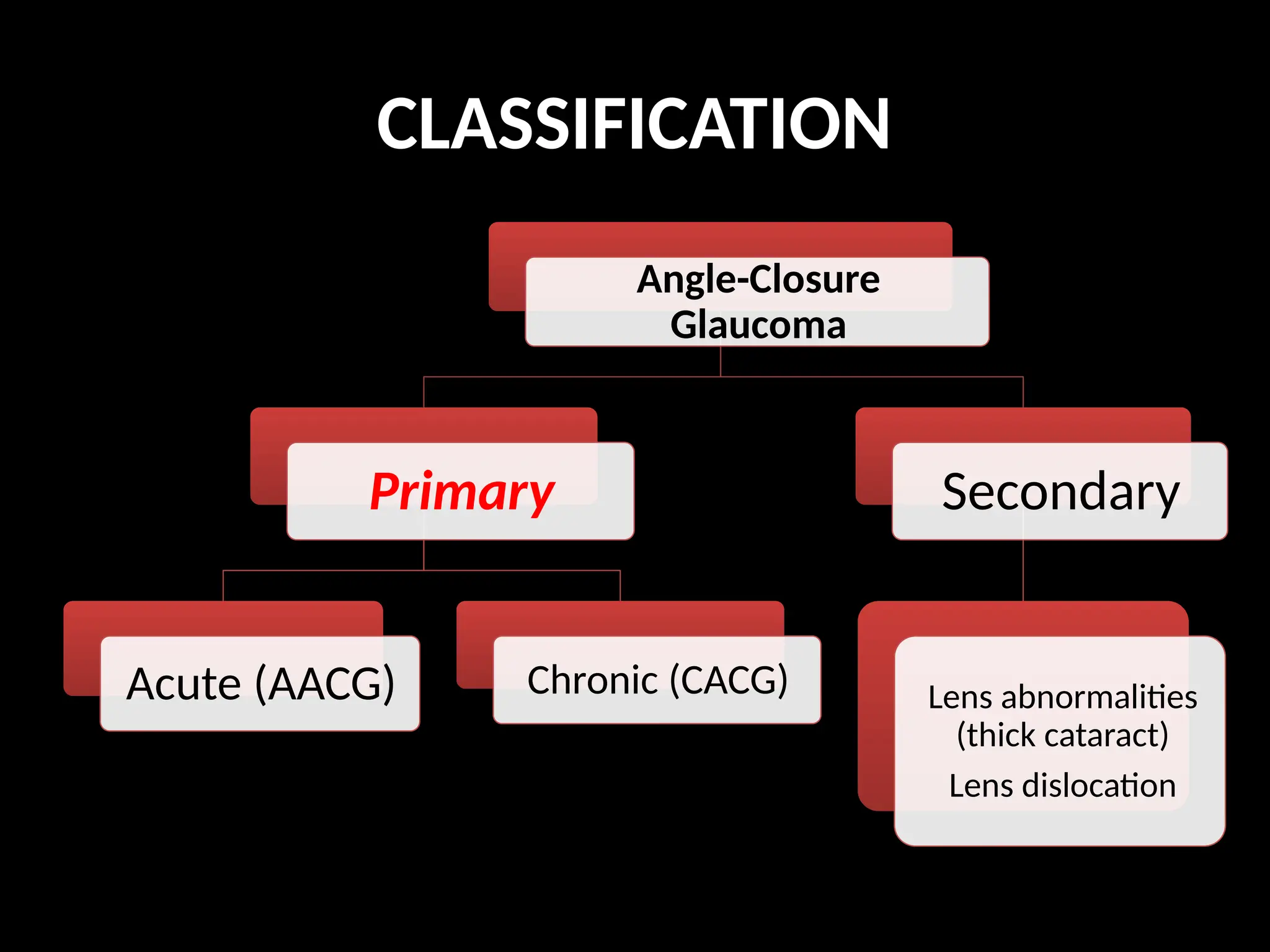
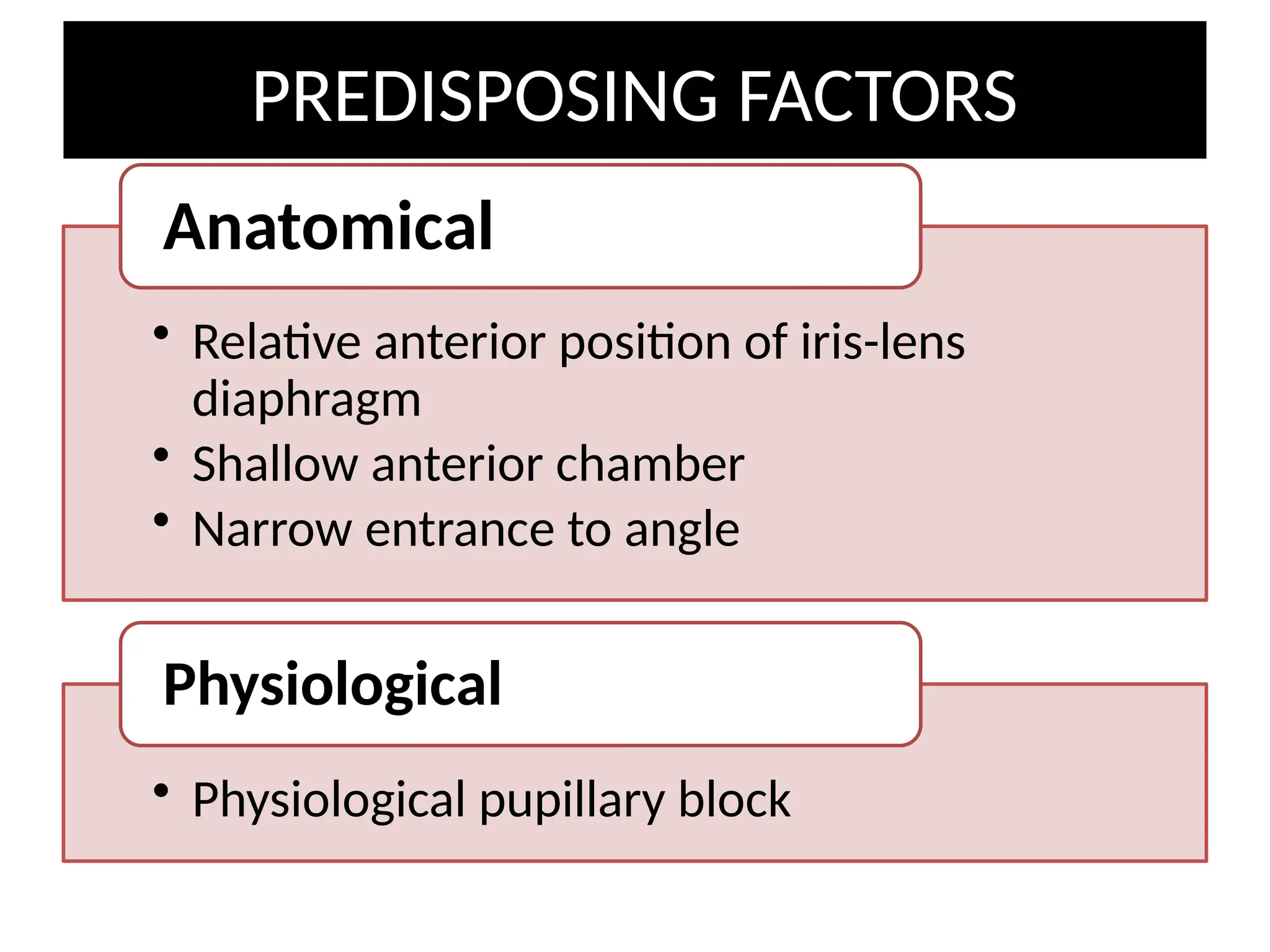
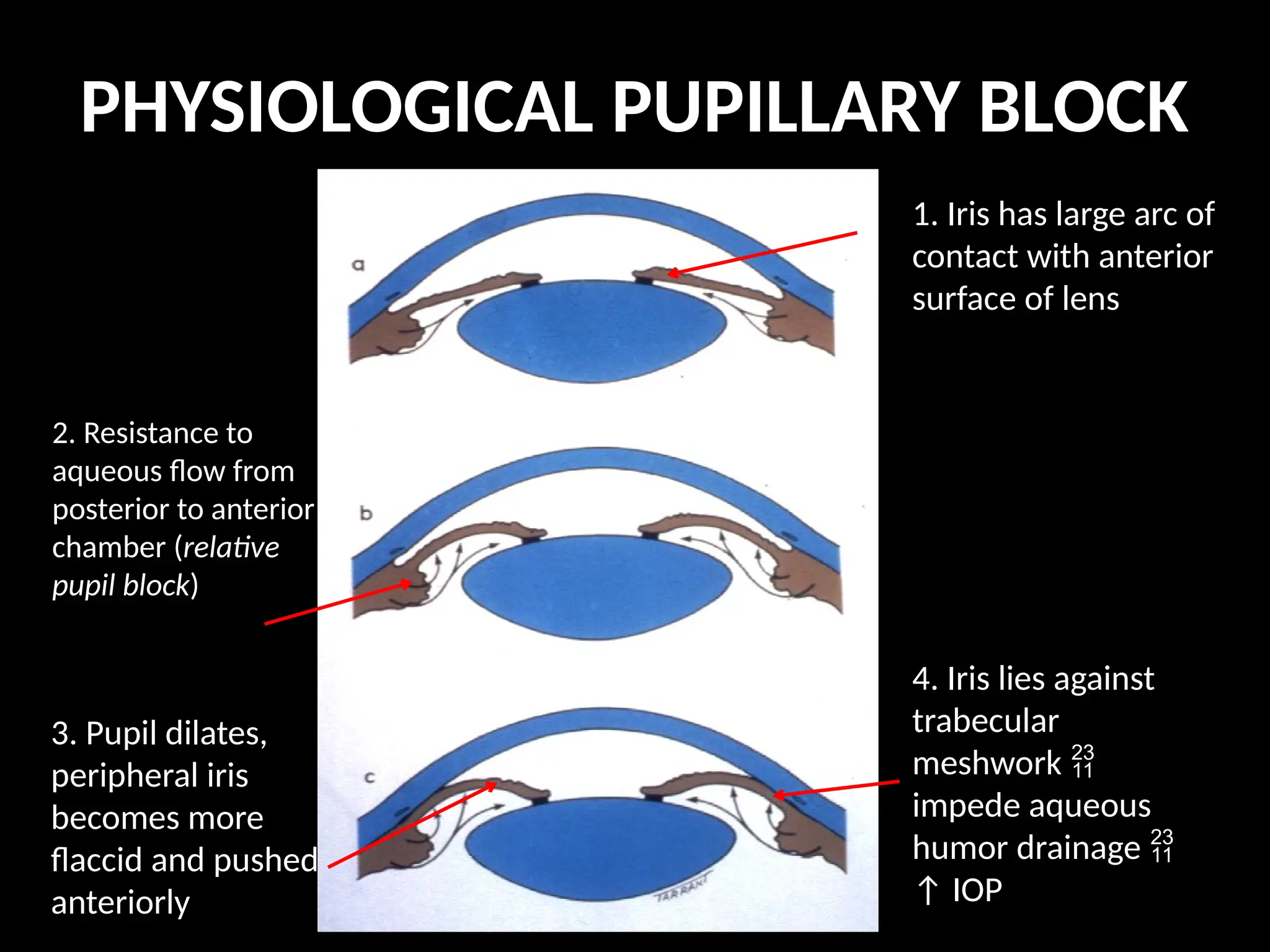
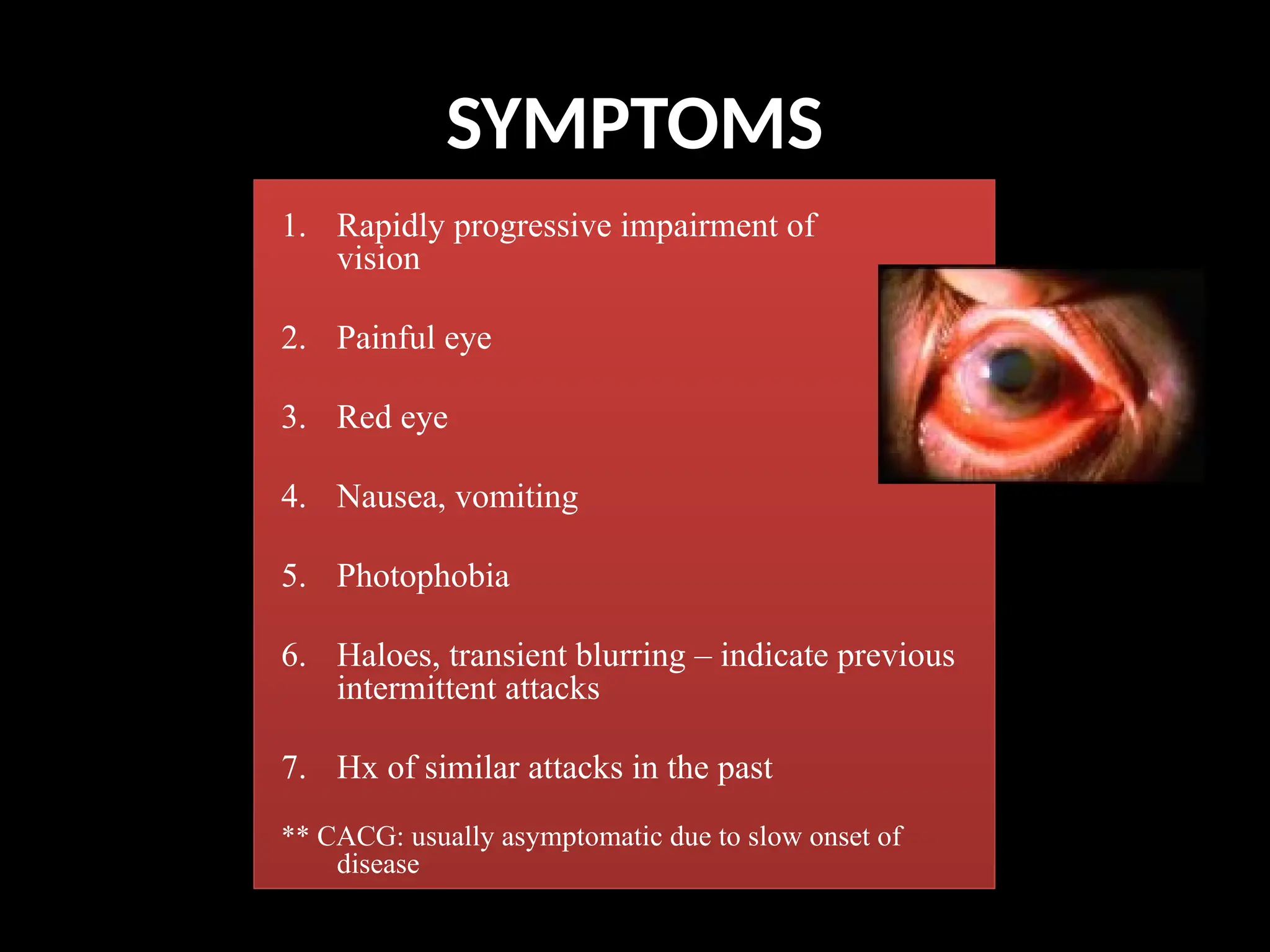
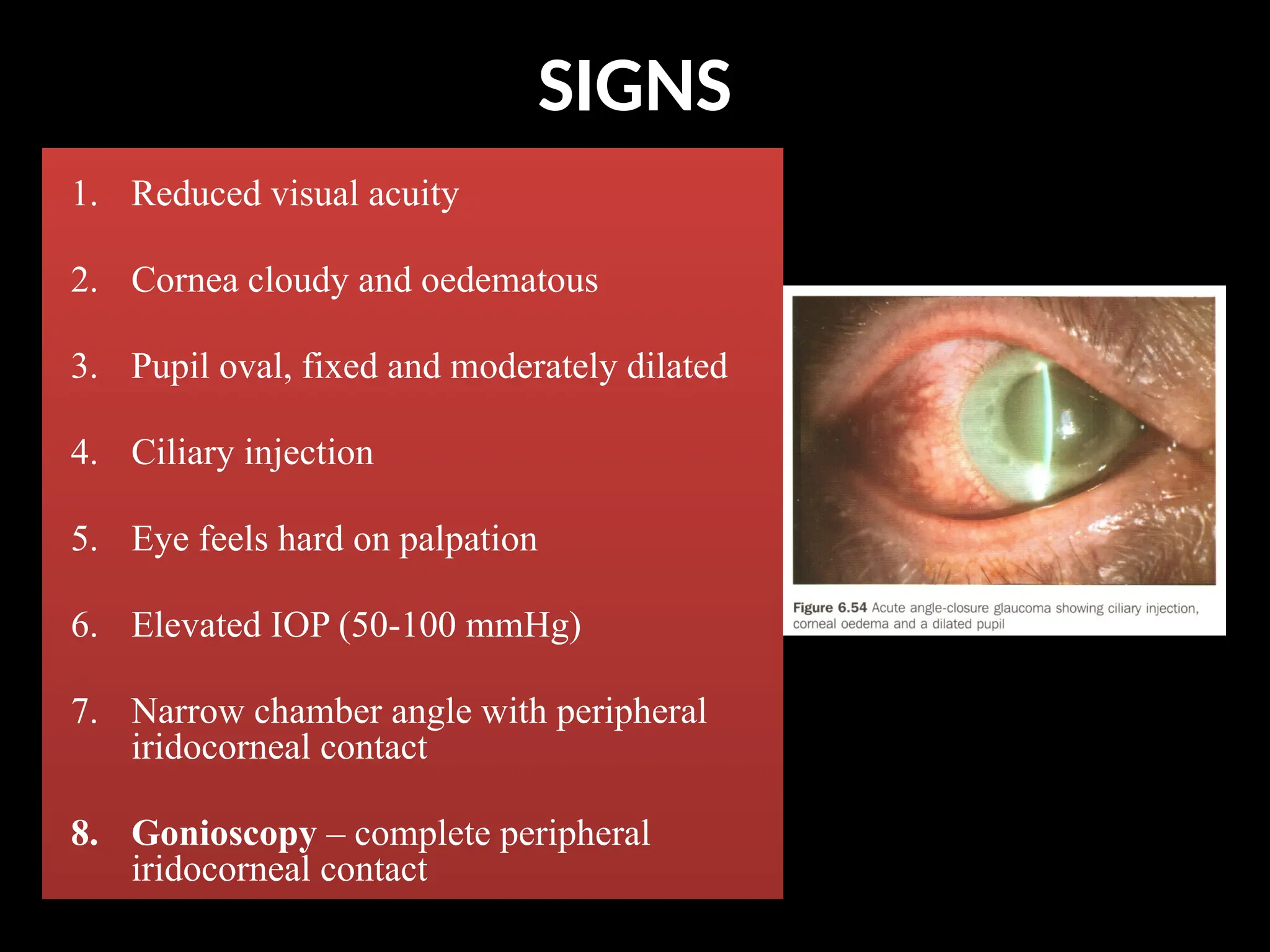
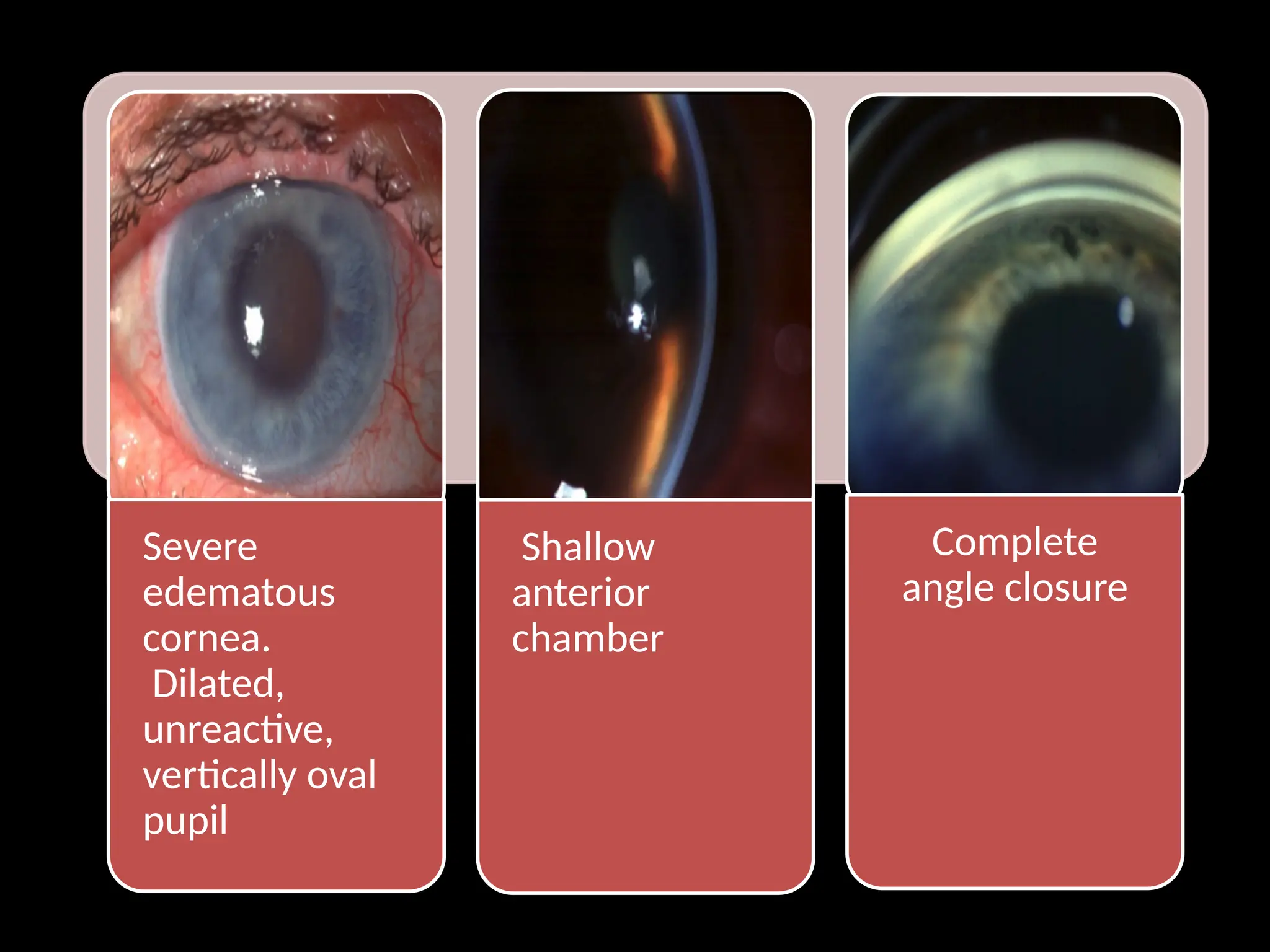
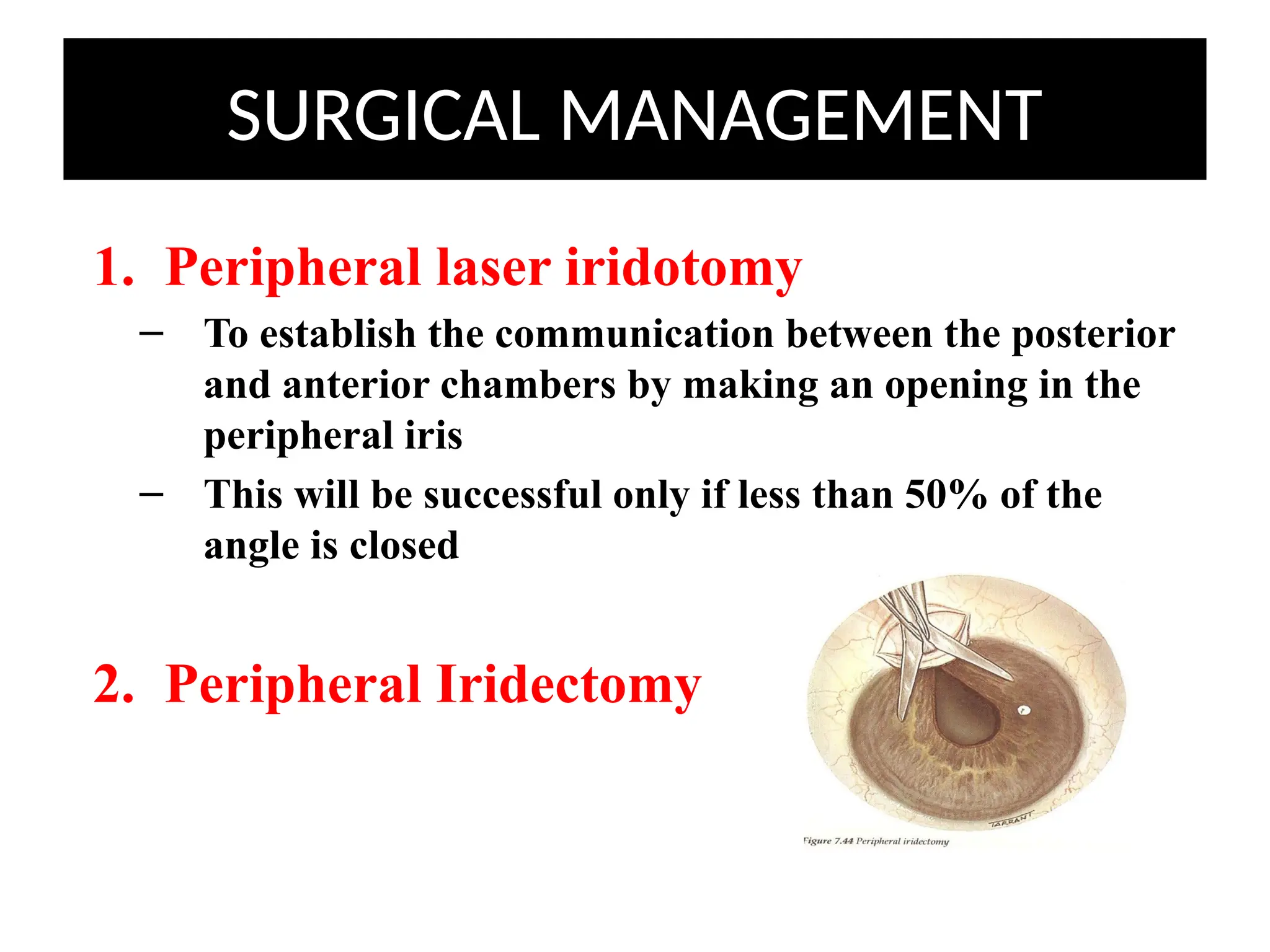
Angle closure glaucoma (ACG) is characterized by obstruction of aqueous humor drainage due to the closure of the angle between the iris and cornea, leading to increased intraocular pressure. It primarily affects individuals over 60 years, with a higher prevalence in females and Asians, and can be classified into acute, chronic, and secondary forms. Management includes systemic treatments, topical therapies, and surgical interventions to preserve vision.