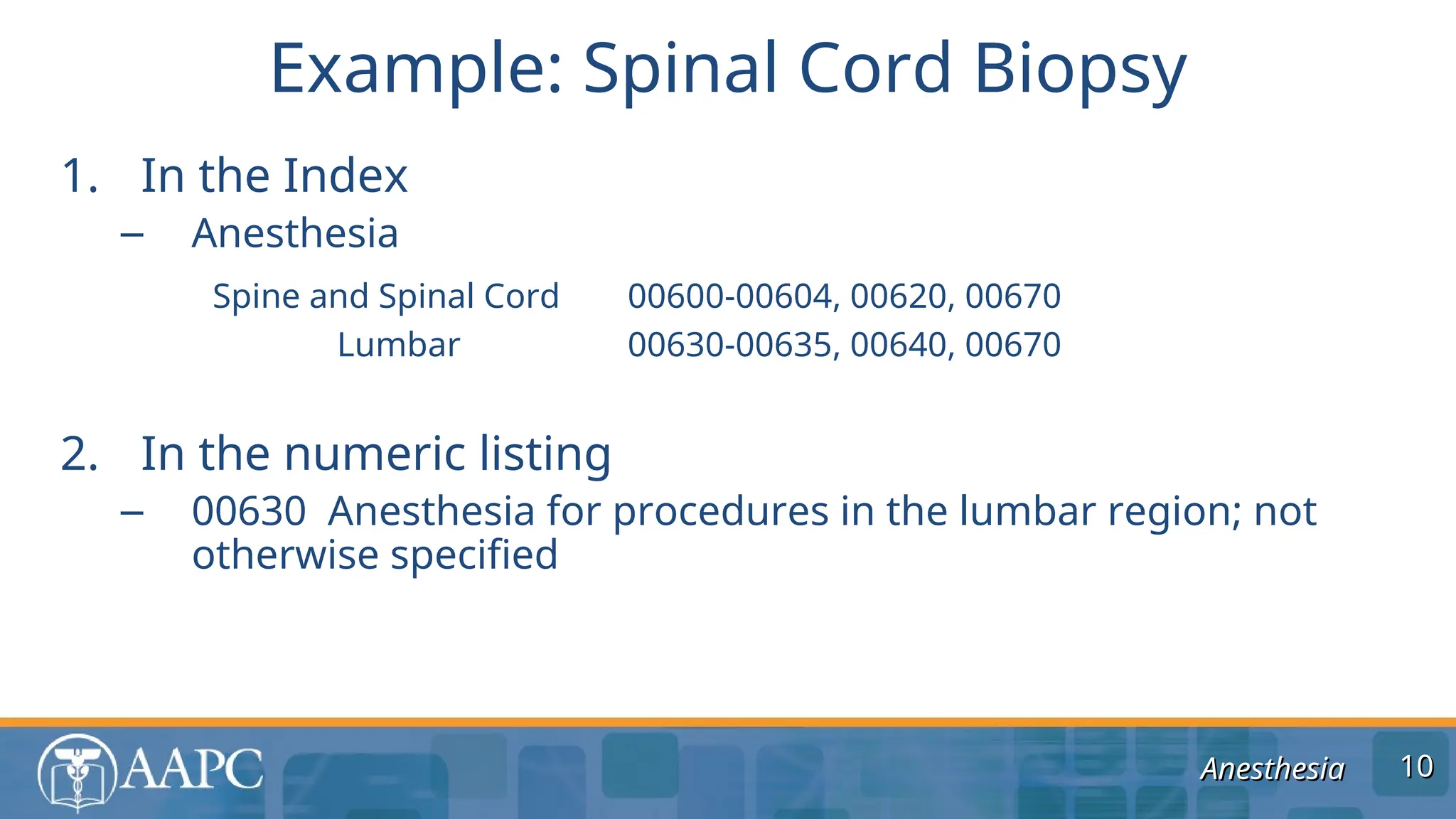
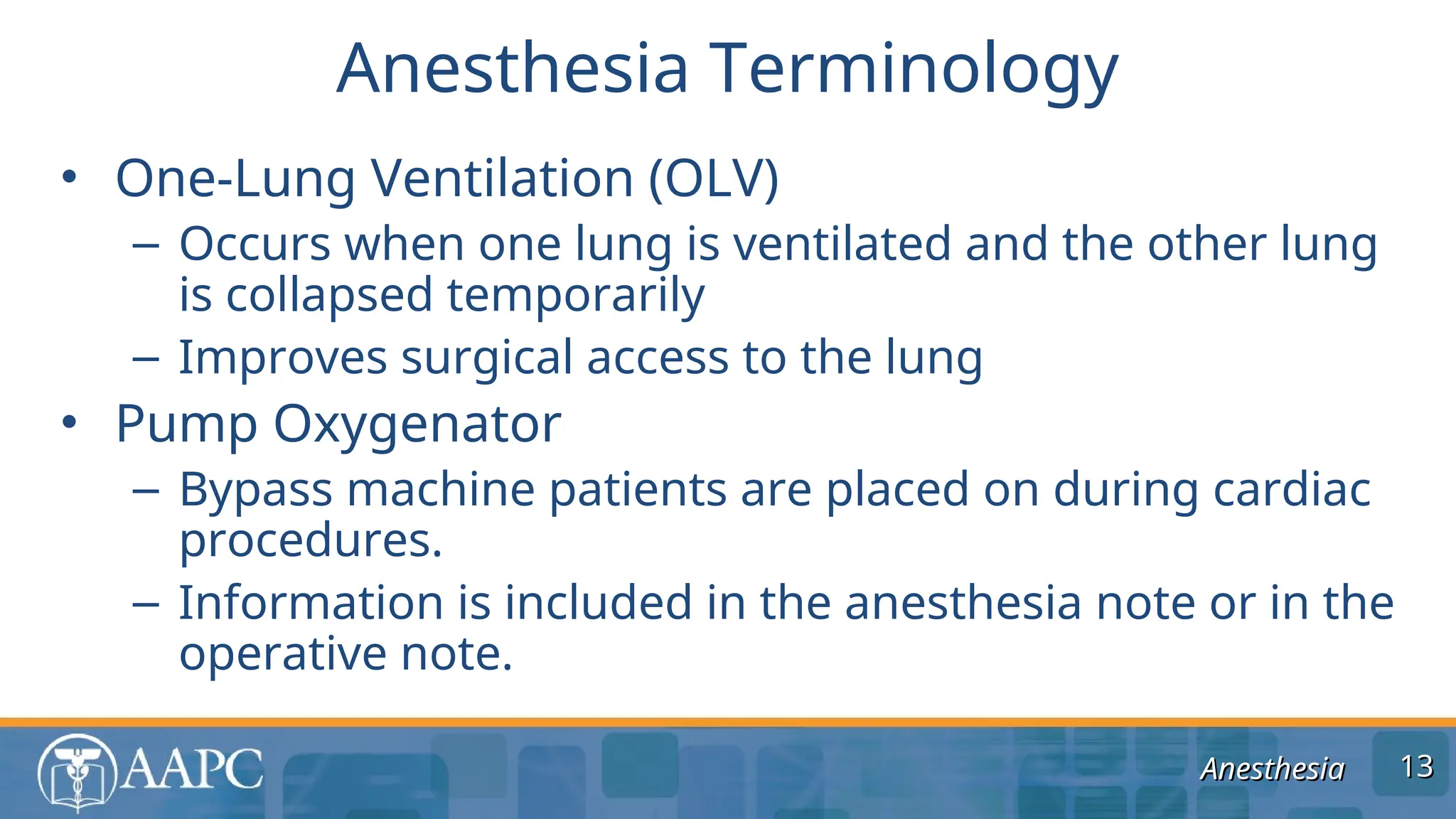
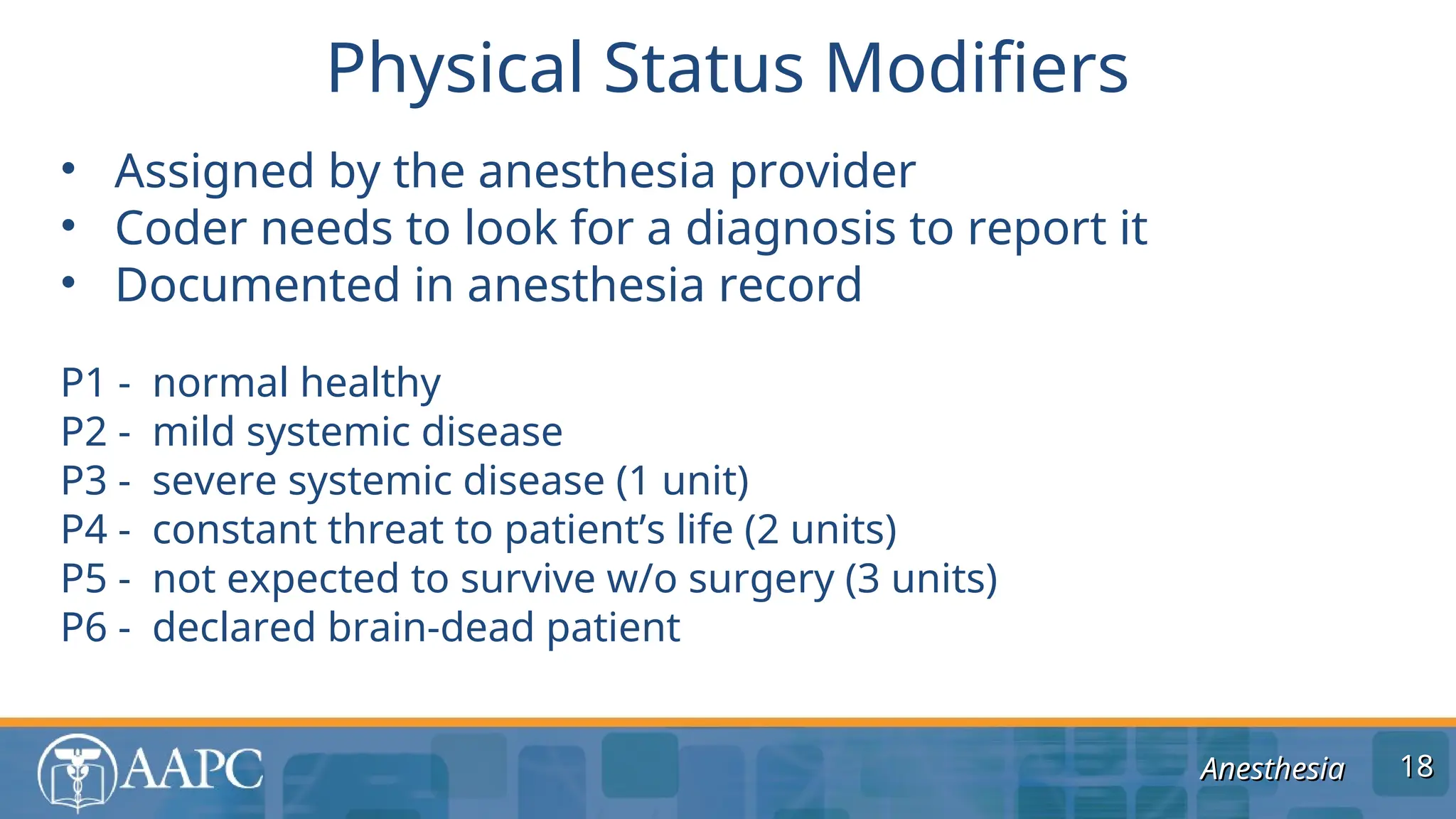
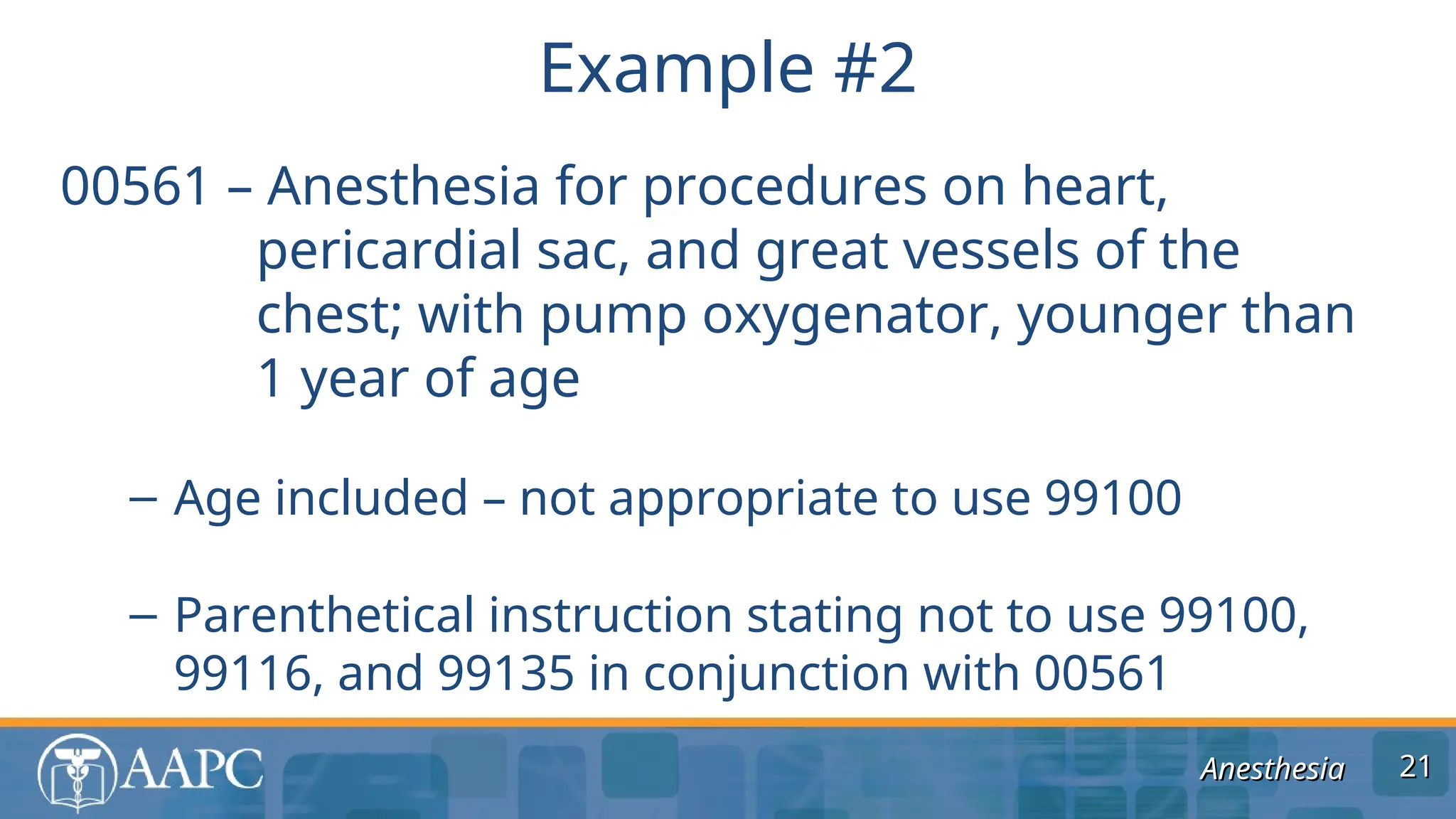
The document outlines guidelines and coding practices for anesthesia services, including the classification of anesthesia codes based on anatomical locations and types of procedures. It emphasizes the importance of understanding modifiers, billing units, and the documentation necessary for accurate coding and reimbursement. The guidelines also specify when separate anesthesia codes can be billed and the roles of different modifiers in managing anesthesia care.