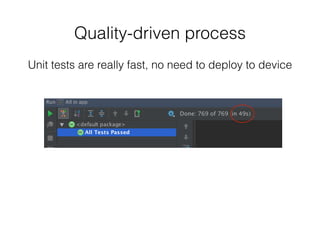
Unit testing Android apps
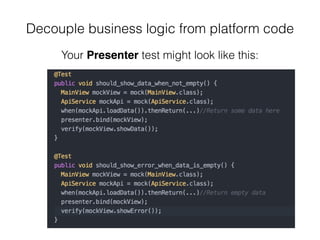
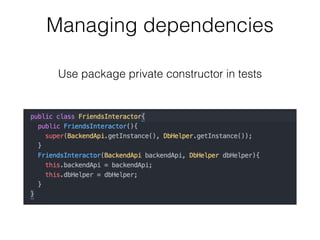
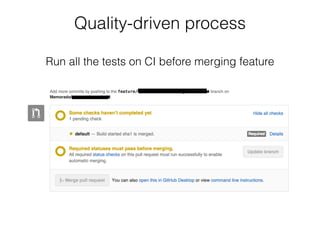
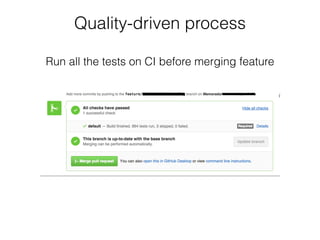
The document discusses the importance of unit testing Android apps. It recommends separating business logic from platform code using patterns like Model-View-Presenter. Unit tests should focus on individual classes and replace collaborators with test doubles. Key tools for unit testing Android include JUnit, Robolectric, and Mockito. Following software best practices like SOLID principles makes code more testable and easier to develop with a test-first approach.