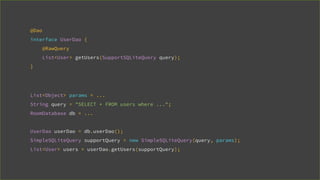
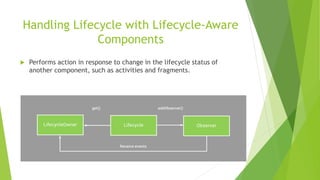
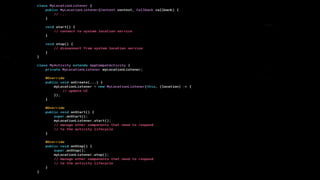
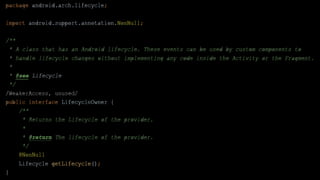
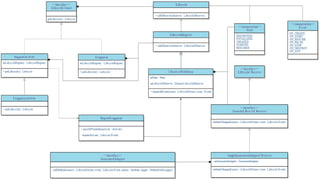
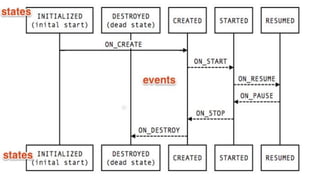
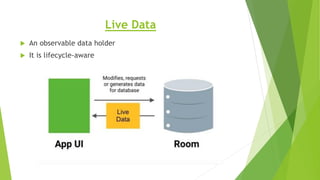
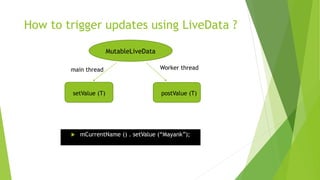
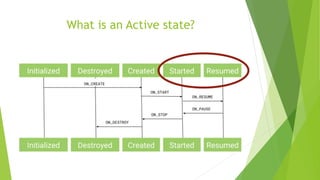
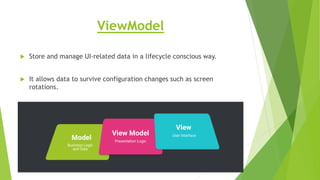
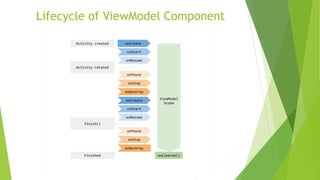
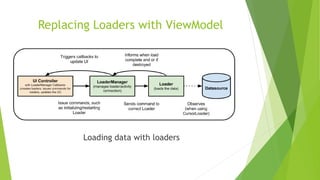
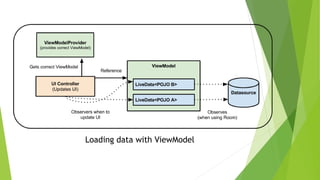
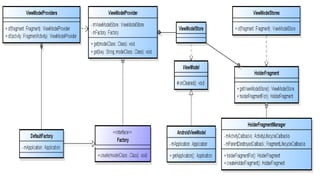
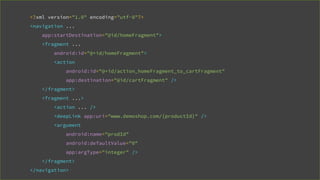
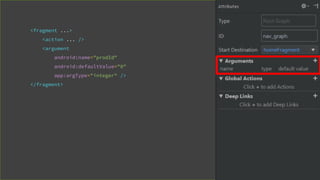
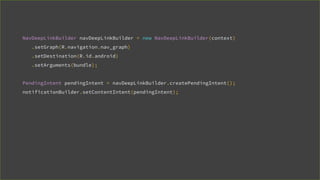
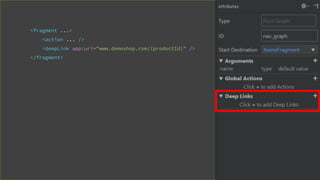
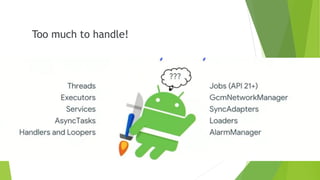
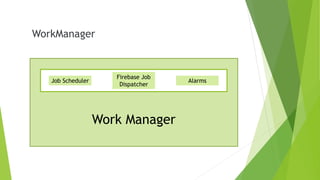
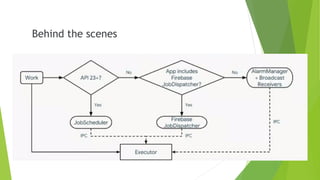
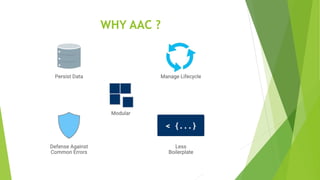
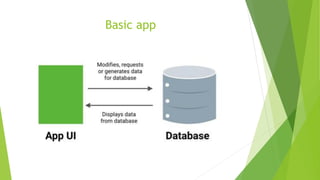
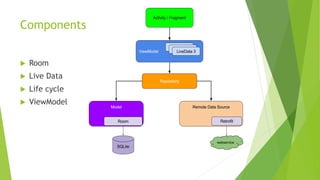
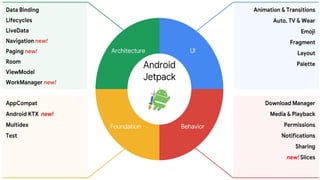
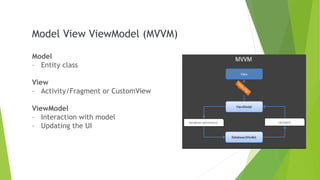
This document provides an overview of Android Architecture Components (AAC). It discusses the key components of AAC including Room for database access, LiveData for observable data, ViewModel for UI-related data, Lifecycle-aware components for handling lifecycle changes, and WorkManager for background tasks. It describes how these components help address issues with traditional approaches, provide benefits like lifecycle awareness, and encourage decoupled app architecture. Examples are given throughout to illustrate how each component works and is used within an Android app.





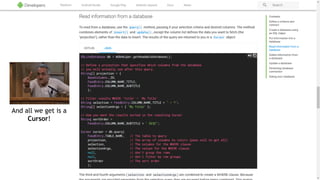








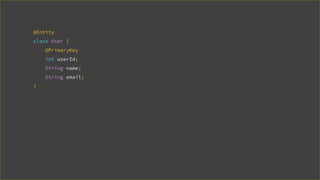

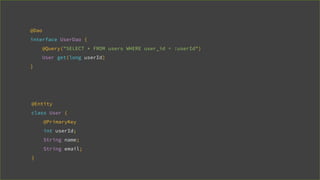

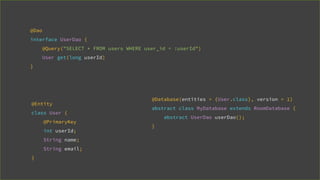


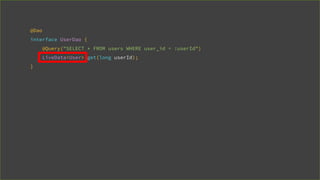
![@Dao
interface UserDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM userss WHERE user_id = :userId")
User get(long userId);
}
[SQLITE_ERROR] SQL error or missing database(no such table: userss)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidarchitecturecomponents-181101170035/85/Android-Architecture-Components-27-320.jpg)