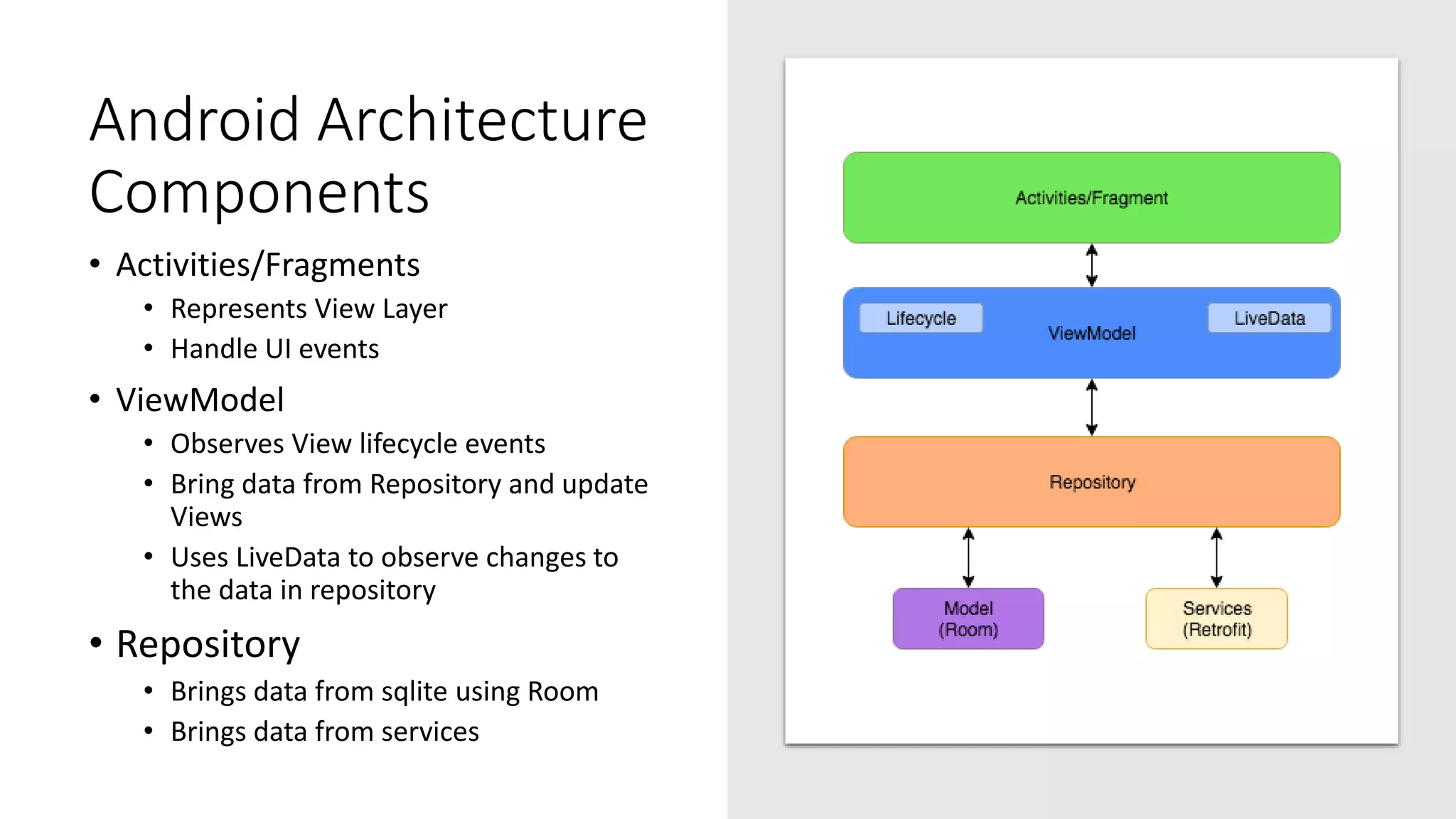
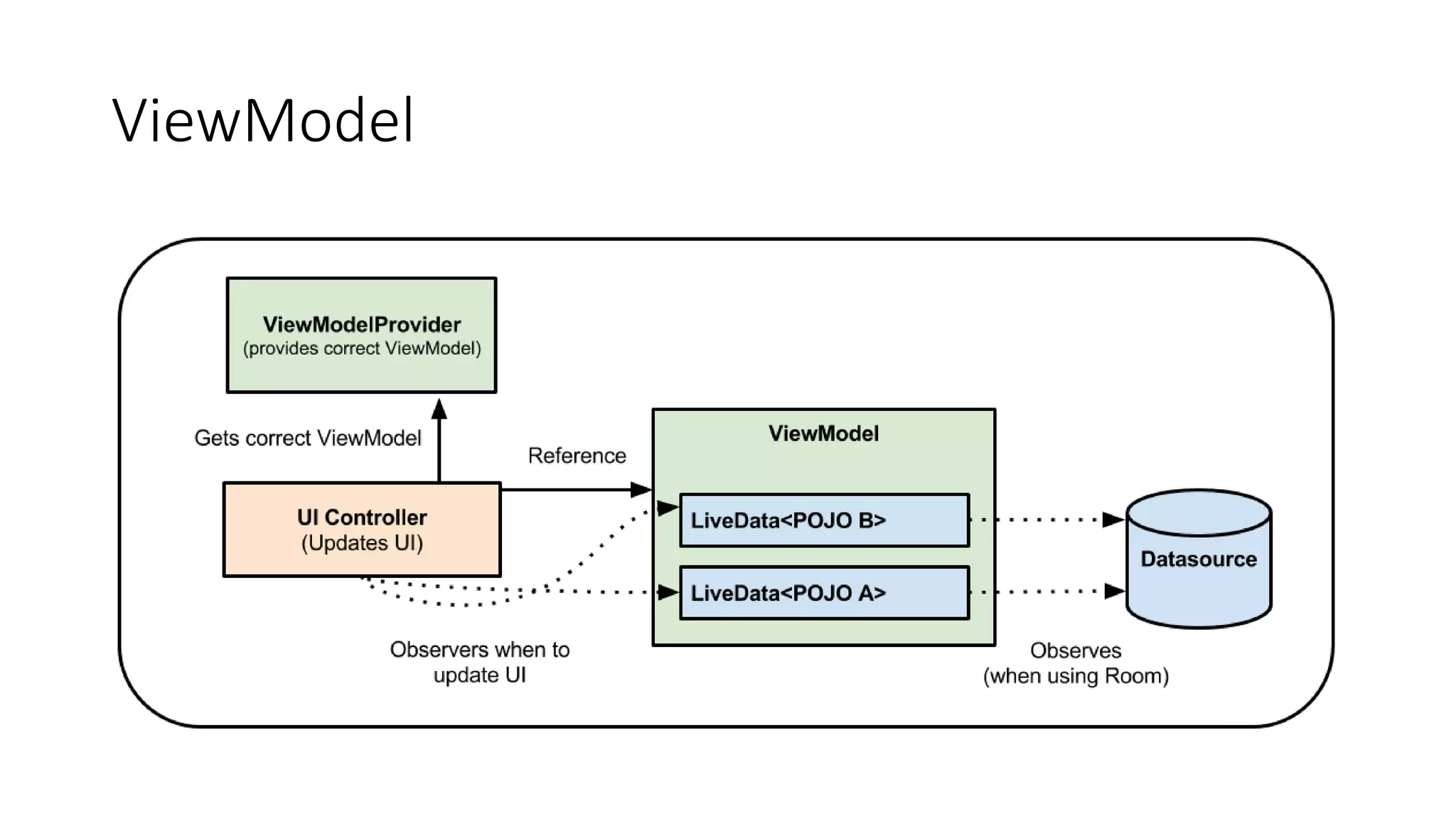
The document discusses Android architecture components, outlining their purpose and differences from design, popular patterns like MVC, MVP, MVVM, and VIPER, and Google's guidelines for efficient application architecture. It emphasizes the importance of lifecycle management, with components like ViewModel and LiveData for improved UI data management and responsiveness to configuration changes. Additionally, the Room persistence library is introduced as a means to manage app data effectively, mitigating boilerplate code and enhancing maintainability.