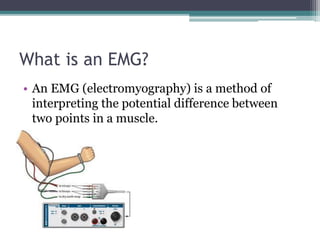
An EMG (electromyography) measures the potential difference in muscle activity and comes in three types: intramuscular, subcutaneous, and surface EMG. Intramuscular EMG uses electrodes within muscle fibers, while subcutaneous EMG involves placing electrodes in the skin layer, which is less effective; surface EMG is the most commonly used and least invasive method. The document also discusses the relationship between EMG signals and muscle force, noting challenges with quantitative analysis due to electromechanical delays.