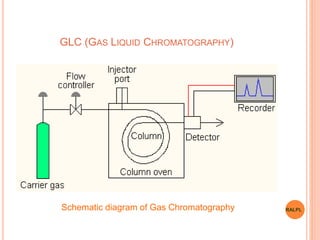
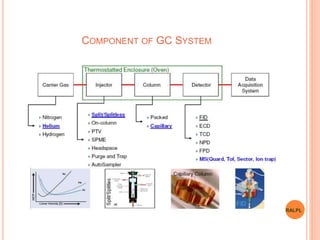
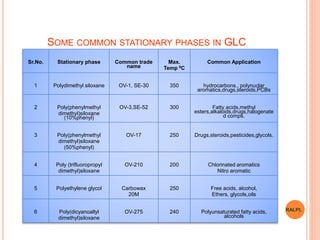
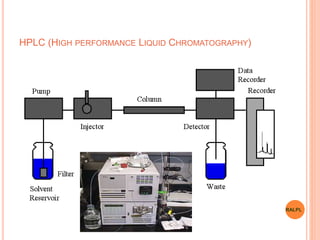
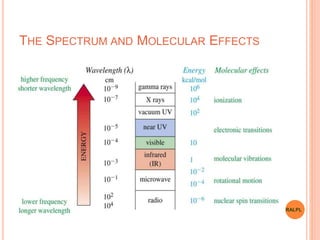
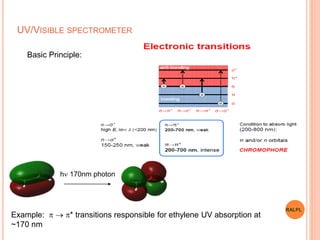
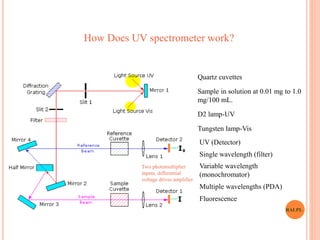
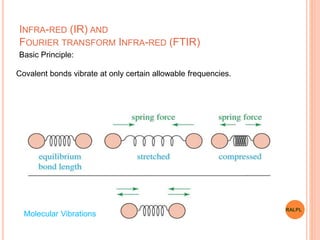
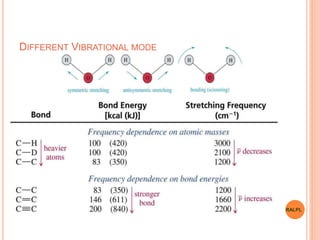
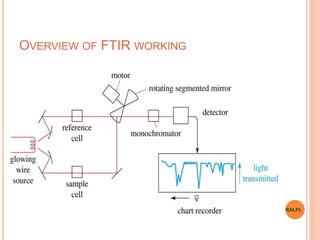
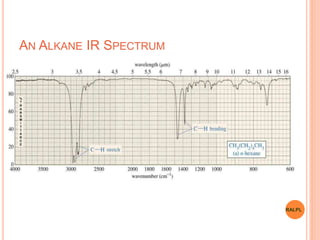
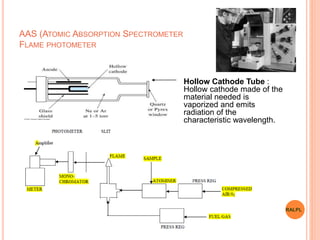
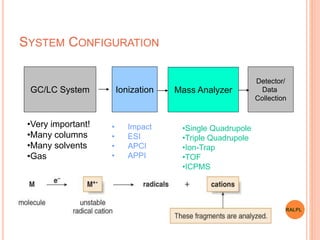
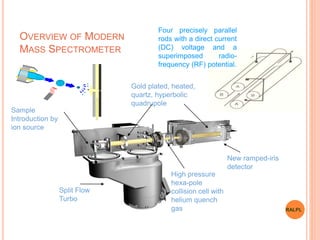
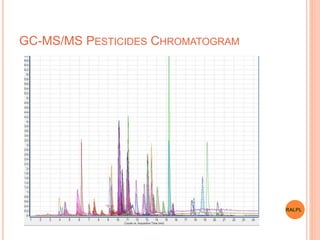
This document discusses analytical instruments and their applications. It describes two main types: chromatography and spectroscopy. Chromatography separates mixtures using mobile and stationary phases, and includes gas chromatography, liquid chromatography (including high performance liquid chromatography). Spectroscopy involves analyzing molecular interactions with different types of radiation or energy, and includes UV-visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and atomic absorption spectroscopy. Analytical instruments have wide-ranging applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, foods, and petroleum, as well as research and clinical settings.