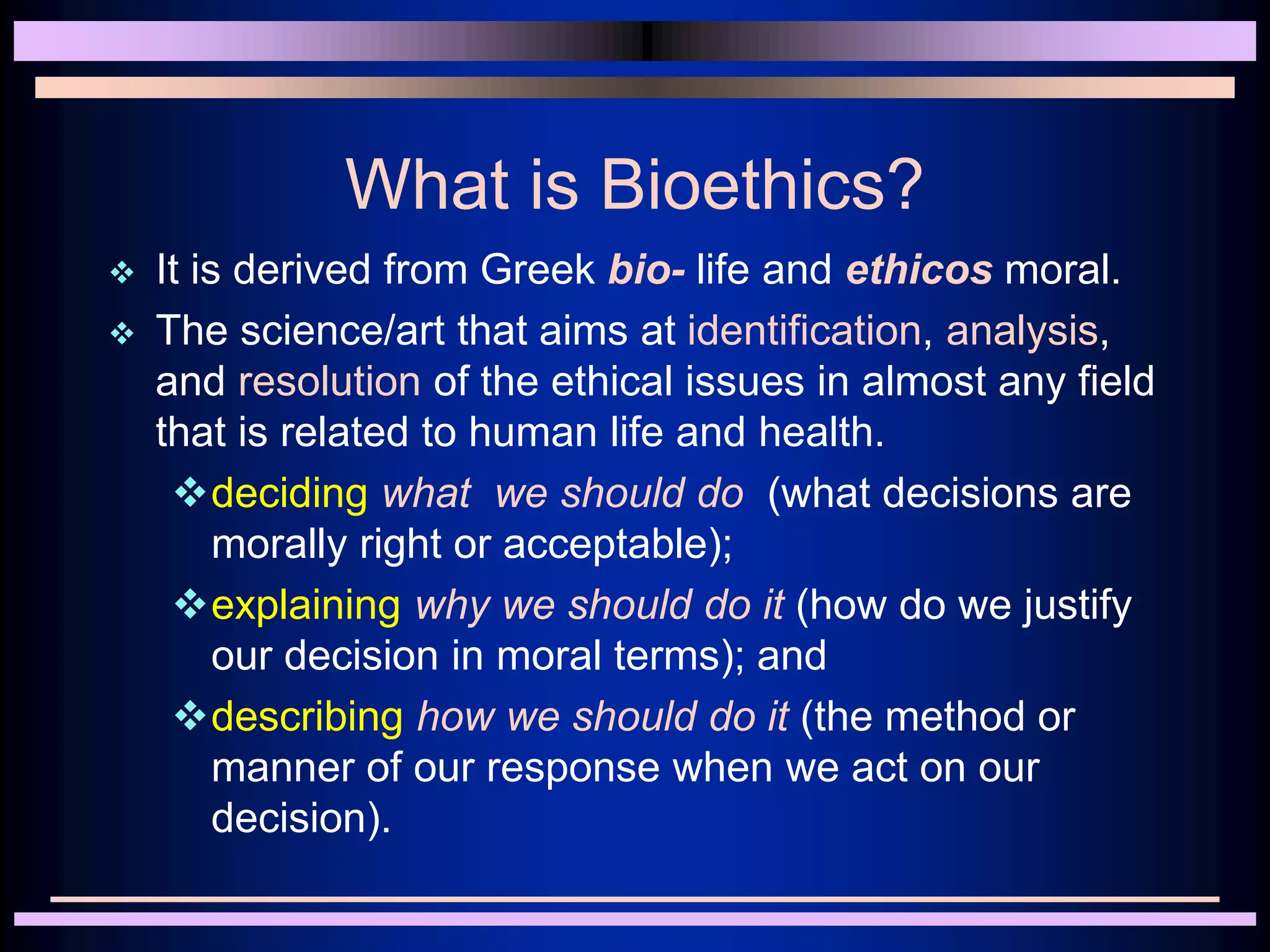
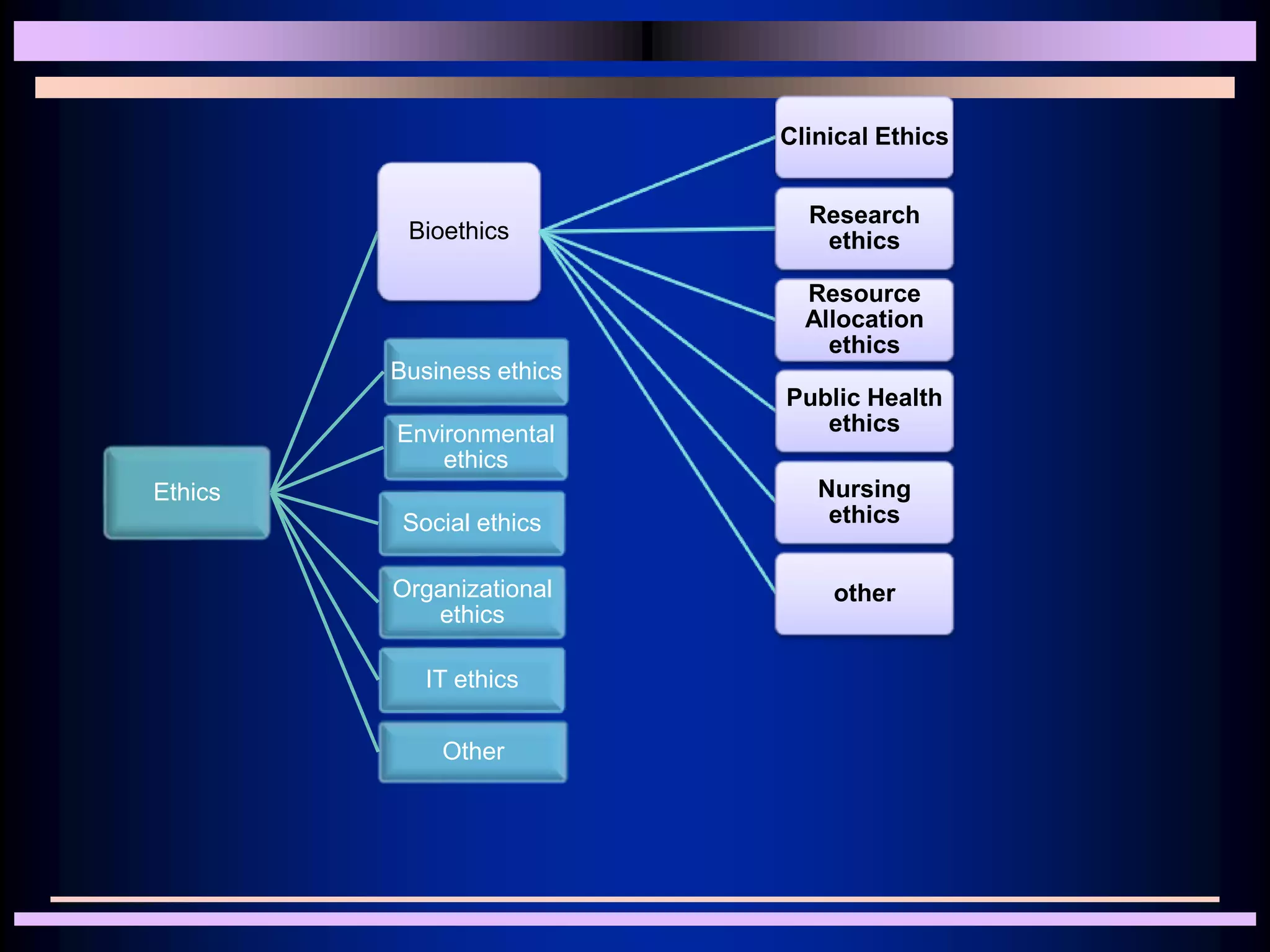
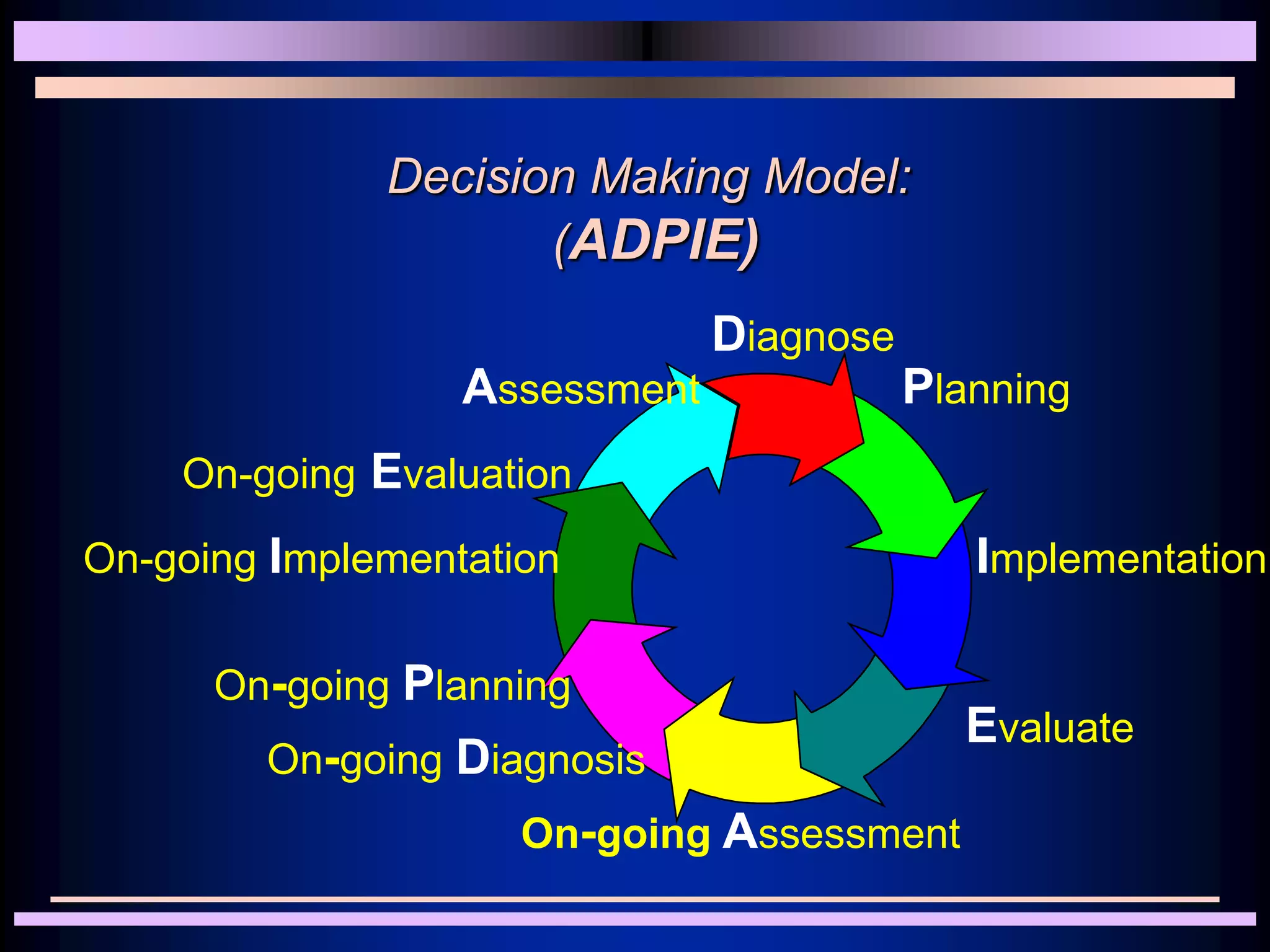
Medical ethics aims to define right and wrong in medical practice. It draws on ethical theories like consequentialism, deontology, and situational ethics. Key principles of medical ethics include autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and informed consent. Doctors have a duty to treat patients compassionately and respect their rights and privacy. Ethical issues arise when there are conflicts between values or responsibilities. Medical ethics provides frameworks for resolving dilemmas in a fair and just manner.