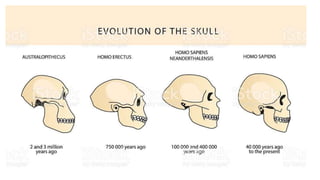
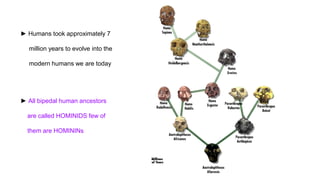
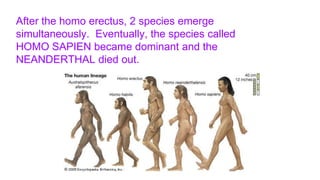
This document provides an introduction to human evolution. It begins by outlining why teaching evolution is important, then defines evolution and discusses key figures like Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace. It explains that humans evolved from primate ancestors approximately 12 million years ago, with the hominin lineage evolving to walk upright on two legs. Key stages in human evolution included Homo erectus, and later the emergence of Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, with Homo sapiens eventually becoming dominant. Evolutionary features like tool use and control of fire are noted. The document concludes with a brief discussion of human migration.