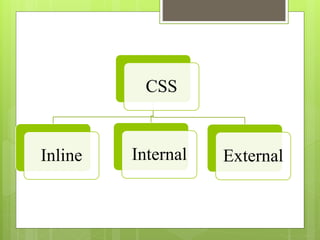
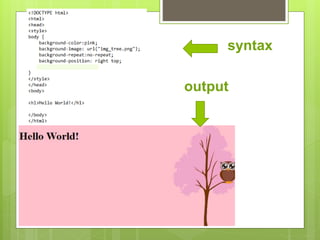
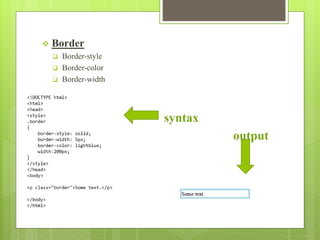
This document provides a comprehensive overview of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), detailing their definitions, uses, and various tags along with their attributes. It covers the structure of HTML, including headings, paragraphs, and lists, as well as CSS styling properties such as color, background, and layout. Overall, it serves as a foundational guide for creating and styling web pages.




















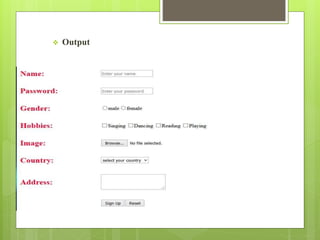
![ Checkbox
Syntax: <input type="checkbox" name="qw[]"
value=""/>Singing
<input type="checkbox" name="qw[]" value=""/>Dancing
File: used to upload the file.
syntax: <input type="file" name="qwe" value=""/>
Textarea: it is paired tag.
syntax:<textarea name="asd">
</textarea>
Button: it is unpaired.
Syntax:<input type="submit" name="qas" value="Sign Up"/>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html-160914031245/85/Html-26-320.jpg)