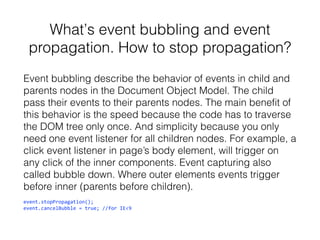
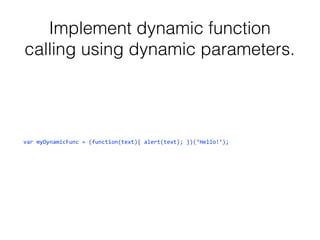
The document is a collection of technical questions and answers related to JavaScript, covering topics such as prototypal inheritance, closures, event handling, and the use of the 'this' keyword. It includes code examples that demonstrate JavaScript concepts like object creation, variable scope, and error handling. Additionally, the document addresses the differences between various equality checks and provides insights into handling DOM elements and timer functions.


![What’s prototyping?
Javascript does’nt use classical ‘inheritance’ model. It uses
prototypal inheritance. We will want to declare methods on the
prototype class, not in the constructor, mainly because when the
use new the object would create each time a new copy of the
methods instead of using the common one from the prototype.
//Guitar function constructor
function Guitar(color, strings) {
this.color = color;
this.strings = strings;
}
//Guitar prototype method
Guitar.prototype.play = function(chord){
return chord;
}
var myguitar = new Guitar(‘blue’,[‘A’,’F’,’G’]);
--------Guitar.prototype = {
play : function(chord){ return chord; },
getColor : function(){ return this.color; }
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptquiz-140213215557-phpapp02/85/Javascript-quiz-Questions-to-ask-when-recruiting-developers-3-320.jpg)

![Implement dot and literals object
notation. What’s the difference?
There is no practical difference.
var man = new Object();
man.name = “Albert”; // man[‘name’] = “Albert”;
man.age = 29; // man[‘age’] = 29;
---------var man = { ‘name’ : “Andrew”, ‘age’ : 27 };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptquiz-140213215557-phpapp02/85/Javascript-quiz-Questions-to-ask-when-recruiting-developers-5-320.jpg)












![Implement an associative
array.
I will use a literal object notation to create one.
var myArray={key1: 'value1', key2:'value2' };
alert(myArray[‘key1’]); // Also myArray.key1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptquiz-140213215557-phpapp02/85/Javascript-quiz-Questions-to-ask-when-recruiting-developers-20-320.jpg)

