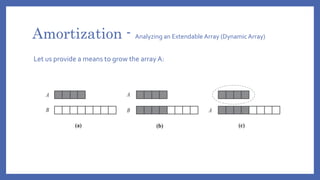
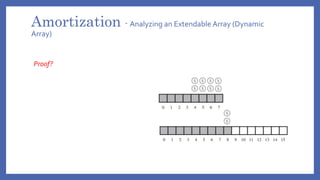
The document discusses amortized analysis, which analyzes an algorithm's time complexity by calculating the amortized cost per operation rather than worst-case cost. It describes common amortization techniques like aggregate analysis and accounting method. Aggregate analysis calculates total cost T(n) of n operations and divides by n. The accounting method assigns credits and debits to operations to show actual cost equals amortized cost minus accumulated credits. An example of dynamic array growth using amortization is given, with a theorem stating n add operations on an initially empty array have total time O(n).


![Amortization – Aggregate Analysis
Aggregate analysis determines the upper bound T(n) on the total cost of a sequence
of n operations, then calculates the amortized cost to be T(n) / n.
Example:
A = {0, 0, …, 0} // size of k
Function increment(k):
i = 1
while i <= k and A[i] == 1 :
A[i] = 0
i = i + 1
if i < k:
A[i] = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amortizedanalysis-210412153839/85/Amortized-analysis-3-320.jpg)
![Amortization – Aggregate Analysis
Aggregate analysis determines the upper bound T(n) on the total cost of a sequence
of n operations, then calculates the amortized cost to be T(n) / n.
Example:
A = {0, 0, …, 0} // size of k
Function increment(k):
i = 1
while i <= k and A[i] == 1 :
A[i] = 0
i = i + 1
if i < k:
A[i] = 1
FunctionT(n):
for i <- 1 until n:
increment(k)
Amortization Cost ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amortizedanalysis-210412153839/85/Amortized-analysis-4-320.jpg)

![Amortization – Accounting Method
Example:
A = {0, 0, …, 0} // size of k
Function increment(k):
i = 1
while i <= k and A[i] == 1 :
A[i] = 0
i = i + 1
if i < k:
A[i] = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amortizedanalysis-210412153839/85/Amortized-analysis-6-320.jpg)