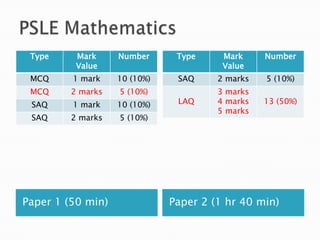
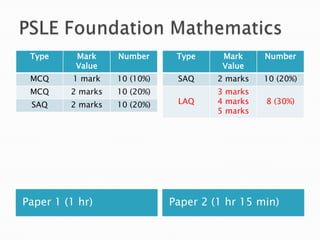
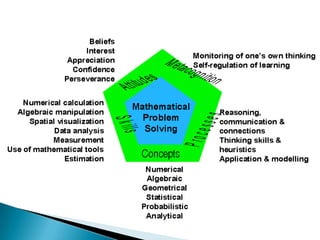
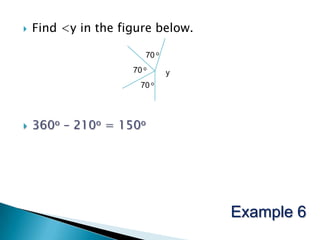
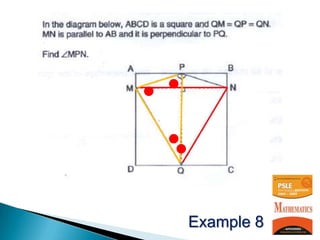
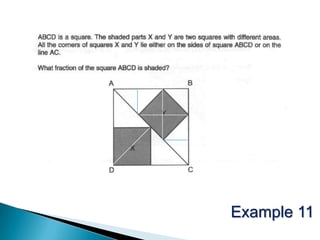
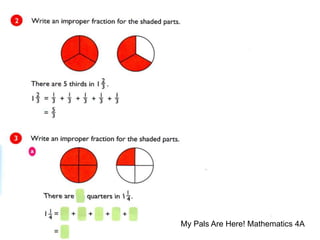
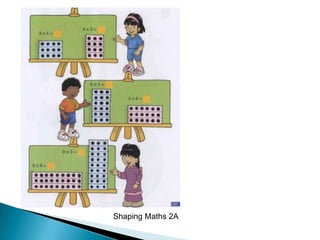
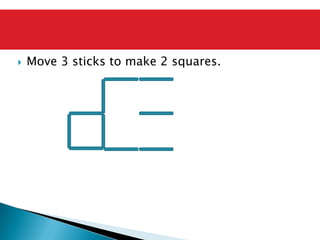
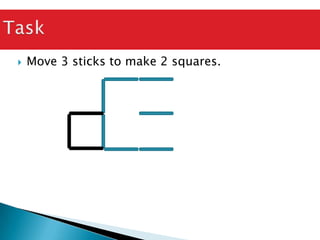
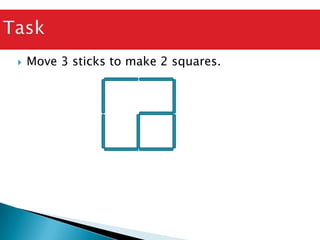
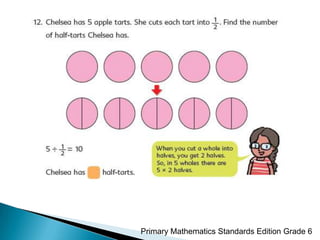
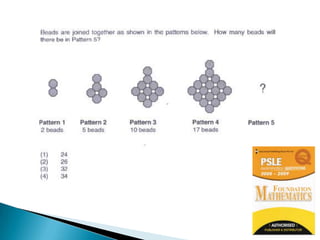
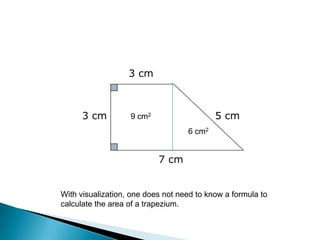
The document discusses the PSLE mathematics curriculum and its emphasis on problem-solving as a key competency. It highlights concerns from parents regarding the difficulty of recent exams, particularly with the introduction of calculators. Additionally, it outlines various teaching strategies and competencies necessary for effective mathematics learning, including visualization and metacognition.