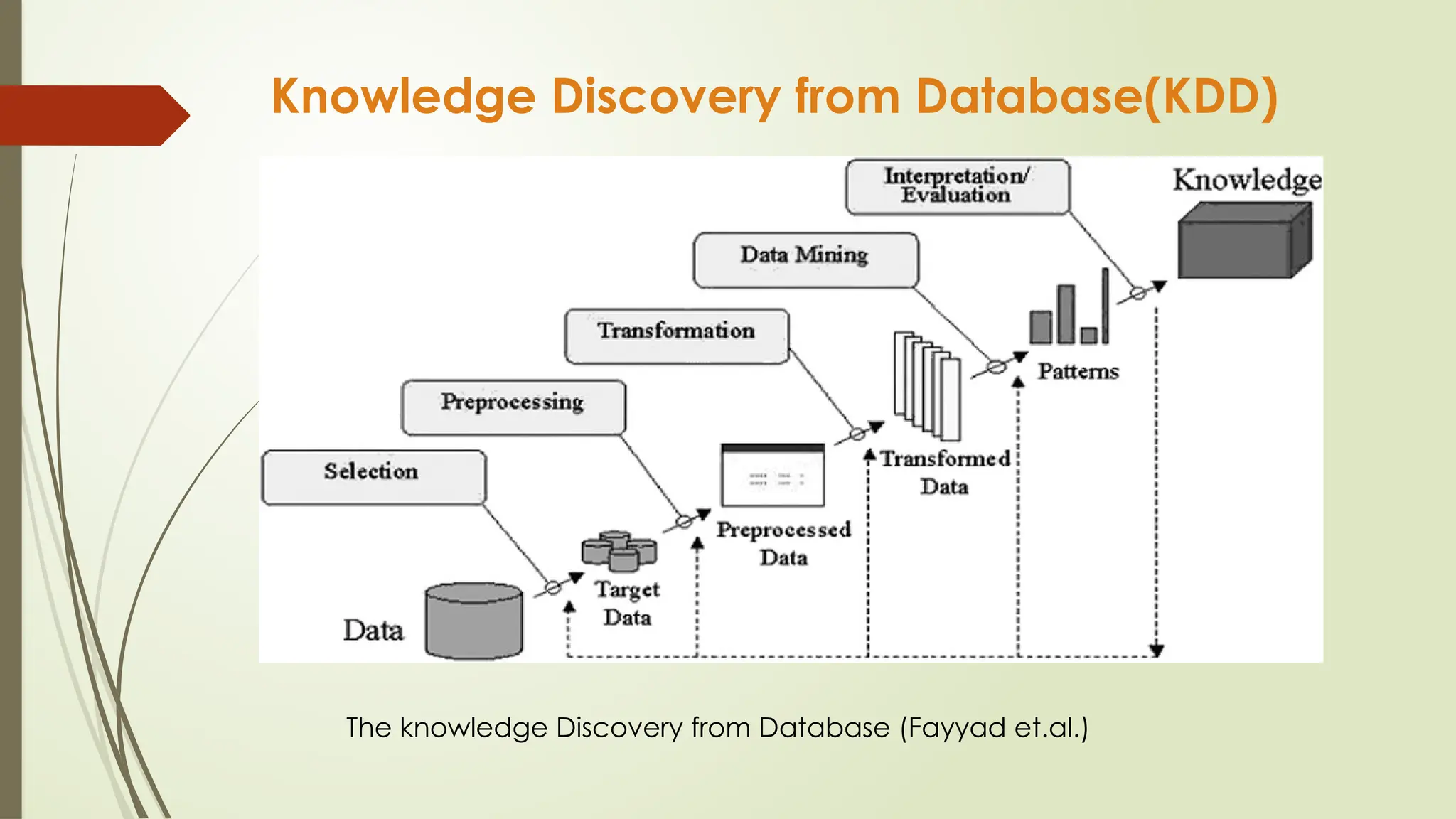
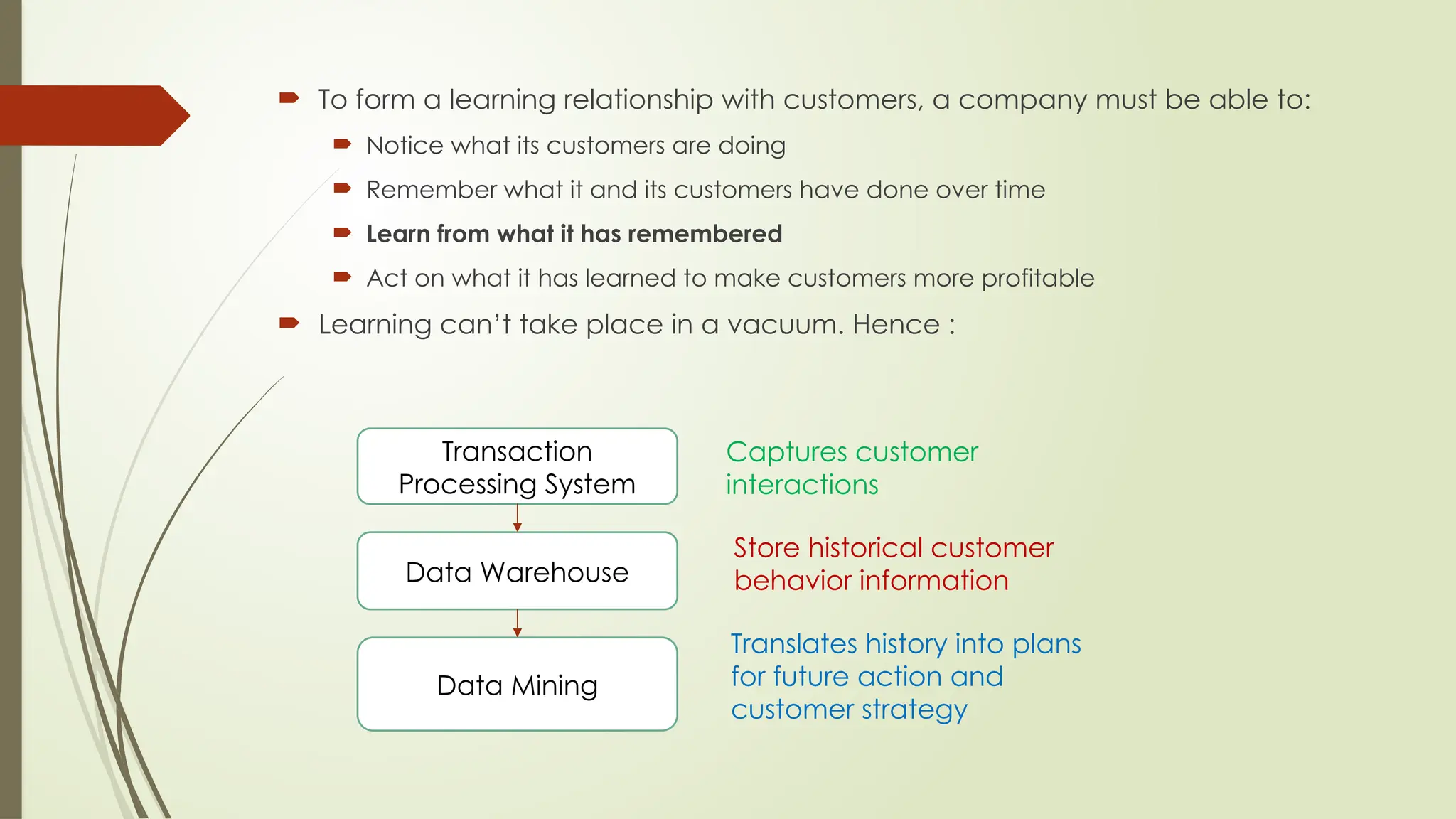
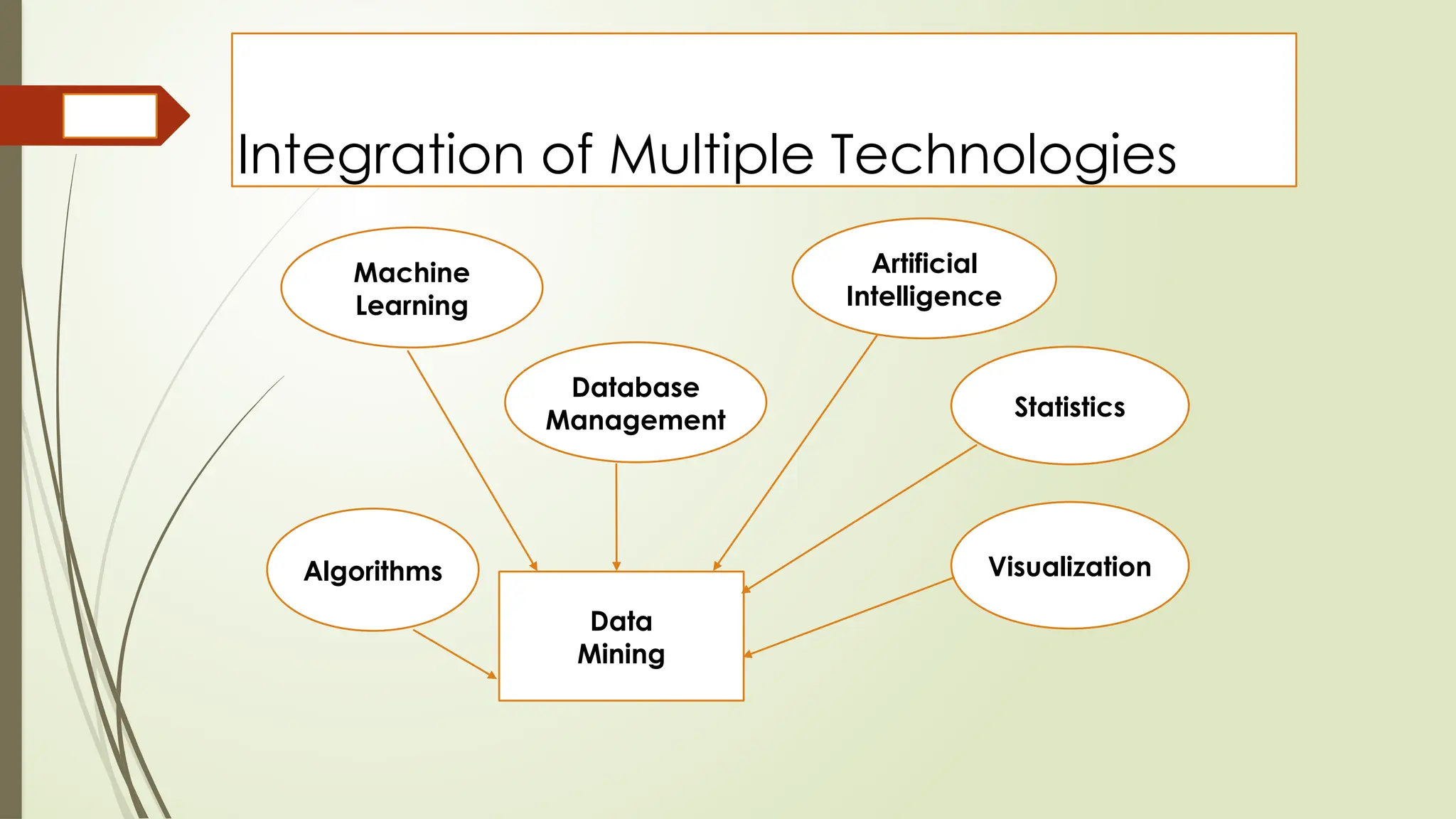
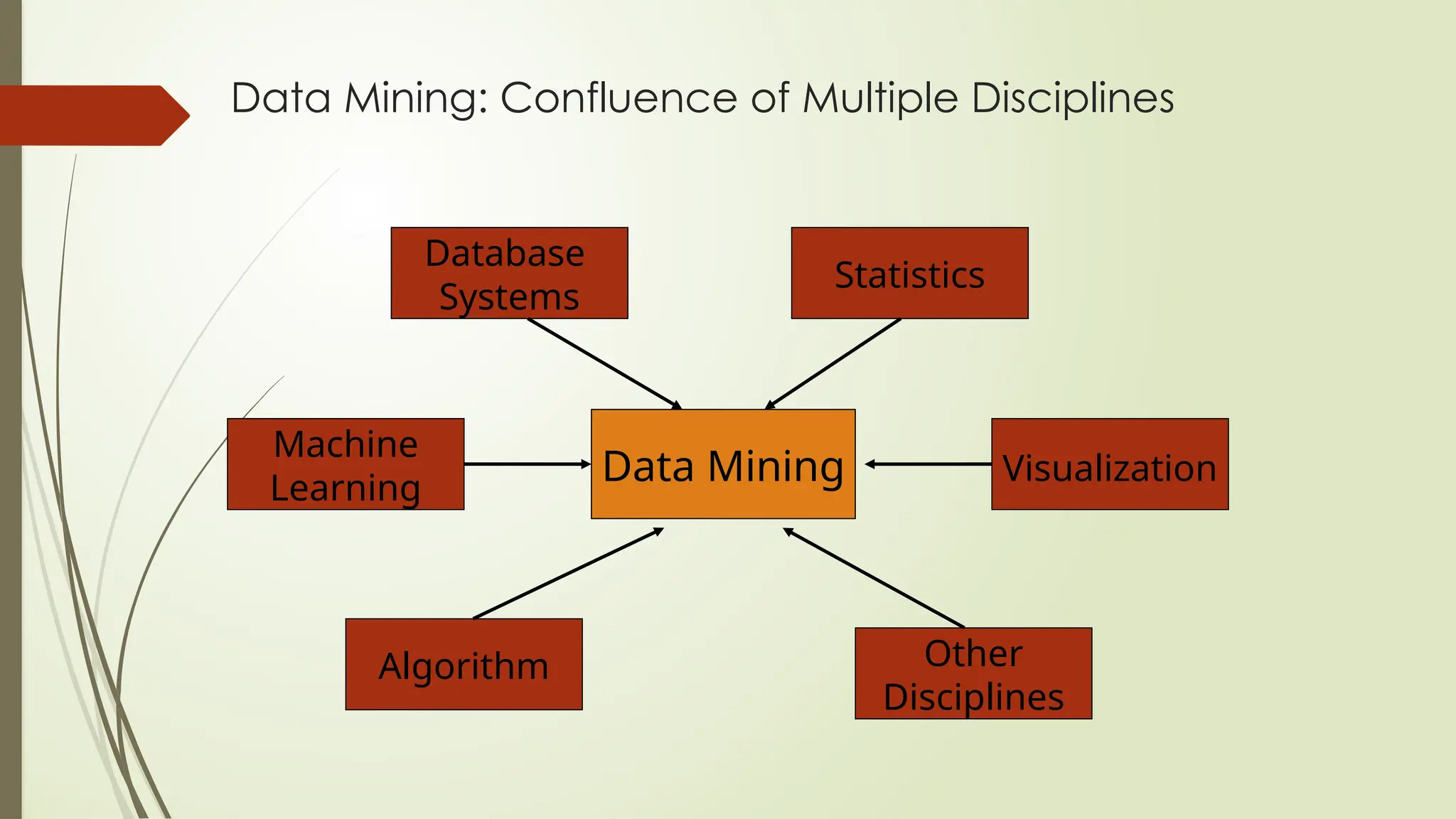
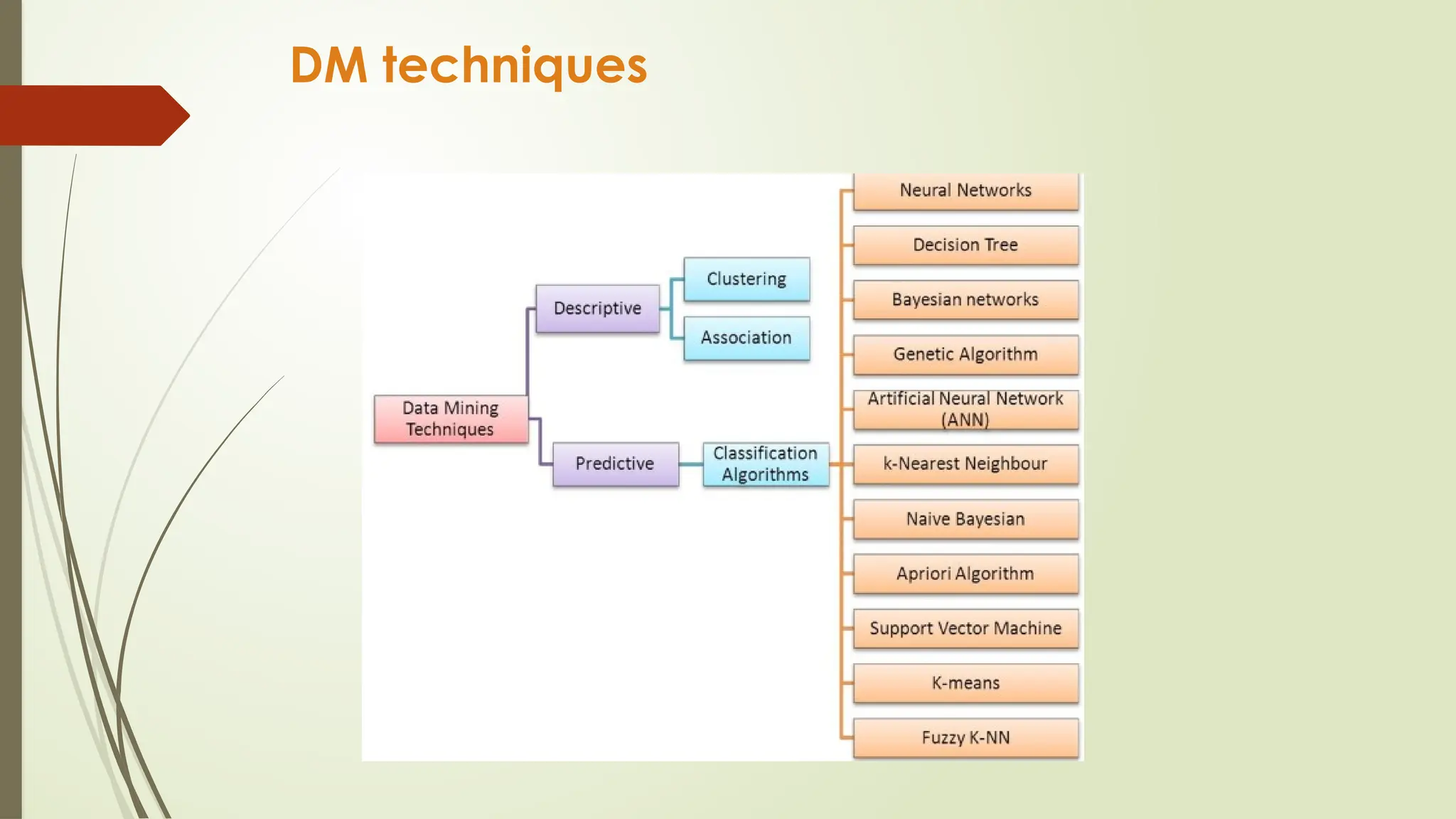
The document outlines a course on data mining and big data analytics, focusing on the advanced concepts, strengths, and limitations of data mining models. Data mining is presented as a business process for extracting meaningful patterns from large datasets, with applications in customer relationship management and market research. It highlights the growing importance of data mining due to the increase in data availability, affordable computing power, and the need for businesses to adopt customer-centric models.