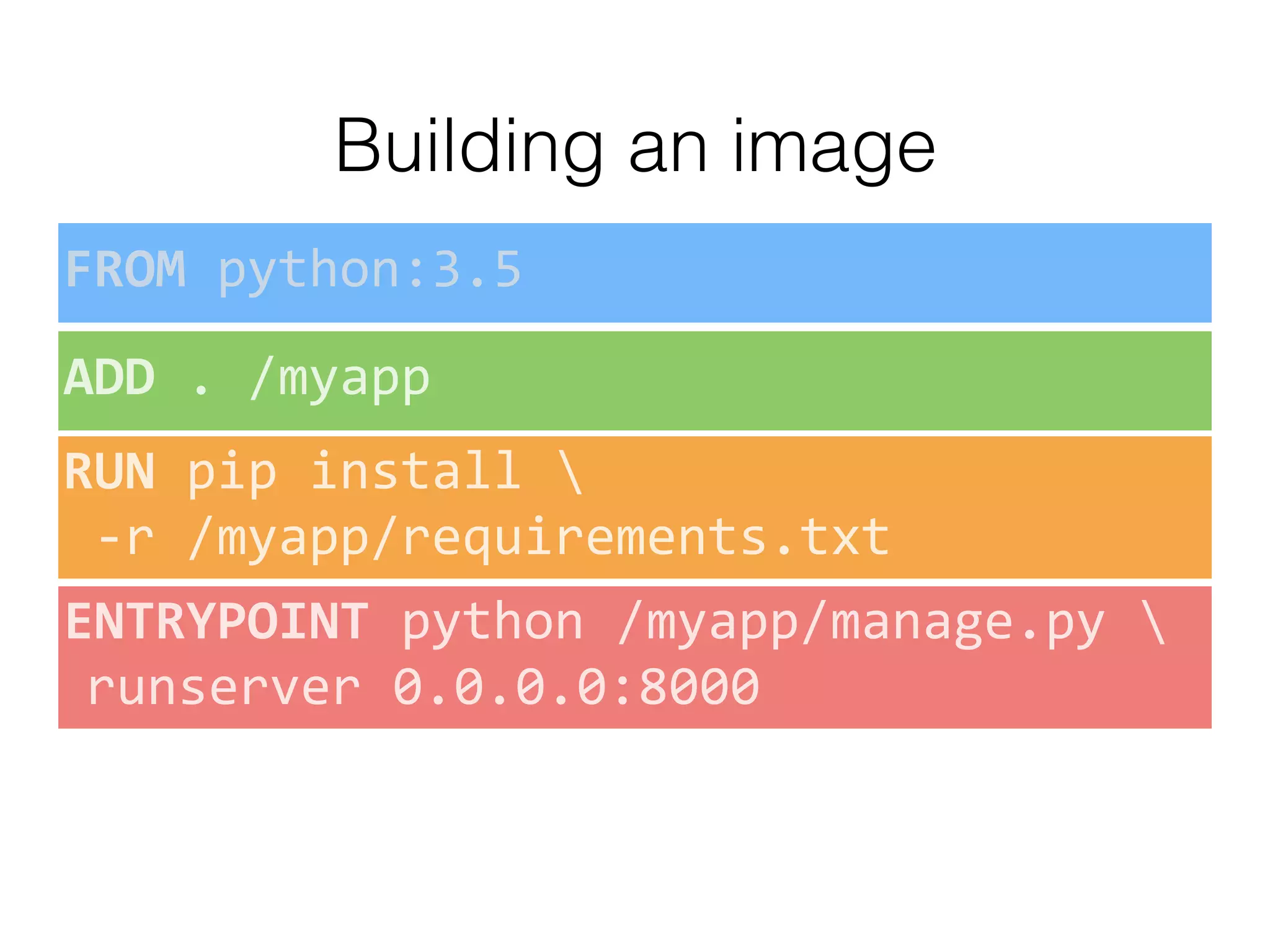
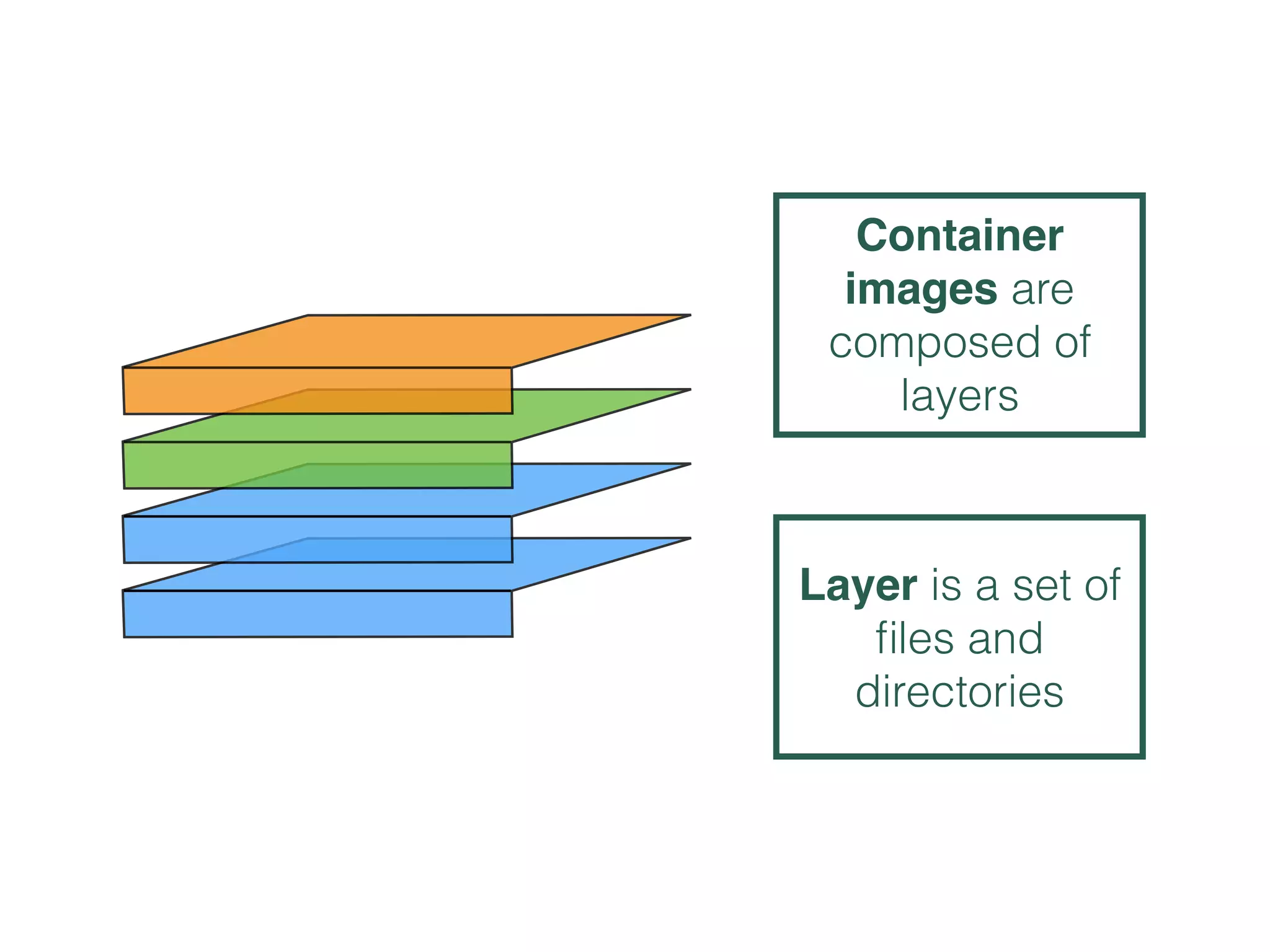
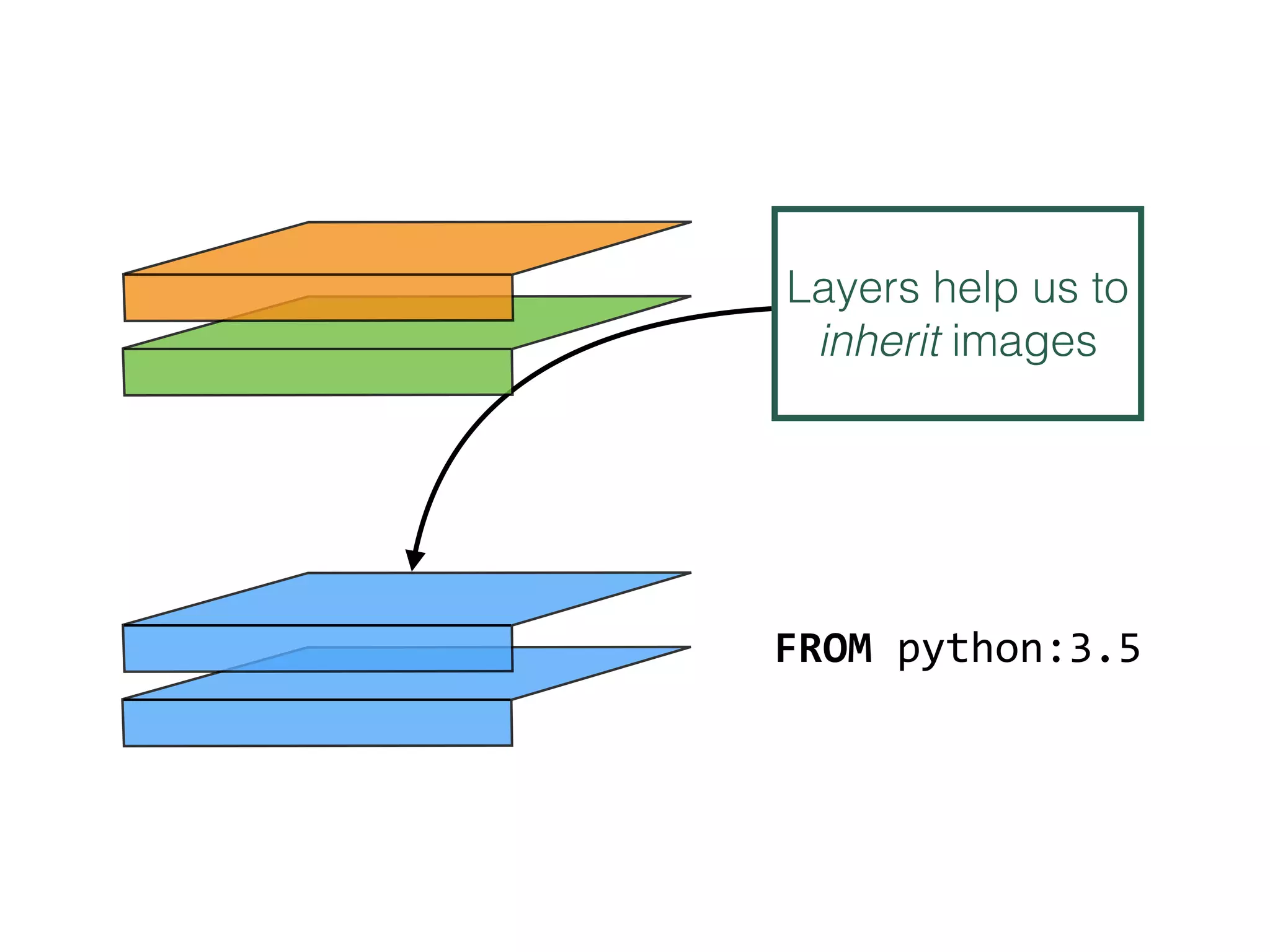
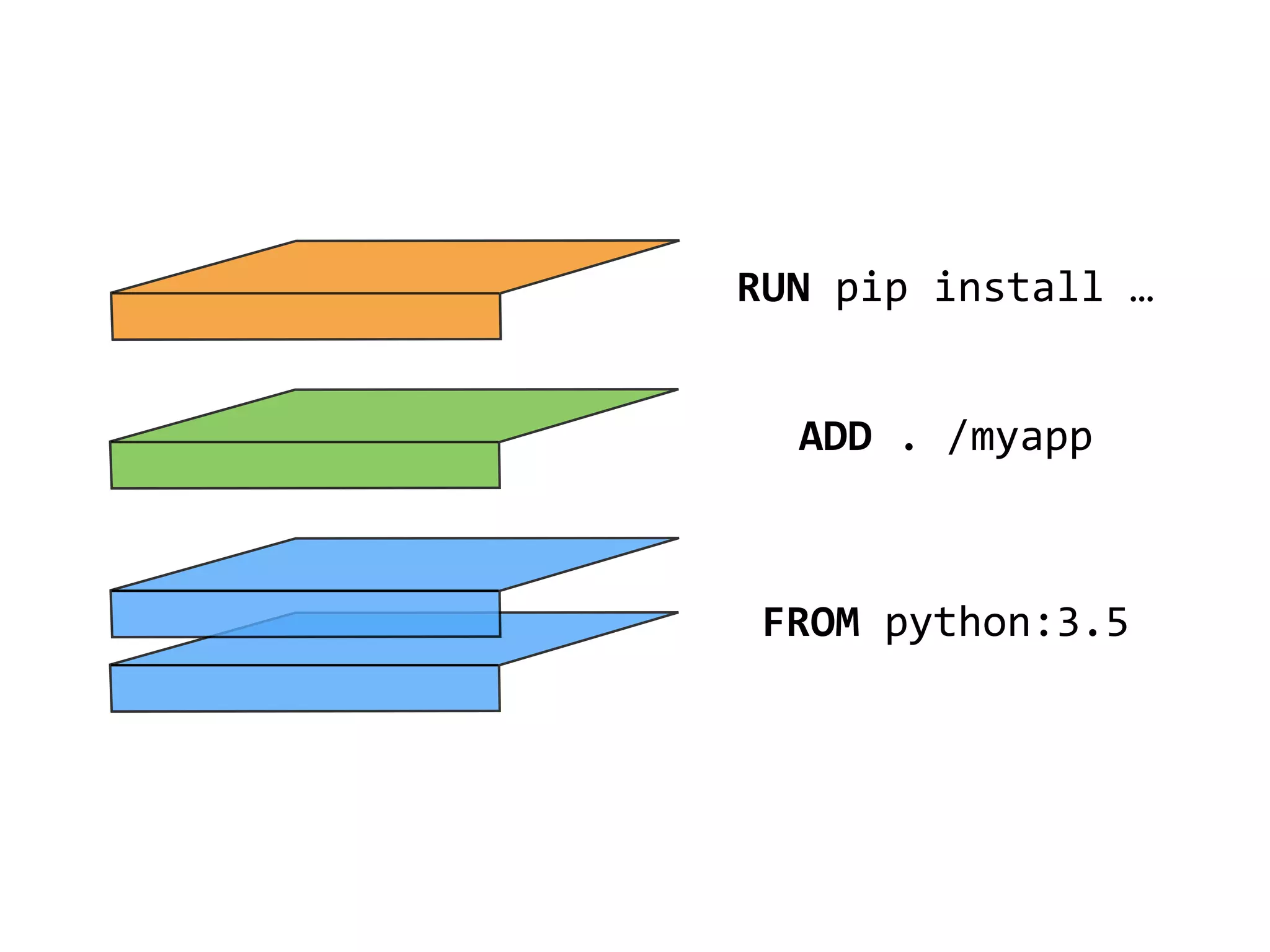
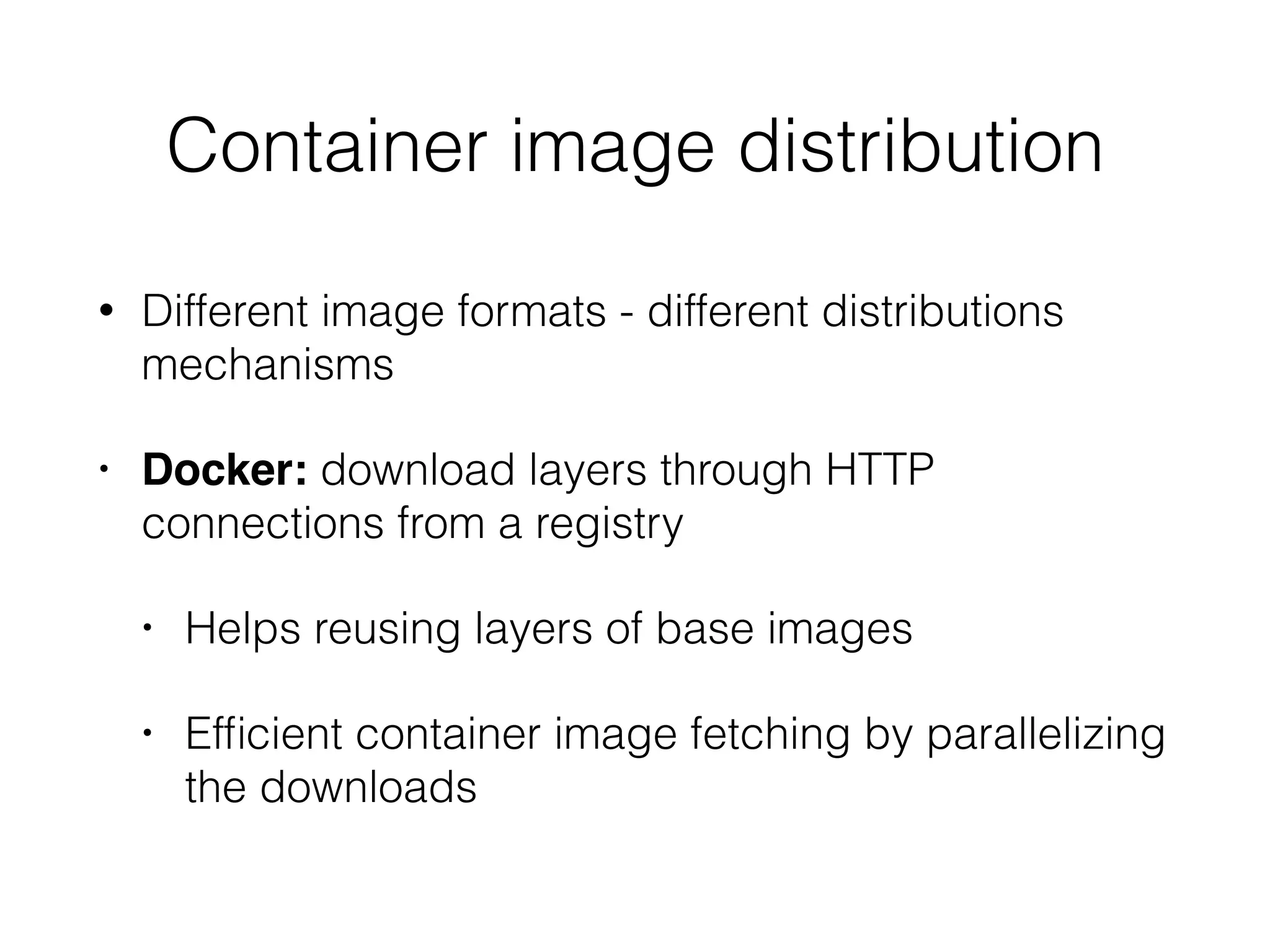
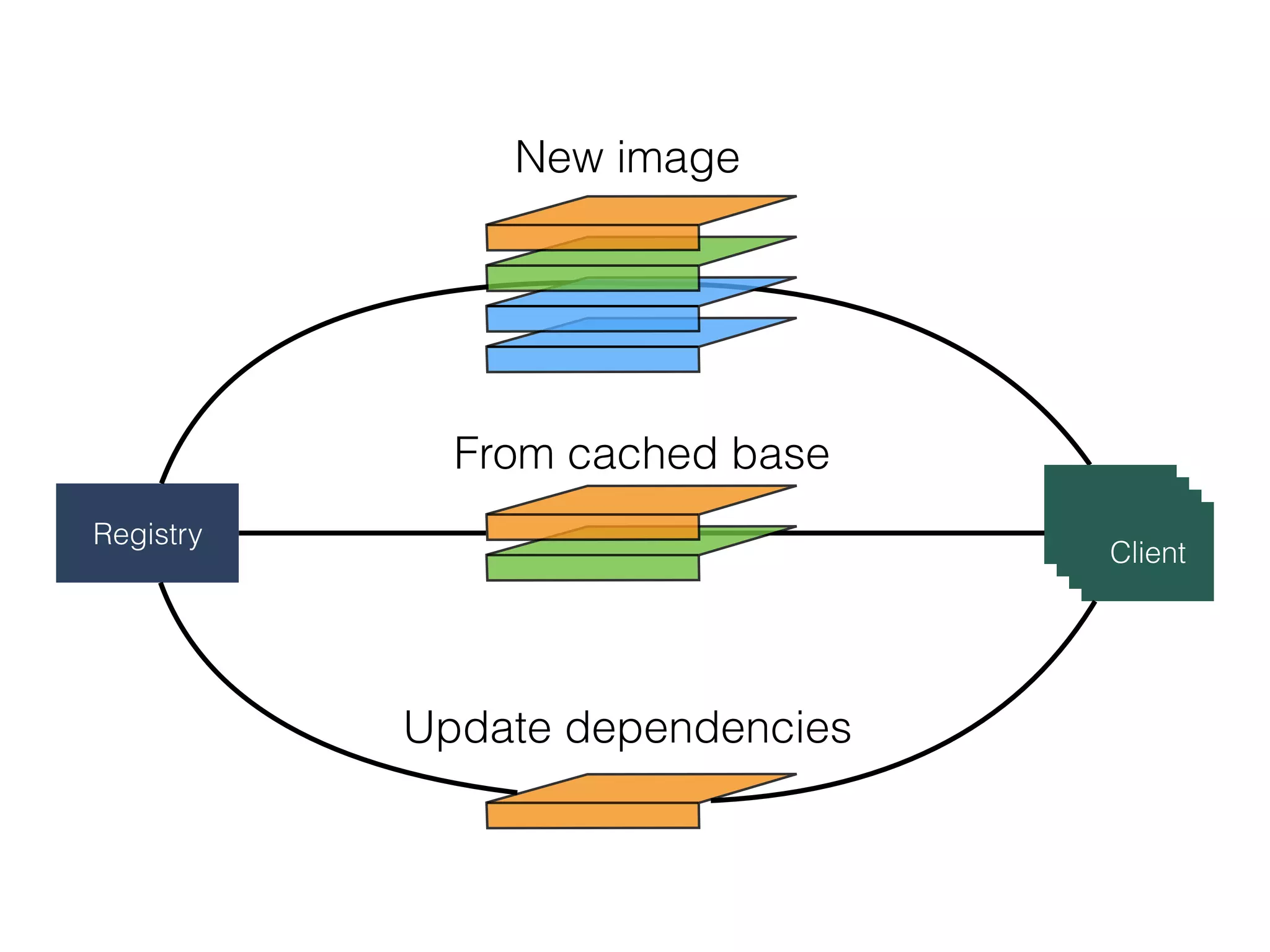
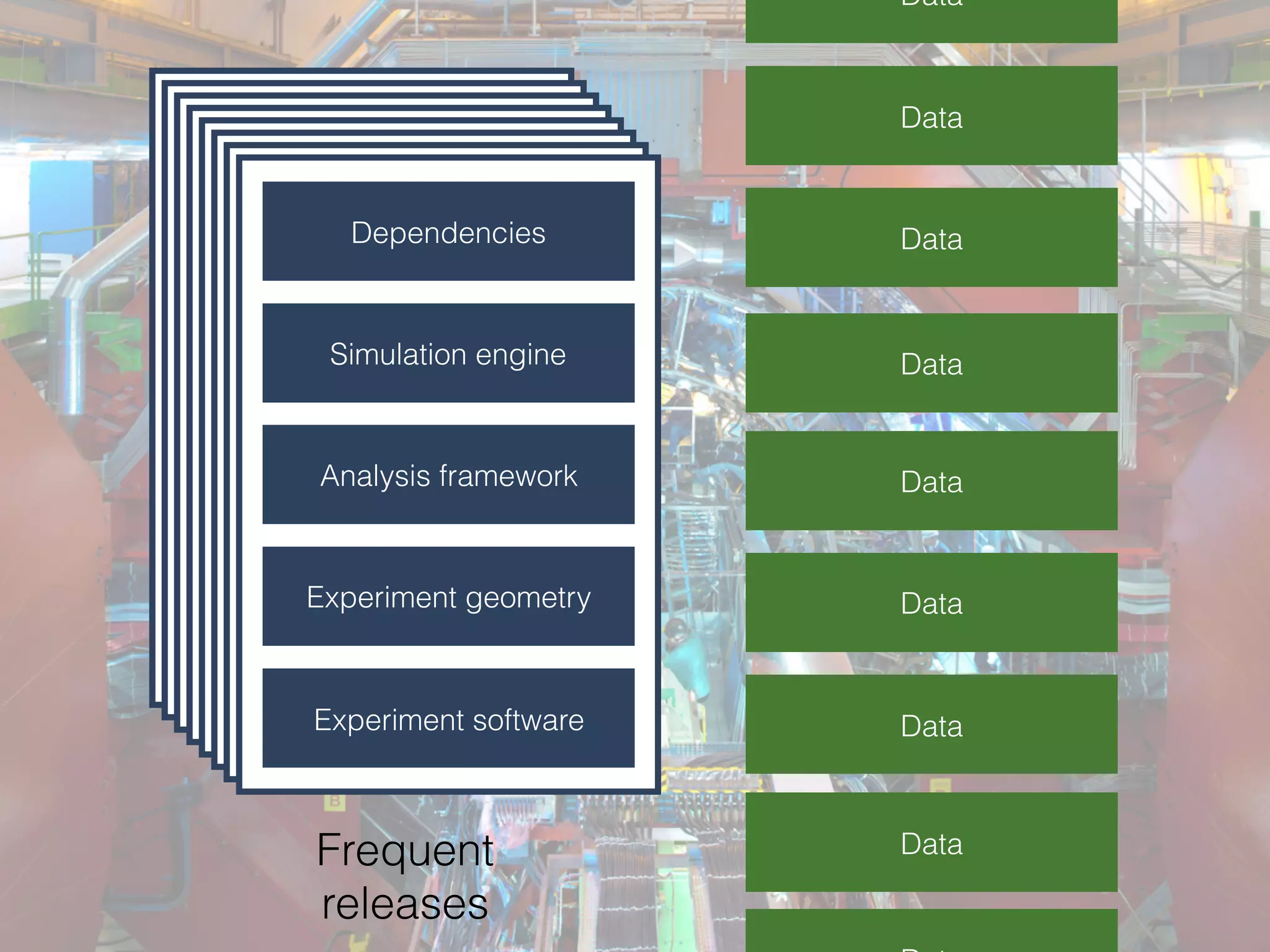
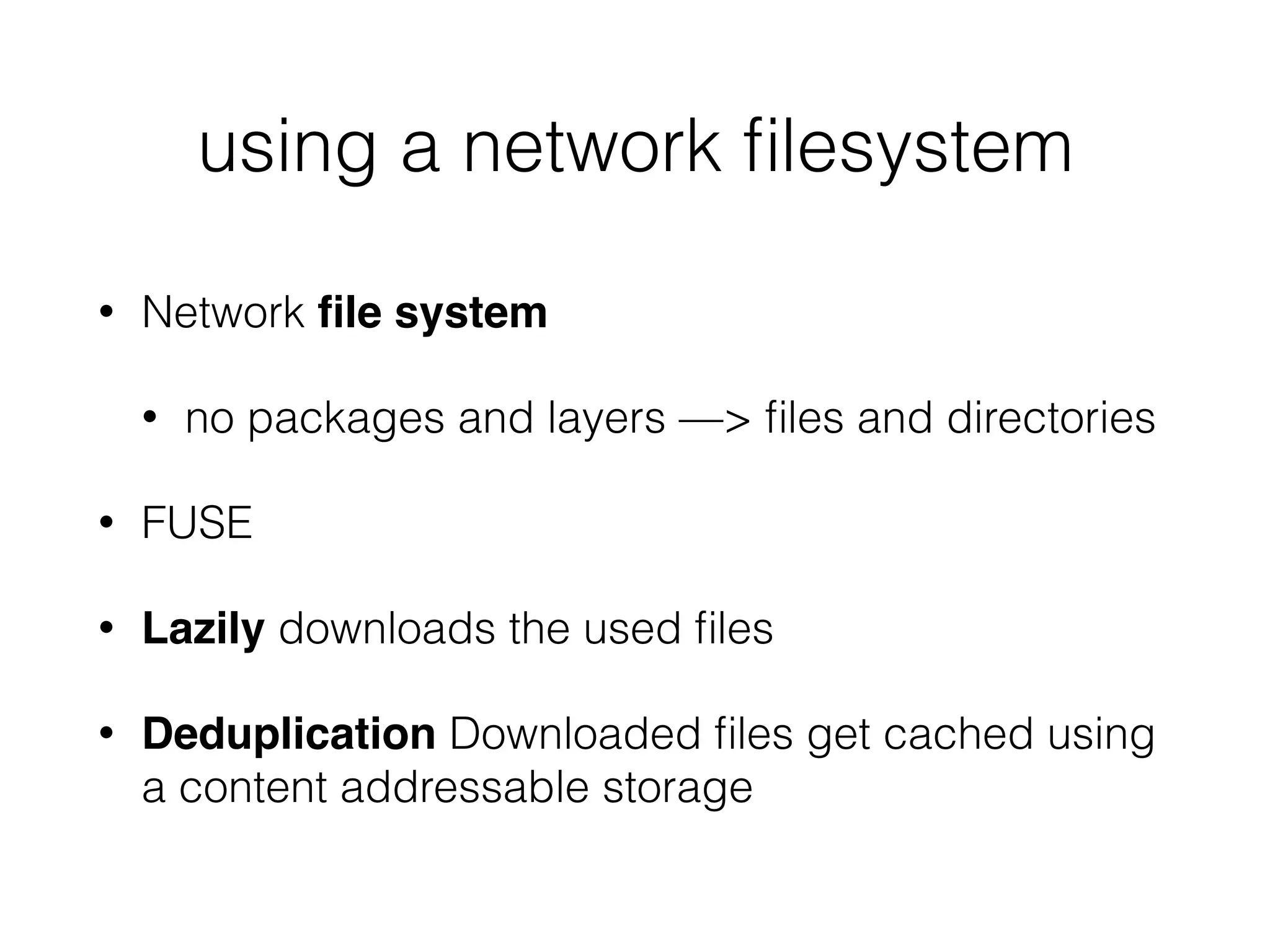
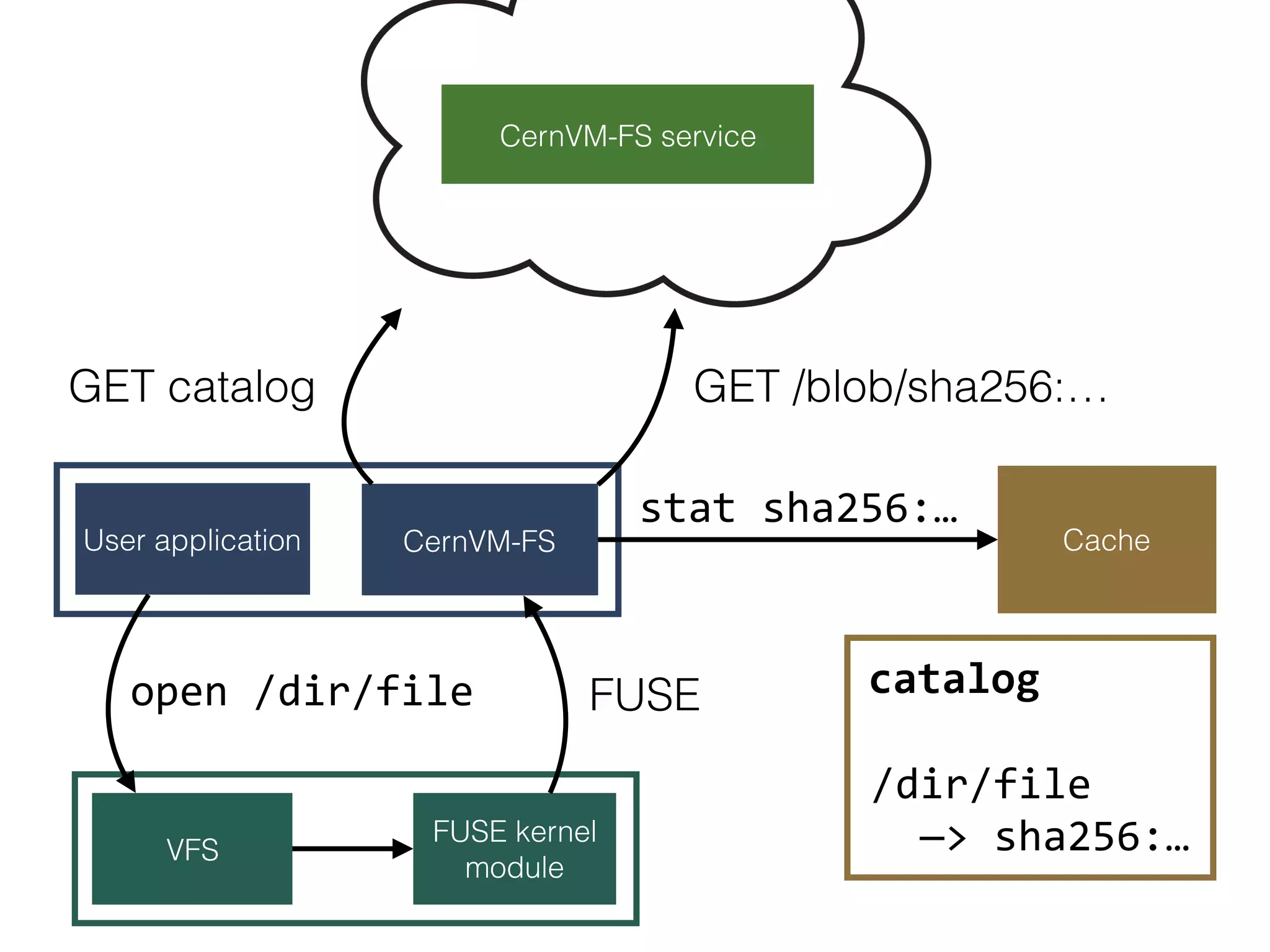
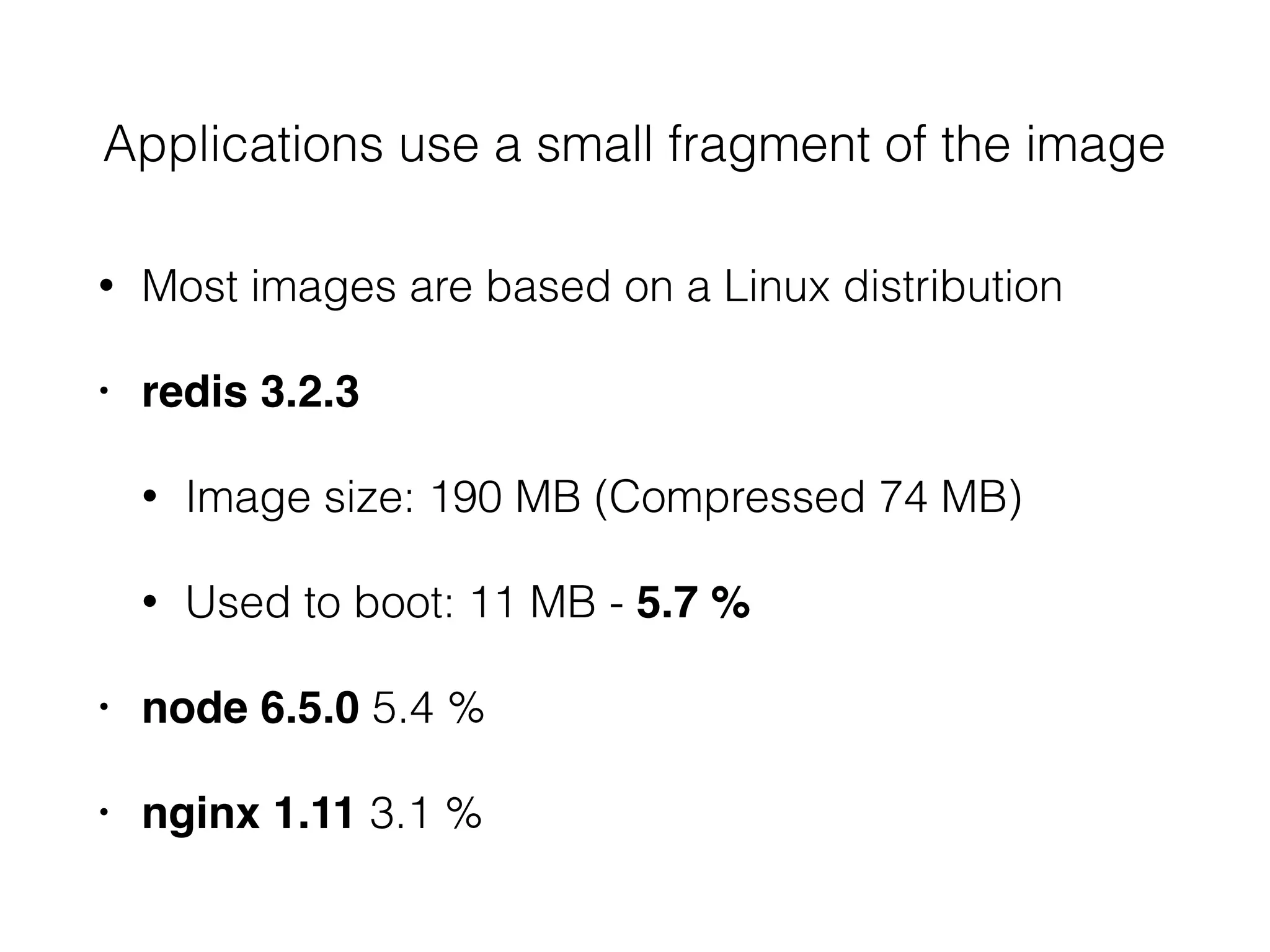
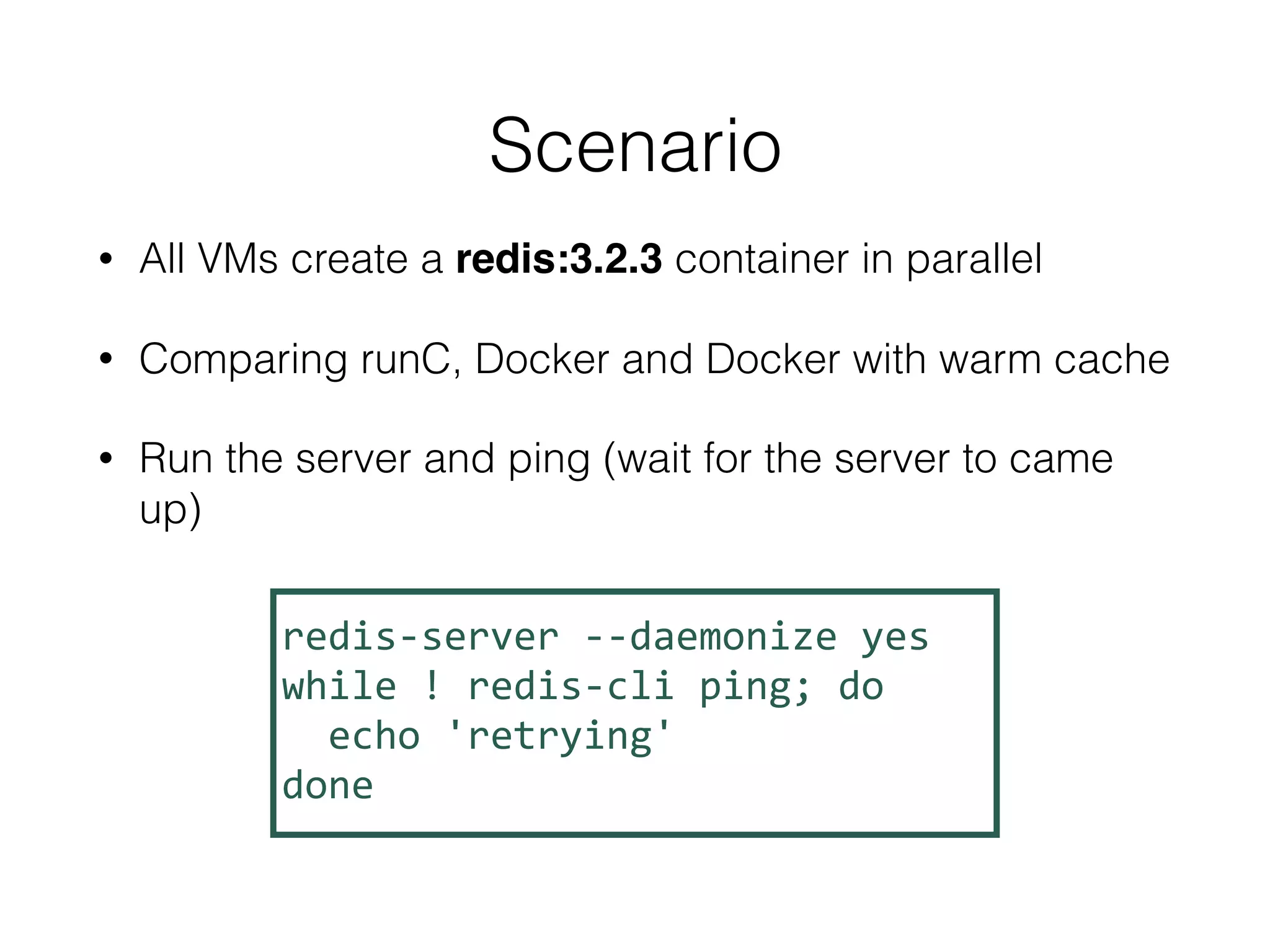
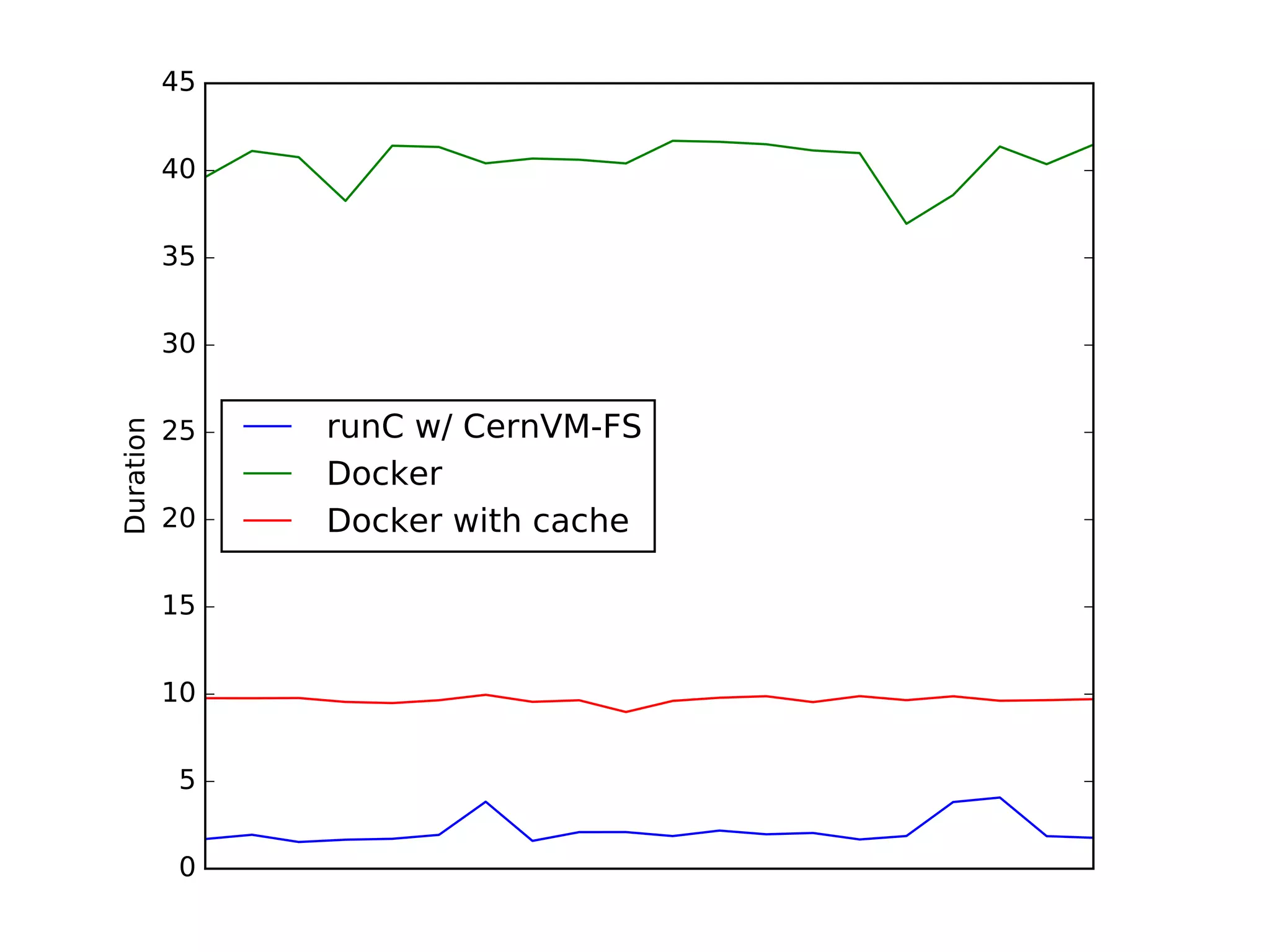
The document discusses alternatives to layer-based image distribution using a CERN filesystem for container images. It highlights the structure of container images, including layers and metadata, and introduces CERNVM-FS, a network file system that supports efficient file fetching and caching. Additionally, it compares performance metrics and explores other distribution approaches, including decentralized systems and serverless options.