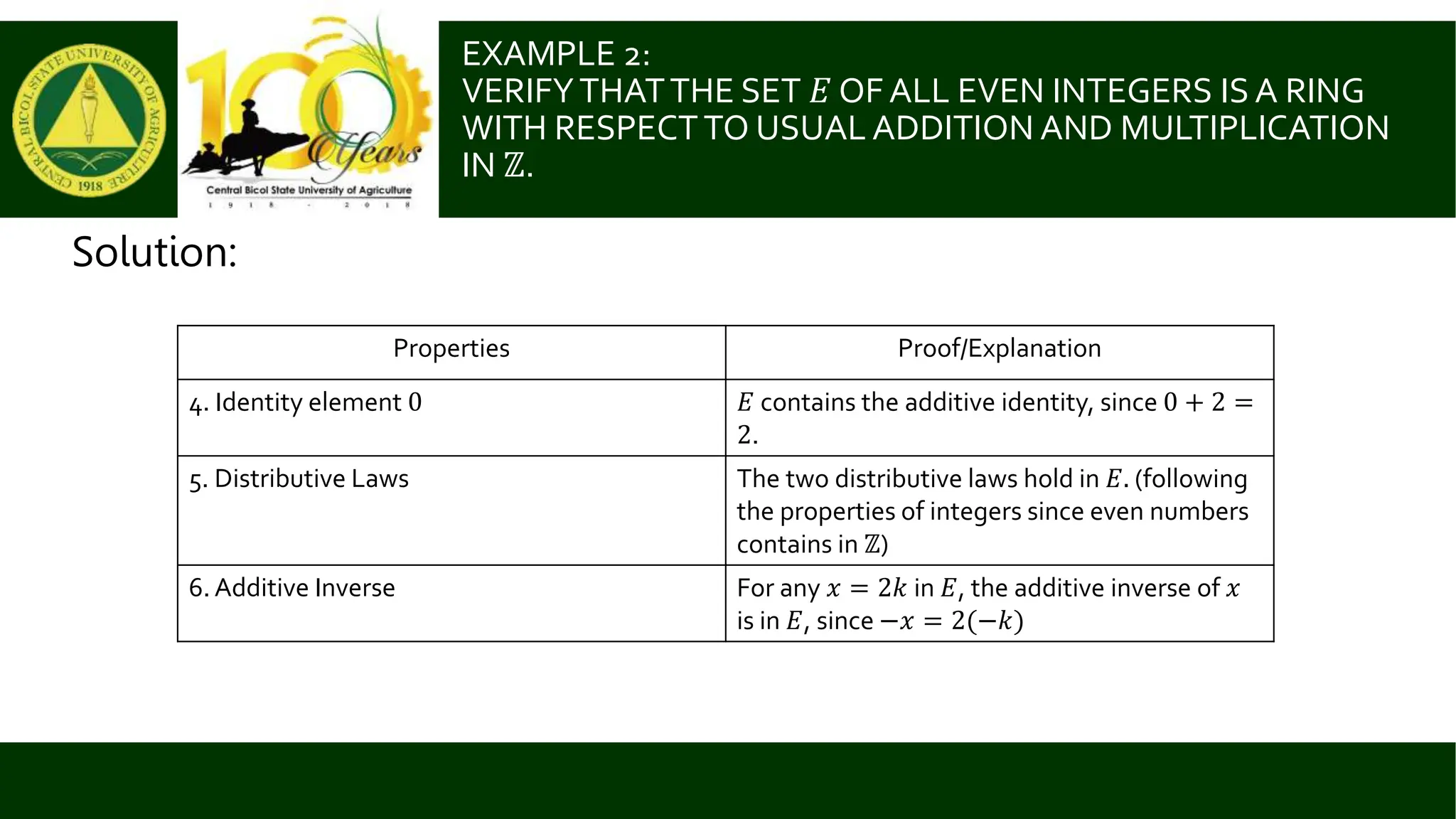
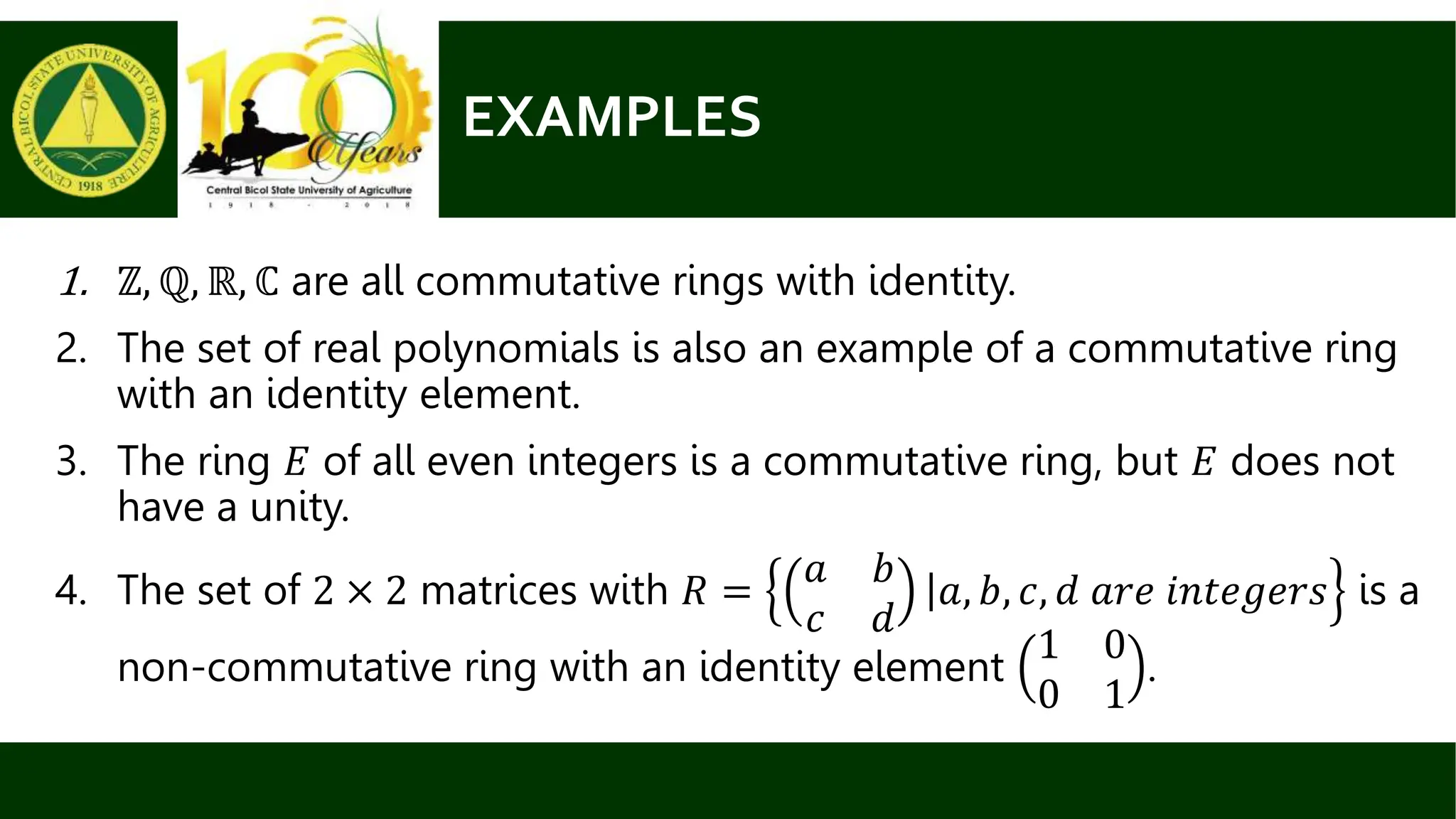
This document defines and provides examples of rings. A ring is a set with two binary operations, addition and multiplication, that satisfy certain properties: 1) addition forms an abelian group, 2) multiplication is associative, and 3) the distributive laws hold. Simple examples of rings include the integers Z, rational numbers Q, real numbers R, and complex numbers C. The document also verifies that the set of even integers E is a ring and provides another example of a ring defined by addition and multiplication tables. Rings can be commutative or non-commutative and may or may not have an identity element.